Caedmon Primary School – Year 6 Curriculum Guide Autumn 1
advertisement
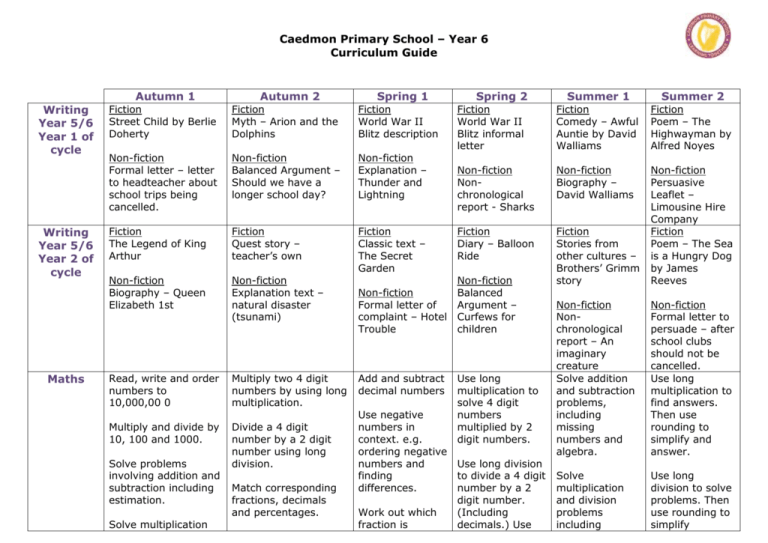
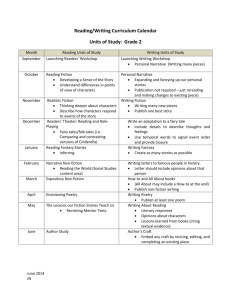
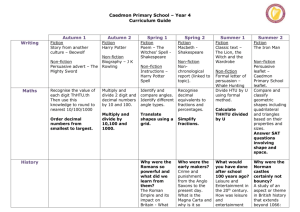
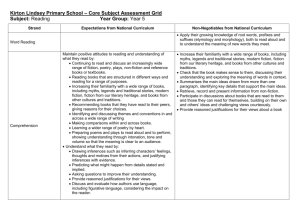
Caedmon Primary School – Year 6 Curriculum Guide Autumn 1 Writing Year 5/6 Year 1 of cycle Writing Year 5/6 Year 2 of cycle Maths Autumn 2 Spring 1 Fiction Street Child by Berlie Doherty Fiction Myth – Arion and the Dolphins Fiction World War II Blitz description Non-fiction Formal letter – letter to headteacher about school trips being cancelled. Non-fiction Balanced Argument – Should we have a longer school day? Non-fiction Explanation – Thunder and Lightning Fiction The Legend of King Arthur Fiction Quest story – teacher’s own Fiction Classic text – The Secret Garden Non-fiction Biography – Queen Elizabeth 1st Non-fiction Explanation text – natural disaster (tsunami) Read, write and order numbers to 10,000,00 0 Multiply two 4 digit numbers by using long multiplication. Multiply and divide by 10, 100 and 1000. Divide a 4 digit number by a 2 digit number using long division. Solve problems involving addition and subtraction including estimation. Solve multiplication Match corresponding fractions, decimals and percentages. Non-fiction Formal letter of complaint – Hotel Trouble Add and subtract decimal numbers Use negative numbers in context. e.g. ordering negative numbers and finding differences. Work out which fraction is Summer 1 Summer 2 Fiction World War II Blitz informal letter Spring 2 Fiction Comedy – Awful Auntie by David Walliams Fiction Poem – The Highwayman by Alfred Noyes Non-fiction Nonchronological report - Sharks Non-fiction Biography – David Walliams Fiction Diary – Balloon Ride Fiction Stories from other cultures – Brothers’ Grimm story Non-fiction Persuasive Leaflet – Limousine Hire Company Fiction Poem – The Sea is a Hungry Dog by James Reeves Non-fiction Nonchronological report – An imaginary creature Solve addition and subtraction problems, including missing numbers and algebra. Non-fiction Formal letter to persuade – after school clubs should not be cancelled. Use long multiplication to find answers. Then use rounding to simplify and answer. Solve multiplication and division problems including Use long division to solve problems. Then use rounding to simplify Non-fiction Balanced Argument – Curfews for children Use long multiplication to solve 4 digit numbers multiplied by 2 digit numbers. Use long division to divide a 4 digit number by a 2 digit number. (Including decimals.) Use Caedmon Primary School – Year 6 Curriculum Guide problems and division problems using multiplication grids and short division. Calculate mean, mode and range. Find area and perimeter of shapes using formulae. Explore the order of operation s. (BODMAS ) Interpret and construct pie charts Draw 2 and 3D and line graphs. shapes using given angles and lengths. Calculate missing angles in a straight line, a triangle and a parallelogram. Identify opposite angles and the angle sizes. History larger/smaller by cancelling common factors. Convert fractions to decimals and percentages. Then use this to order fractions using <>. Conversion graphs to convert units. Then use their knowledge of conversion to check answers. this to calculate fractions and percentages of amounts. Solve problems which involve the relative size of 2 quantities and that involve unequal sharing and grouping. (Ratio and proportion) Draw and translate shapes. Reflect these in the X and Y axis. Interpret and construct line and pie charts. Who were the Mayans and what have learnt from them ? Were the Vikings always victorious and vicious? A non European society that provides contrast with British The Viking and Anglo-Saxon struggle for the Were the Tudors really terrible? A Study of an aspect or theme in British history, beyond 1066 missing numbers and algebra. Convert units, including km to metres and km to miles. Compare and order fractions. Move to adding and subtracting fractions with different denominators and mixed numbers. Draw shapes/ objects through scaling. Calculate the areas of cubes and cuboids using the units cm3 answers. Multiply 2 fractions and then write the answer in its simplest form. Divide proper fractions by whole numbers. Illustrate and name parts of a circle. Write formula for finding the areas of a variety of shapes. Calculate missing angles including exterior angles for a range of regular polygons. Caedmon Primary School – Year 6 Curriculum Guide history - Mayan civilization around 900AD Geograph y Why is Brazil in the news again? Locate the world’s countries, using maps to focus on South America and concentrating on their key physical and human characteristics, countries, and major cities. kingdom of England - Viking raids - Edward the confessor I’m a Year 6 pupil, can you get me out of here? Use the eight points of a