View
advertisement
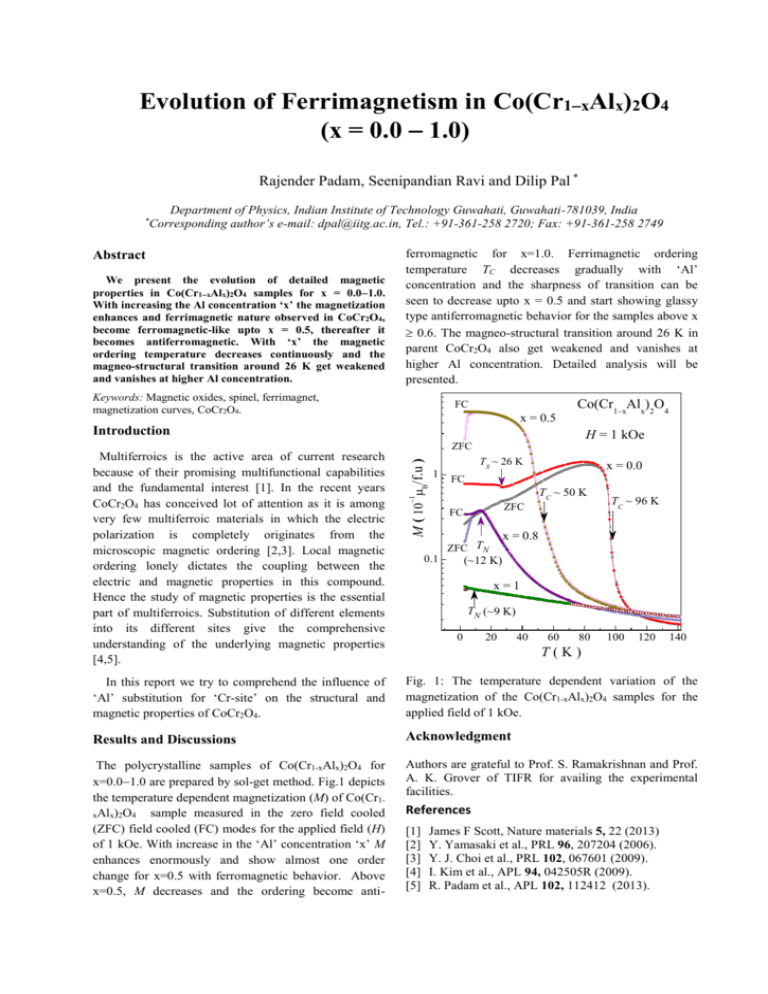
Evolution of Ferrimagnetism in Co(Cr1xAlx)2O4 (x = 0.0 1.0) Rajender Padam, Seenipandian Ravi and Dilip Pal * Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati, Guwahati-781039, India Corresponding author’s e-mail: dpal@iitg.ac.in, Tel.: +91-361-258 2720; Fax: +91-361-258 2749 * Abstract We present the evolution of detailed magnetic properties in Co(Cr1xAlx)2O4 samples for x = 0.01.0. With increasing the Al concentration ‘x’ the magnetization enhances and ferrimagnetic nature observed in CoCr2O4, become ferromagnetic-like upto x = 0.5, thereafter it becomes antiferromagnetic. With ‘x’ the magnetic ordering temperature decreases continuously and the magneo-structural transition around 26 K get weakened and vanishes at higher Al concentration. ferromagnetic for x=1.0. Ferrimagnetic ordering temperature TC decreases gradually with ‘Al’ concentration and the sharpness of transition can be seen to decrease upto x = 0.5 and start showing glassy type antiferromagnetic behavior for the samples above x 0.6. The magneo-structural transition around 26 K in parent CoCr2O4 also get weakened and vanishes at higher Al concentration. Detailed analysis will be presented. Keywords: Magnetic oxides, spinel, ferrimagnet, magnetization curves, CoCr2O4. FC x = 0.5 Co(Cr1xAlx)2O4 Introduction H = 1 kOe 1 TS ~ 26 K x = 0.0 FC TC ~ 50 K Multiferroics is the active area of current research because of their promising multifunctional capabilities and the fundamental interest [1]. In the recent years CoCr2O4 has conceived lot of attention as it is among very few multiferroic materials in which the electric polarization is completely originates from the microscopic magnetic ordering [2,3]. Local magnetic ordering lonely dictates the coupling between the electric and magnetic properties in this compound. Hence the study of magnetic properties is the essential part of multiferroics. Substitution of different elements into its different sites give the comprehensive understanding of the underlying magnetic properties [4,5]. M ( B/f.u ) ZFC ZFC FC x = 0.8 ZFC TN 0.1 TC ~ 96 K (~12 K) x=1 TN (~9 K) 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 T(K) In this report we try to comprehend the influence of ‘Al’ substitution for ‘Cr-site’ on the structural and magnetic properties of CoCr2O4. Fig. 1: The temperature dependent variation of the magnetization of the Co(Cr1-xAlx)2O4 samples for the applied field of 1 kOe. Results and Discussions Acknowledgment The polycrystalline samples of Co(Cr1-xAlx)2O4 for x=0.01.0 are prepared by sol-get method. Fig.1 depicts the temperature dependent magnetization (M) of Co(Cr1sample measured in the zero field cooled xAlx)2O4 (ZFC) field cooled (FC) modes for the applied field (H) of 1 kOe. With increase in the ‘Al’ concentration ‘x’ M enhances enormously and show almost one order change for x=0.5 with ferromagnetic behavior. Above x=0.5, M decreases and the ordering become anti- Authors are grateful to Prof. S. Ramakrishnan and Prof. A. K. Grover of TIFR for availing the experimental facilities. References [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] James F Scott, Nature materials 5, 22 (2013) Y. Yamasaki et al., PRL 96, 207204 (2006). Y. J. Choi et al., PRL 102, 067601 (2009). I. Kim et al., APL 94, 042505R (2009). R. Padam et al., APL 102, 112412 (2013).