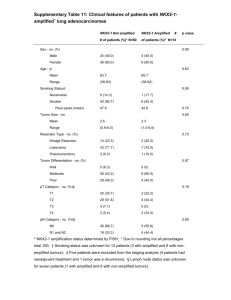
AACR Annual meeting 2013 Abbreviations: ECM: Extracellular
advertisement

AACR Annual meeting 2013 Abbreviations: ECM: Extracellular Matrix EMT: Epithelio-Mesenchymal transition TME: Tumor Microenvironment 7/4, 7am, MEET-THE-EXPERT SESSION Jeffrey Wrana Dysregulated morphogenesis and polarity in cancer Polarity is a key control of morphogenesis, which is controlled by a limited number of pathways (TGFb, WNT, Notch…). Dysmorphogenesis occurs during cancer development, but little is known about the integration of morphogen pathways into higher order networks that define the contextual cues driving cancer progression. The tumor stroma plays a critical role in cancer progression, but how it promotes metastasis is poorly understood. Fibroblast conditioned media (ACM) MDAK cells activated breast cancer cells (BCC)! Fibroblasts secrete exosomes sufficient to promote BCC protrusive activity, motility and metastasis. Smurf1 & 2 (ubiquitine ligases) are regulators of cell polarity, protrusive activity and BCC motility. Their KO by siRNA inhibits ACM activity. As they are PCP (planar cell polarity) regulator, they verified if the ACM-induced motility was mediated through the core PCP pathways. Downregulation of the core PCP component reduces metastasis, suggesting their specific role in metastasis. Wnt ligands are key regulators of the PCP pathways. Their KO in fibroblast has surprisingly no effect. On the contrary, their KO in BBC inhibits ACM activity! It indicates that ACM stimulates autocrine Wnt pathways that activate PCP signaling during BCC protrusive activity and motility. To identify the factors that promote autocrine Wnt-PCP signaling in BCCs, they separated the purified ACM in single activity fractions. Among several exosomes markers, the loss of Cd81-positive exosomes inhibits ACM-induced BCC protrusive activity and motility. Cd81 KO tumors do not present metastasis, but grow as fast as a Cd81+ tumor. Indeed, CD81 expression is upregulated in human breast tumor-associated stroma. Exosome-driven metastasis is dependent on the core PCP pathways. Cd81-positive exosomes are internalized by BBC with Wnt11. It reveals a key role for fibroblasts-derived exosomes in mobilizing autocrine Wnt-PCP signaling in BCC to stimulate invasive behavior and metastasis. Luga, Wrana et al, Cell 2012 7/4, 3pm, MINISYMPOSIUM TISSUE ORGANIZATION, MECHANICAL MICROENVIRONMENT FORCES, AND 3-D MODELING OF THE Thimothy Fessenden Dynamic multicellular mechanics controlling protrusion in 3D Tension maintained across the actin cortex mechanically restrict protrusions, and may be transmitted across multiple cells via adherens junctions, as it exists in epithelia. How is tissue organization disrupted to allow invasive behavior? He studied the MDCK acini morphogenesis upon HGF exposure as a model for rupture of epithelial integrity and protrusion. Jonathan Celli Microrheology studies in 3D pancreatic tumor models Pancreatic tumors are very rigid and have hyperdense stroma, which increase invasiveness and reduce drug delivery. Key questions about the role of mechanical microenvironment remain unanswered. Cocultures (fibroblasts and cancer cells) are embedded in collagen matrix containing fluorescent tracer probes. The Brownian motion of the probes is used as a reporter of spatiotemporal changes in viscoelastic properties of the ECM and correlated with the architecture changes and the cytotoxic response. Preliminary results show heterogeneity in ECM rigidity and a role from fibroblasts to restore ECM uniformity. Hal Crosswell The 3DKUBE segregated co-culture system Coculture of MCF7 spheroids in IrECM next to hFFB fibroblasts in scaffold to mimic the stroma, and both perfused with controlled flow rates and cycling times. This system promotes spheroid maintenance and growth, and is applicable across multiple different tumor types. The assay with PI3K inhibitors show a reduced activity in the 3D perfusion model compared to the 3D and 2D models. 8/4, 6:45am, MEET-THE-EXPERT SESSION Andrew Futreal Inter- and intratumor heterogeneity in human cancer In our sequencing generation, it is nowadays possible to extract either a single mutation or the whole genomic of every unique cancer. However, the multiple heterogeneity in cancers increases the complexity of deducing information from cancer genome sequencing. 1) Heterogeneity between the same cancer types For example chondrosarcoma can be mutated on different genes: IDH1/2, TP53, Hedgehog pathway, Col2A1, etc. And even for one mutated gene, it often exists several possible mutations: Col2A1 is often truncated, but also presents missense mutation but never silent mutation. 