compass, fourfigure grid references, symbols and key (including the use of Ordnance Survey maps) to build their knowledge of the United Kingdom and the wider world use fieldwork to observe, measure and record the human and physical features in the local area using a range of methods, Will you ever see the water you drink again? Understand the water cycle Caedmon Primary School – Year 6 Curriculum Guide including sketch maps, plans and graphs, and digital technologies. Science Could Spiderman really exist? • • Could you be the next Nintendo apprentice? describe how living things are • classified into broad groups according to common observable characteristics and based on • similarities and differences, including microorganisms, plants and animals give reasons for classifying plants • and animals based on specific characteristics identify and name the basic parts of a simple electrical circuit, including cells, wires, bulbs, switches and buzzers associate the brightness of a lamp or the volume of a buzzer with the number and voltage of cells used in the circuit compare and give reasons for variations in how components function, including the brightness of bulbs, the loudness of buzzers and the on/off position of switches. Have we always looked like this? • • • recognise that living things produce offspring of the same kind, but normally offspring vary and are not identical to their parents describe how adaptation leads to evolution recognise how and why the human skeleton has changed over time, since we separated from other primates. How can you light up your life? • • • understand that light appears to travel in straight lines use the idea that light travels in straight lines to explain that objects are seen because they give out or reflect light into the eye use the idea that light travels in straight lines to explain why shadows have the same shape as the objects that cast Assessment What would a journey through your body look like? • identify and name the main parts of the human circulatory system, and explain the functions of the heart, blood vessels and blood (including the pulse and clotting). Caedmon Primary School – Year 6 Curriculum Guide them, and to predict the size of shadows when the position of the light source changes. Computin g E-Safety use technology safely, respectfully and responsibly; recognise acceptable/unacce ptable behaviour; identify a range of ways to report concerns about content and contact Computer Science 2D shapes Scratch design, write and debug programs that accomplish specific goals, including controlling or simulating physical systems; solve problems by decomposing them into smaller parts Digital Literacy Web Publishing Google Sites Digital Literacy 3D Modelling Google Sketchup understand computer networks, including the internet; how they can provide multiple services, such as the World Wide Web, and the opportunities they offer for communication and collaboration Digital Literacy Podcasting Audacity select, use and combine a variety of software (including internet services) on a range of digital devices to design and create a range of programs, systems and content that accomplish given goals, including collecting, analysing, evaluating and presenting data and information Computer Science Tables Game Scratch select, use and combine a variety of software (including internet services) on a range of digital devices to design and create a range of programs, systems and content that accomplish given goals, including collecting, analysing, evaluating and presenting data and information Digital Literacy Spreadsheets Excel design, write and debug programs that accomplish specific goals, including controlling or simulating physical systems; solve problems by decomposing them into smaller parts use sequence, selection, and repetition in programs; select, use and combine a variety of software (including internet services) on a range of digital devices to design and create a range of programs, systems and content that accomplish given goals, including collecting, analysing, evaluating Caedmon Primary School – Year 6 Curriculum Guide P.E. P.S.H.E. French use sequence, selection, and repetition in programs; work with variables and various forms of input and output use logical reasoning to explain how some simple algorithms work and to detect and correct errors in algorithms and programs Zenith Zenith Children’s Rights, Anti-Bullying Responsibilities and Risks Continue to use Continue to the vocabulary learn about learnt in years 3, 4 syntax and and 5, and they make learn new comparison vocabulary between French consisting of and English and nouns, verbs, other languages adjectives, they know. conjunctions and Can follow a verbs. They strategic develop their use approach to of sentence phoneme/graph starters, which eme work and comprise simple have regular Zenith Third World Continue to develop pronunciat ion and fluency