Energy Flow in Ecosystems
advertisement

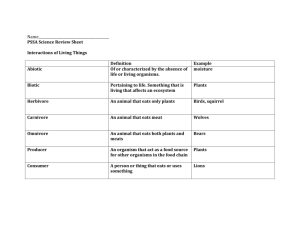
Energy Flow in Ecosystems An organism’s energy role is determined by how it obtains energy and how it interacts with the other living things in its ecosystem. An organism’s energy role in an ecosystem may be that of a producer, consumer, or decomposer. Plants, algae or phytoplankton, and some microorganisms can carry out photosynthesis. In this process, the organism uses the sun’s energy to turn water and carbon dioxide into glucose. Decomposers An organism that-can make its own food is a producer or an autotroph. Producers are the source of all the food in an ecosystem. Other organisms cannot make their own food. They depend on producers for food and energy. An organism that obtains energy, by feeding on other organisms is a consumer or heterotroph. They can be primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary consumers. Consumers are classified by what they eat. Consumers that eat only plants are called quaternary consumer consumer tertiary consumer consumercinsumer secondary consumer herbivores. Consumers that eat only other animals are called carnivores. A consumer that eats both plants and animals is called an omnivore. (omni=all + vore= one that eats) A scavenger is a carnivore that feeds primary consumer on the bodies of dead organisms. An organism may play more than one role in an producers ecosystem. What do you notice about the about of calories as you move from one trophic level to the next? Organisms that break down wastes and dead organisms and return the raw materials to the environment are consumers called decomposers. As decomposers obtain energy for their own needs, they return simple molecules to the environment to be used again by other organisms like producers to help them grow. Examples of decomposers are worms, bacteria, and fungi. The flow of energy through an ecosystem can be shown in diagrams called food chains and food webs. A food chain is a series of events in which one organism eats another and obtains energy. The first organism in a food chain is always a Food chain The arrow shows the direction of the energy. For example, energy goes from the sun to the grass; from the grass to the grasshopper, etc. producer. The second organism, called a primary consumer, eats the producer. The next consumer, called a secondary consumer, eats the primary consumer. The next levels would be tertiary and even quaternary consumers. A food chain shows just one possible path of energy through an ecosystem. Terrestrial food web Most producers and consumers are part of many food chains. A more realistic way to show the flow of energy through an ecosystem is a food web. A food web consists of the many overlapping food chains in an ecosystem. Food webs may be aquatic (marine) or terrestrial (land). When an organism makes its own food or eats other organisms, it obtains energy. The organism uses most of this energy for its own life processes. Only some of the energy will be available to the next organism in the food web. A diagram called an energy pyramid (see page 1) shows the amount of energy that moves from one feeding level to another in a food web. The most energy is available at the producer level. At each level in the pyramid, there is less available energy than at the level below. In general, only about 10% of the energy at one level of a food web is transferred to the next higher level. For this reason, most food webs have only three or four feeding levels, with few organisms at the highest level in a food web. Name_____________________ Energy Flow in Ecosystems 1. What is an energy role? _____________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Name the three energy roles in an ecosystem . 1._________________________ 2. __________________________ 3. _____________________ 3. Name some producers._____________________________________________________ 4. Who are the source of all the food in an ecosystem? _________________ and What is its other name? ____________________________ 5. What is a consumer? ______________________________________________________________ and what is its other name? _________________________________ 6. Name the levels of consumers that are in a food pyramid. __________________________________________________________________________________ 7. Match the following; omnivore _______ a. only eats plants herbivore _______ b. only eats other animals carnivore _______ c. eats both plants and animals 8. What is a carnivore that feeds on the bodies of dead organisms? ________________________ 9. What is the niche of a decomposer? _______________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 10.Give examples of decomposers? _________________________________________________ 11. How can the flow of energy be represented? _____________________ and ________________________ 12. How is a food chain different from a food web? ___________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ 13. What is the first level in either a food chain or a food web? _________________________________ 2500 kcal 1000 kcal 14. Which organism in the food web is sometimes a primary consumer and sometimes a secondary consumer? ______________ Explain your answer._________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 15.. Choose one food chain in the web above. Name all the organisms in that chain. Start with the producer and end with the top-level consumer ___________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ 16. a. Draw on the energy pyramid the food chain you chose above. Write the names of the organisms in the trophic level on the pyramid b. Label the pyramid Include these words: primary, secondary , tertiary consumers producers the energy available at each level. 17. What is a terrestrial food web? ___________________________________________________ 18. What is another name for an aquatic food web? _________________ 19. How much energy is lost from one trophic level to the next? ______________________ Name_____________________ Period______ Date_________ Food Webs at Hydrothermal Vents Deep below the ocean’s surface are strange ecosystems called hydrothermal vents. Here, heated water rises up through cracks in the ocean floor. The water contains minerals from Earth’s interior. No sunlight ever reaches these vents. No plants or algae live there. The table below lists the organisms found at hydrothermal vents. Use the information in the table to respond to the following items. 1. Which organisms are the producers at hydrothermal vents? ___________________________________________ 2. Which organisms are primary consumers? _______________________________________________________ 3. What type of consumer are the crabs? ___________________________________________________________ 4. In the space below, draw the food web (use words) at a hydrothermal vent. Label each organism to identify its energy role (producer or consumer) in the ecosystem. http://puzzling.caret.cam.ac.uk/game.php?game=foodchain