2) Heterogeneity within the same tumor A multiregion exome sequencing in CCRCC revealed that 65% of mutations from a single biopsy are heterogeneous. The mutations can be ordered and draw a tree of mutations evolution. Moreover, mutations can have different impacts on cell phenotype. Gerlinger et al, 2012, NEJM 3) Heterogeneity over time Exome sequencing of longitudinal sample indicate the % of mutated reads of each mutation (Variant Allele Frequency, VAC) and can reveal a shift in subclone distribution during a tumor treatment. There are 4 possible evolutions during a treatment: - No evolution - Appearance of a dominating subclone - Developing of a new subclone which was absent at the early stage - Completely different evolutions between the early and late stages. Is the complexity subclonal architecture a prognostic? Where do the drivers and targets live? Does it matter? Could these types of analyses be reduced to clinical practice? Are there patterns of timing metastasis? 8/4, 1pm, MAJOR SYMPOSIUM THE RUTH SAGER MEMORIAL SYMPOSIUM: CANCER HETEROGENEITY Elaine Mardis The impact of therapy on tumor heterogeneity Elaine Mardis bring complementary information to the Andrew Futreal presentation. 1) They hypothesized that an older mutation is more frequent, and consequently the study of mutation frequencies in primary tumor and metastases could let draw the tree of metastatic evolution of the cancer. They show the result of a case study from patients near to death with multiple metastases. 2) They compared the VAC of breast tumor treated with different drugs to define the effect of drugs on cellular heterogeneity. 3) They compared the VAC of xenografts from primary tumor and metastasis of the same tumor to analyze the preservation or alteration during metastasis and xenografts process. Their work reveal a good correlation between the changed observed from the primary tumor and metastasis, and the changed observed between the corresponding xenografts. This could be a good mean to extend the comparison of primary tumor and metastases to better evaluate the resistance of the tumor. Peter Campbell Patterns of subclonal heterogeneity across tumor types They studied the impact of driver mutation on the patient prognosis, in a cohort of patients with myelodysplasic tumors. First, they analyzed the frequencies of driver mutation in the tumors. They found 3 classes of driver mutation: known oncogenic mutations, possible oncogenic mutation, and variants with unknown significance. Around 40% of the patients have more than one driver mutation. Second, they analyzed the association of mutated genes. It appeared that some mutated genes are strongly associated, but some other mutations never happen together. Thirdly, they verified if the driver mutation accumulation could decrease the prognostic. Indeed, the more patients accumulate driver mutations, the more the risk of bad prognostic is soon. However, there is no difference in survival between a clonal and a subclonal mutation of the same driver mutation. Personal remarks All those talks on cancer heterogeneity were very enriching and remind the complexity of the tumors. It is likely that the cellular heterogeneity mimicked in MCTS is largely reduced compared to the one found in tumors. If we consider that two genetically different cells might have two different phenotypes, two tumors with different heterogeneity might evaluate in different ways. From my point of view, those studies are sometimes far from the cellular process and the biological steps of tumor development and evolution. 8/4, 3pm, MINISYMPOSIUM MICROENVIRONMENT DRIVING TUMOR INITIATION Tracy Pritchett Novel conditional knockout of VHL in the kidney leads to precancerous lesions that exhibit an inflammatory response As the VHL gene is mutated in 80% of renal cancers, they produced transgenic mice with a conditional knockout of VHL in the kidney. They used the CreLoxP method, with Cre expressed in kidney collective ducts. Mice presented precancerous lesions with infiltration, clear cells, epithelial cells pill up, high proliferation, high vascularization and high fibrosis. One major function of VHL is to act as en E3 ubiquitin ligase. Consequently of the KO, its major target HIF is high, as are HIF targets Glut1 and CAIX. They contribute in fibrotic defects. Pritchett and coworkers produced double KO of VHL and HIF, and they observed a great reduction in lesions appearance. This model reproduces renal precancerous and cancerous lesions, and thus can be used to better understand the mechanisms of switch from fibrosis to cancer. Aubie Shaw Myeloid cells promote fibroblast invasion and lead mammary adenocarcinoma cell invasion Alenxander and Friedl 2012 Fibroblasts and macrophages are important for extravasation processus. Macrophages regulate invasion and metastasis. They are localized near vessels. CD4+ cells promote macrophages that participate to tumor progression. It appears essential to inhibit macrophages to limit metastasis. On the other hand, fibroblasts lead collective cell migration through ECM remodeling (Khalil and Friedl 2010, Gritsenko, Ilina and Friedl 2012). Shaw and coworkers wanted to verify the hypothesis of collaboration between fibroblasts and macrophages. They separated myeloid cells, carcinoma cells and fibroblasts from primary cells