when speaking or when reading aloud, and continue to apply knowledge of liaison and Zenith Conflict Continue to listen to stories and to join in reading aloud, and become familiar with stories known and loved by French children Consider work with variables and various forms of input and output use logical reasoning to explain how some simple algorithms work and to detect and correct errors in algorithms and programs Zenith Equality Listen to and sing along with songs by the popular singer Henri Dès Become familiar with the works of the painters and presenting data and information Zenith Fair Trade Become familiar with the town of Vichy and the surroundi ng volcanic region in France by regularly looking at photograp hs on Caedmon Primary School – Year 6 Curriculum Guide adverbial phrases of place, e.g. dans la cuisine, dans le jardin, dans la piscine and also adverbial phrases of time such as aujourdhui, À trois heures et demie. They begin to develop an understanding of tense by changing the verb and using an adverb of time. They have opportunities to use the following tenses:present, futur proche, passé compose and impa rfait. practice in developing reading skills by using either Le Manuel Phonique or Met hode dapprendre à lire Pas a Pas. The PowerPoint slides that are an integral part of the scheme of work model the phonemes and show the graphemes. elision.. Use speaking frames and writing frames to create simple and more complex spoken and written sentences, e.g. Aujourdh ui je vais nager dans la piscine.. Hier jai entendu un petit loup gris qui chantait dan la forêt. Practise reading aloud, or reciting from memory, short stereotype s and role models Listen to and sing along with traditional French and British folk songs and learn and perform French folk dances Toulouse Lautrec and Magritte and the music of the composer Chopin PowerPoi nt slides, and using webcams to make virtual visits Practise regular physical fitness routines listening to music such as France Gall. Caedmon Primary School – Year 6 Curriculum Guide passages of text from a book about the history of France. Music School of Rock and Pop – Rock Star Rookies School of Rock and Pop – Rock Star Rookies Tudor Music Tudor music from the Tudor Court. • Evaluate how the venue, occasion and purpose affects the way a piece of music is created • Analyse features within different pieces of music • Compare and contrast the impact that different composers from different times will have had on the people of the time. Caedmon Primary School – Year 6 Curriculum Guide Art Brazilian Artwork • • • D&T Tudor Artwork Combine graphics and text based on their research. Combine visual and tactile qualities. Learn about the work of others by looking at their work in books, the Internet, visits to galleries and other sources of information. Local Painting Use water colour • painting to create a landscape or still • life painting which shows light and shadow. • Mayan Masks • Work within constraints. • Follow and refine their plan if necessary • Justify their plan to someone else. • Consider culture and society in their designs. Build a Viking Longboat • Use a range of information to inform their design • Use tools and materials precisely • Change the way they are working if needed • Test and evaluate their final product. Explain what their own style is. Use a wide range of techniques in their work Explain why they have chosen specific painting techniques. Waterpowered toy • Justify why they selected specific materials • Work within a budget • Ensure that their work is precise and accurate • Hide joints so as to improve the look of their product. Caedmon Primary School – Year 6 Curriculum Guide R.E. Why is the Buddha important for Buddhists? To think about different famous people and why they are famous To find out the basic facts of the Buddhist religion. To identify key events in the life of the Buddha. To understand why the life of the Buddha is important for Buddhists. To understand the significance of the Buddhist shrine and how Buddhists can worship at home. To explore how Theravadin Buddhists express their faith. To explore the concept of community in the Buddhist tradition and beyond. Why are Good Friday and Easter Day the most important days for Christians? To understand the Easter story and realise its significance for Christians. To identify ways in which Christians celebrate Easter. To know that Good Friday is the anniversary of the Crucifixion. To understand why Christians believe Jesus is the Light of the World. To compare and contrast the church on Good Friday and Easter Sunday and recognise the significance of Easter Sunday. How and why do some religious people inspire others? To understand what an inspirational person is and what makes them one. To understand how people have inspired others by actions and words. To compare these inspirational people and the techniques they have used.