Landforms Study Guide Answers
advertisement

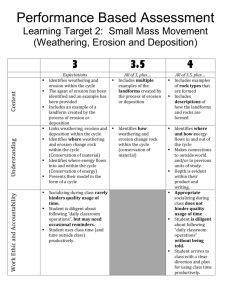
Landforms Study Guide Vocabulary (These are words that you will need to know to fully understand the material. Not all of them will be on the test.) 1. Agriculture - _ cultivating soil, producing crops, and raising livestock; farming 2. Chemical Weathering the erosion or disintegration of rocks, building materials, etc., caused by chemical reactions 3. Conservation the action of conserving something 4. Construction - the building of something 5. Constructive Forces - Processes that create landforms 6. Deposition - dropping, or depositing, of sediments by water, wind, or ice. 7. Destructive Forces Processes that destroy landforms 8. Dissolve - become or cause to become incorporated into a liquid so as to form a solution. 9. Earthquakes vibrations on Earth’s surface caused by sudden movement in Earth, often along a fault, a break in Earth’s surface. 10. Erosion movement of sediments and soil by wind, water, ice, and gravity 11. Fault - a crack in the earth's crust resulting from the displacement of one side with respect to the other; 12. Flood When large amount of water covers land that is usually dry. 13. Fossil Fuel a natural fuel such as coal or gas, formed in the geological past from the remains of living organisms. 14. Gravity the force that attracts a body toward the center of the earth 15. Landform a natural feature of the earth's surface 16. Landslide mass movements of land due to gravity. 17. Lava - Molten rock that reaches the earth's surface through a volcano or fissure 18. Magma – molten material beneath or within the earth’s crust. 19. Mining - - the process or industry of obtaining coal or other minerals from a mine. 20. Natural Resources - materials or substances such as minerals, forests, water, and fertile land that occur in nature and can be used for economic gain 21. Negative – harmful or bad 22. Organism – an individual living thing 23. Physical Weathering - - braking down of the earth's surface through the process of natural or physical means 24. Pollution - the presence in or introduction into the environment of a substance or thing that has harmful or poisonous effects. 25. Positive good or useful 26. Recycle convert (waste) into reusable material 27. Reduce make smaller or less in amount, degree, or size. 28. Reuse - use again or more than once. 29. Sediments Solid fragments of inorganic or organic material that come from the weathering of rock and are carried and deposited by wind, water, or ice. 30. Tsunami A very large ocean wave caused by an underwater earthquake or volcanic eruption. 31. Volcanic Eruption the sudden occurrence of a violent discharge of steam and volcanic material 32. Volcano - mountains with openings in Earth’s crust through which magma, gases, and ash reach Earth’s surface. 33. Weathering - processes that break down rocks at or near the surface of the earth. Classify the following as constructive, destructive, or both as we study these throughout the unit. volcanic eruption erosion earthquake flood weathering landslide deposition Constructive Both Destructive Deposition Volcanic Eruption Weathering Erosion Landslide Earthquake Flood 1. Earth’s oceans and land can be affected in __constructive_ ways and __destructive__ ways by natural processes. 2. What is the difference between constructive and destructive forces? Constructive forces create landforms while destructive forces destroy them. 3. Give three examples of landforms that were created by these forces. Mountains, canyons, deltas, etc 4. Give three causes of erosion. Water, wind, ice, gravity, etc 5. Explain how erosion is different from weathering? Weathering is only the breaking down of materials while erosion is when the weathered material is moved from one place to another. 6. Give two examples of landforms that are created as a result of deposition. Delta, sand dune 7. Describe the sequence of events that lead to the development of a river delta. weatheweweathering weathering erosion deposition ring 8. Compare physical and chemical weathering. Give two examples of each. Physical Changing rocks into smaller pieces while the type of rock remains the same Chemical Breaking down rock into smaller piecesin water, air, Chemicals plants etc change what the rock is made of. Physcial – ice, water, plants (root), temperature break apart rock Chemical – water & air combine with iron to create rust, chemicals secreted from lichens 9. How was the Grand Canyon formed? The Colorado River eroded the Colorado Plateau along with wind. 10. When deposition occurs, the smaller/larger particles settle to the bottom first. Why? Because they are heavier and need more energy to move them. 11. Find two examples of erosion around the school or in your neighbor. Insert or draw a picture and describe the process taking place. 12. Slower moving water will cause less/more erosion compared to faster moving water. 13. A flatter sloped river will have less/more erosion than a steeper sloped river. 14. Flood conditions in a river basin will contribute to less/more erosion than drought conditions. 15. Give three possible causes of a tsunami. Underwater earthquakes, landslides, and volcanic eruptions 16. Why do earthquakes occur along faults? Earthquakes occur along faults because of the buildup of pressure. 17. List three possible causes of a landslide. Storms, earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, fires, alternate freezing or thawing 18. Give two examples of how volcanoes can affect the surface of the land. It can build new land and damage the top of the volcano. 19. Give two examples of how landslides affect people. Destroy homes, roads, power and gas lines break 20. Find two different natural resources around the school or in your neighbor. Insert or draw a picture. 21. Explain the slogan “Reduce, Reuse, Recycle”. Reduce – use less of something Reuse – use something over again Recycle – make something new from and old product 22. Give a specific examples for how you could reduce, reuse and recycle in your everyday life at home or at school. Give an example for each. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 23. Give a specific example of air, water and land pollution. Give an example for each. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________