from mice and cocultivated them in collagen or IBME matrix. They observed fibroblasts migration towards specific myeloid cell types. It appeared that many myeloid cells secreted factors to promote fibroblasts invasion. FGFR1K is a crucial factor for migration. Indeed, its inhibition blocks fibroblasts migration. They wondered if there was a direct cell-to-cell interaction. Ongoing studies are identifying specific subpopultions of tumor-associated myeloid cells participating to collective cell migration. Valentino Audrito Extracellular form of NAMPT (eNAMPT) contributes to creating a proinflammatory environment in chronic lympocytic leukemia NAD is a signaling molecule regulating metabolic enzymes such as NAMPT. It acts as a cytokine. Its secretion is increased in leukemia, making this biosynthetic pathway an attractive target for cancer treatment. The aim of their work is to test whether eNAMPT played a role in shaping the leukemic environment, by generating proinflammatory conditions. NAMPT is more secreted after B lymphocytes activation. However, NAMPT does not act directly on fibroblasts. It enhances differentiation and phagocyte activity of nurse-like cells. The data suggest that eNAMPT contributes to the formation of a proinflammatory environment. Adriana Albini Innate immunity driving tumor angiogenesis: the role of natural killer cells (NK) in NSCLC NK represent 5-10% of lymphocytes. They use granzime and perforin killing means. But among their different subsets, one of them, CD56+/++ and CD16- does not kill: it produces cytokines and participates to tissue construction. CD56+ NK predominate in cancers, while they are low in blood and adjacent tissues. The analyses of biopsies and blood from patients revealed the production of IL8 and INFγ by NK. Those cytokines stimulate endothelial cells chemotaxis and formation of capillarylike structures in vitro. It also appeared that TFGb , associated with a poor prognostic, mediated NK recruitment towards an angiogenic activity. To conclude, CD56+ NK could be targeted to prevent angiogenesis. Could NK be a marker of prognosis and complication? David Nguyen Biologically distinct mammary tumors develop from Trp53 null tissue transplanted to juvenile versus adult gland The risk of breast cancer is higher during puberty, due to stem cells expansion. They investigated the impact of the age of transplantation on tumor development. They transplanted Trp53 null mammary fragments into inguinal fat pads of 5 week-old or 10 week-old mice. Pubertal mice presented bigger tumors with higher mitotic indexes. 80% of their tumors were ER+. A microarray analysis revealed a luminal transcriptional program. To conclude, factors determining breast cancer molecular subtype may not be epithelial autonomous, but can be influenced by the host environment. Tomohiro Umezo Hypoxia modulates tumor exosomes, which function as mediators of angiogenesis Exosomes are mediators of communication. They contain proteins, mRNA, miRNA, etc. The aim of the study was to clarify whether hypoxia promote angiogenic activity through tumor exosomes. To answer the question, they cultivated endothelial cells with conditioned media from normoxia (20% O2) or hypoxia (1% O2) cancer cells, then analyzed exosomes by using nanoparticules tracking and exosome miRNA profiling. Hypoxic exosomes promote tube formation of endothelial cells. miR210 was elevated in hypoxic conditions. It regulates the target genes of a hypoxic response in endothelial cells. Hypoxic exosomes play a role in inducing angiogenesis. 9/4, 7am, MEET-THE-EXPERT SESSION Chi Van Dang Links between Metabolism and cancer Cells are replicating bioreactors. In homeostasis condition, they use amino acids, glucose and fatty acids by oxydation to produce ATP and waste. In growth condition, growth factors induce glycolysis and Krebs cycling to increase cell biomass and lead to cell division. Glucose (Glc), but also glutamine (Glt) can feed the Krebs cycle to produce lipids, nucleic acids and ATP. Growth factors are necessary to activate cell growth. They activate the gene MYC, which can activate the three m, r and tRNA and numerous metabolic pathways. P53 and Art keep MYC quiet enough to control proliferation except if they are mutated. 1) Can metabolism cause cancer? It has been shown that Glc deprivation induced mutant Ras. Indeed, Ras or Braf mutation can activate the Glc1 transporter. Many other metabolic genes are known to be altered in cancers. (Shih, Levine, NRC, 2013) To conclude, oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes are more and more linked with metabolic genes, increasing the complexity of the genes network. 