6 - EngageNY
advertisement
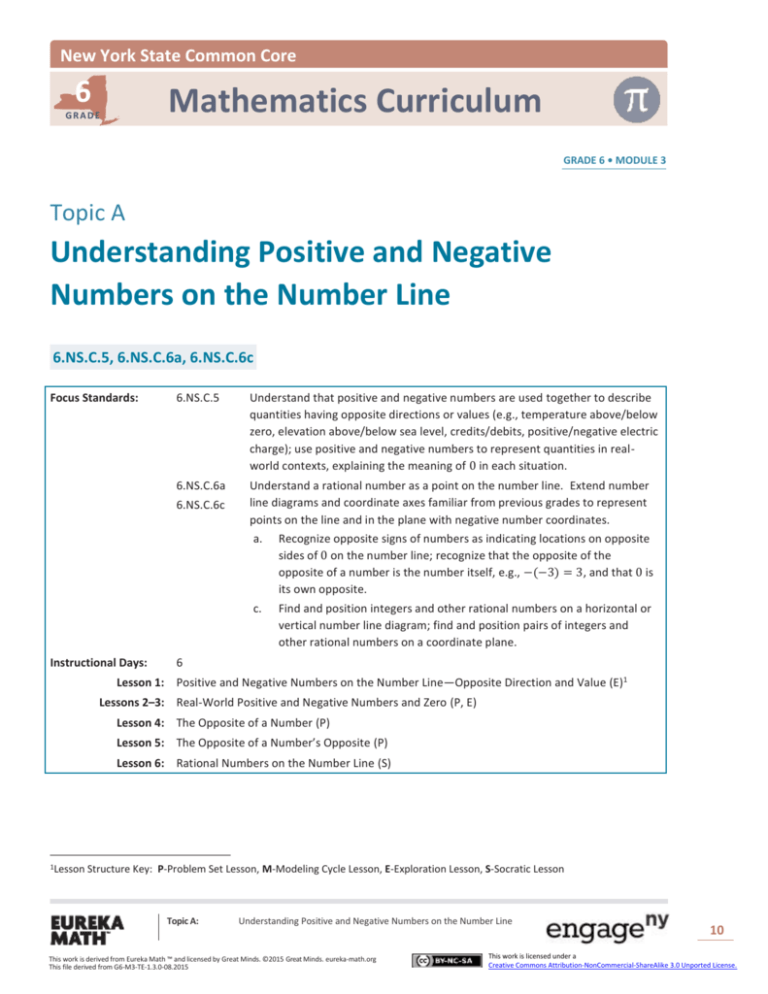
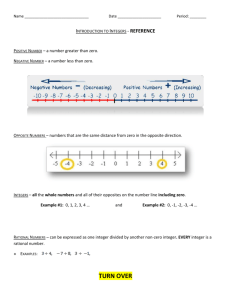
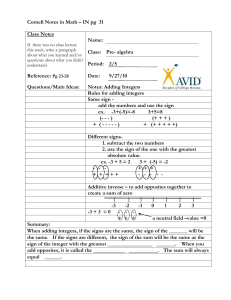
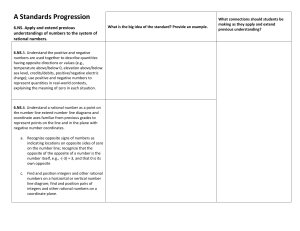
New York State Common Core 6 Mathematics Curriculum GRADE GRADE 6 • MODULE 3 Topic A Understanding Positive and Negative Numbers on the Number Line 6.NS.C.5, 6.NS.C.6a, 6.NS.C.6c Focus Standards: 6.NS.C.5 Understand that positive and negative numbers are used together to describe quantities having opposite directions or values (e.g., temperature above/below zero, elevation above/below sea level, credits/debits, positive/negative electric charge); use positive and negative numbers to represent quantities in real‐ world contexts, explaining the meaning of 0 in each situation. 6.NS.C.6a Understand a rational number as a point on the number line. Extend number line diagrams and coordinate axes familiar from previous grades to represent points on the line and in the plane with negative number coordinates. 6.NS.C.6c Instructional Days: a. Recognize opposite signs of numbers as indicating locations on opposite sides of 0 on the number line; recognize that the opposite of the opposite of a number is the number itself, e.g., −(−3) = 3, and that 0 is its own opposite. c. Find and position integers and other rational numbers on a horizontal or vertical number line diagram; find and position pairs of integers and other rational numbers on a coordinate plane. 6 Lesson 1: Positive and Negative Numbers on the Number Line—Opposite Direction and Value (E)1 Lessons 2–3: Real-World Positive and Negative Numbers and Zero (P, E) Lesson 4: The Opposite of a Number (P) Lesson 5: The Opposite of a Number’s Opposite (P) Lesson 6: Rational Numbers on the Number Line (S) 1Lesson Structure Key: P-Problem Set Lesson, M-Modeling Cycle Lesson, E-Exploration Lesson, S-Socratic Lesson Topic A: Understanding Positive and Negative Numbers on the Number Line This work is derived from Eureka Math ™ and licensed by Great Minds. ©2015 Great Minds. eureka-math.org This file derived from G6-M3-TE-1.3.0-08.2015 10 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. Topic A NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM 6•3 In Topic A, students apply their understanding of the ordering of whole numbers, positive fractions, and decimals to extend the number line in the opposite direction (6.NS.C.6 stem). In Lessons 1–3, students use positive integers to locate negative integers on the number line, moving in the opposite direction from zero, realizing that zero is its own opposite. They represent real-world situations with integers (6.NS.C.5) and understand the vocabulary and context related to opposite quantities (e.g., deposit/withdraw, elevation above/below sea level, debit/credit). Students use precise vocabulary to state, for instance, that −10 would describe an elevation that is 10 feet below sea level. In Lessons 4 and 5, students focus on locating the opposite of a number and the opposite of an opposite, using zero and the symmetry of the number line to build a conceptual understanding (6.NS.C.6a). In Lesson 6, students extend their understanding of integers to locate signed non-integer rational numbers on the number line (6.NS.C.6c), realizing that finding the opposite of any rational number is the same as finding an integer’s opposite. Topic A: Understanding Positive and Negative Numbers on the Number Line This work is derived from Eureka Math ™ and licensed by Great Minds. ©2015 Great Minds. eureka-math.org This file derived from G6-M3-TE-1.3.0-08.2015 11 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.