2) Does it exist fragility in cancer cells? Nutrients regulate ribosome biogenesis: Glc -> RAS –I Dot6 –I Ribigene expression Glt -> TORC1 –I Ted6 –I Ribigene expression Dot6 and Ted6 are often mutated in cancer, because cancer cells are addicted to Glc and Glutamine but still need Ribigene expression. Myc enhance Glt oxidation x4, while Glc oxidation is only increased x1.2. Is the Glt pathway a possible target? GLS1 converts Glt and Glutamate. GLS+/+ mice develop bigger tumors than GLS-/- mice. They treated mice with BPTES, a GLS inhibitor, and reduced the tumor development resulting in an extended life of animals. Dang gave another example with the pyruvate/lactate pathway. Le et al, PNAS 2010. 3) Is there a therapeutic window? Mutations induce new activities specific to cancer cells, and therefore, that can be targeted. For example, liver cells are GLS2 + while liver cancer cells have GLS2 low expression and GLS1 very high expression. 4) Are there oncogenic alterations of the circadian molecular clock? Organs metabolisms are synchronized with food arrival, activities, light, etc. Does Myc disrupt the cycling expression of metabolic genes? Indeed, under Myc stimulation, expression of metabolic genes becomes permanent and high. This difference in levels of expression opens a new therapeutic window. 9/4, 8am, MAJOR SESSION MITOTIC CHECKPOINTS DRIVING CANCER THERAPEUTIC STRATEGIES Timothy Mitchison Is mitosis the target of “antimitotic” cancer drugs? In tumor, only 2-5% of the cells are in S phase, while there are 40% in bone marrow! 2D cultures are bad predictors of patient response for cytotoxic drugs. Nowadays, two types of drugs are used: - Anti-microtubule drugs which also affect interphase cells - Anti-mitotic drugs which only affect proliferative cells Anti-microtubule drugs induce SAC activation and block cell in anaphase or in G1, leading to cell death or senescence. Consequently, the mitotic arrest becomes toxic only if a normal mitotic exit fails. They used HT1080 expressing Fucci reporter to visualize the behavior and death of injected cells in mice. They revealed a concentration-dependent effect of taxol treatment. Low concentration Aneuploidy with mitotic arrest mitotic arrest High concentration interphase bundle The interphase bundle could be a therapeutically relevant mechanism. However, taxol pharmacokinetics are complicated to control and it is only its accumulation that could raise an effective action. They also showed that anti-mitotic drugs have anti-vascular effects : they disrupt established tumor vasculature and inhibit new blood vessel formation. Peter Senter Tumor targeting with anti-mitotic monoclonal antibody drug conjugates Senter presented various antibodies targeting tumor cells and used as mean to deliver drugs close to tumor. They precised their results obtained with the MMAE linked to an antibody. Guido Kroemer Targeting tetraploidy for cancer therapy by pharmacological and immunological strategies They made a drug screening on cocultures of diploid cells and tetraploid H2B-GFP cells. They analyzed the proliferative effect and the evolution of the diploid/tetraploid rate. The conclusion of their work revealed that tetraploid cells are immunogenic in vivo, and taxanes induce tetraploidy in human cancers. As their elimination correlate with chemotherapeutic effects, they might be used as predictive biomarkers. 9/4, 3pm, MINISYMPOSIUM NEW PATHWAYS IN TUMOR METASTASIS Rosandra Kaplan Breaking metastatic dormancy during surgical resection After surgical resection, bone-marrow derived cells are activated and mobilized at the resection site. There, they induce a local inflamed TME and provide survival signal to the seeding tumor cells. Indeed, vasculogenic monocytes, hematopoietic progenitor cells and endothelial progenitor cells are elevated in blood of mice which underwent tumor resection, while there are not in control mice which underwent a surgery without resection. Those concentrations of circulating cells are correlated with bad prognostic. They observed that surgical resection of primary tumor in mice enhanced metastasis! It is partly due to an increase in mobilized cells. They showed that targeting the circulating cells with Pazopanib prevented the surge in bone-marrow-derived cells into the circulation and abolished the enhanced metatatic spread in mice undergoing surgical resection. It provided a significant prolongation of life. Consequently, inhibiting the mobilization of bone marrow-derived cells following surgery could reduce the metastatic capacity of disseminated tumors. 9/4, 5pm, FORUM THE ROLE OF STROMA IN PANCREATIC CANCER Ben Stanger In pancreatic cancer, cancer cells are minor components of the tumor. As EMT and dissemination precede pancreatic tumor, most tumors have already spread at the time of the detection, resulting in high mortality. The TME is composed of many cell types, it is necessary to understand their behavior in order to target them. The team established a mice model allowing the lineage of KRAS mutated cells. It appeared that stromal cells are derived from KRAS epithelial cells. They present different stage of EMT: regular compartment of E-Cadherin expressing epithelial cells, mesenchymal cells expressing ECadherin, or fully stromal cells. Do the stromal cells have a positive or negative influence on cancer cells? The Hh pathway is strongly activated in pancreatic cancer cells. Hh inhibition increases vessels density and drug delivery (pancreatic cancer is avascular). To answer the question, they produced shh KO mice with KRAS mutation. Tumors stayed undifferentiated with reduced fibroblastic stroma. They were higher vascularized and the drug had a better penetrance. Surprisingly, tumors are more dangerous because the cancer cells proliferated more rapidly and it resulted in faster death! The good point is that the tumors become more sensitive to anti-angiogenic drugs. The better understanding of tumor microenvironment is necessary to understand the perturbation of the expected consequences of a treatment. Philip Beachy With a lineage of basal cells of the bladder, Beachy and coworkers showed that bladder tumors arise from a single urothelial basal cell. 10/4, 8am, PLENARY SESSION CANCER EVOLUTION AND RESISTANCE Jeff Engelman Resistance is due to: - Gene amplification/overexpression - Bypassed pathways - Defect growth/apoptosis/EMT/etc The two first phenomena are the more potent to be inhibited by drugs combination. Engelman and coworkers made a drug combination screen on EGFR inhibitor resistant cells. The EGFR inhibitor resistant cells are produced by multiple passaging in increased drugs concentration. 78 drugs are tested, and some combination appeared to reduce the resistant cell viability. Their validation was made on patient derived models (cell lines and xenograft). From this study, it appears that the tumor cells heterogeneity majors the challenge to overcome resistance. Indeed, the cells cultured from biopsy develop depending on the drug, and it can make a new resistant cell population rises from the sensitive cell background. If the sensitive cells are not killed in totality, they grow up again during treatment release, making the patient sensitive to the drug again. But while, resistant cells grew and the response is less efficient. This might explain why remissions only last few months. A protocol would be to alternate between different combinations without any interruption in the EGFR inhibitor treatment. Todd Golub Microenvironmental contributions to cancer drug resistance Does tumor microenvironment mediate tumor resistance? They studied the effect of fibroblast on cancer cell resistance to several drugs, by cocultures with cancer cells and fibroblasts. It appeared that some fibroblast rescued melanoma treated with Vemurafenib. This rescue was reproduced by adding the fibroblast-conditioned medium to the cancer cells. This underlines the great importance of the secretome! It has been shown that HGF secretion is sufficient to induce resistance. If stromal cells secrete HGF, the downstream pathway is activated in cancer cells, giving them resistance! HGF inhibitors and Verumafenib combination should be more efficient to avoid tumor resistance. It will be tested on patients soon. 10/4, 11am TARGETTING THE CELL CYCLE Marco Malumbres Targeting mitosis for cancer therapy As CDK4/6 inhibitors arrest tumor cells in G0 or G1 and do not induce cell death, mitosis should be a better target to induce cell death. Microtubules poisons might be good candidates but mitotic index is often low in tumors, and cells escape by mitotic slippage. It appears essential to inhibit the mitotic exit to make mitotic poisons efficient. Malumbres and his team are trying to indentify some drugs with this effect. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, T. Fojo 2011 Mitchison 2009 Malumbres 2010 Mariano Barbacid Targeting KRAS cancers: CDKs andf other mechanisms Growth factors activate the RAS pathways, implicated in many cell activities. KRAS mutations turn the RAS pathway ON. KRAS is not druggable but its downstream effectors are. Two questions are not yet answered: -Which kinases are essential? -Which kinases are selective for targeting KRAS? 1) They targeting different kinases by conditional KO in KRAS-mutant mice models, and analyzed the absence, the partial or the complete response of the target inhibition against the KRAS lung adenocarcinoma. Target Tumor development Toxicity A-Raf Yes B-Raf Yes C-Raf NO! NO! CDK2 Yes CDK4 NO! Diabetes CDK6 Yes C-Raf and CDK4 are essential for the KRAS to initiate the tumor. 2) With a second model of conditional KO of target, they induced the tumor and then analyzed the remission by the inhibition of the target. With CDK4/6 inhibitor, the tumor does not disappear even if its volume decreases. With C-Raf inhibition, the tumor remains as big but become PET negative (dormant tumor) and the survivance is reestablished. They hypothesis this partial result was due to an inhibition and not a absence of the proteins. As those proteins are necessary for development, they produced deadkinase that are totally inactive. The first mice with dead kinase seem healthy, meaning that the kinases have non-kinase activities necessary for the embryonic development. Further studies on their role in tumor development are ongoing.