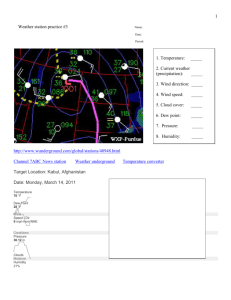
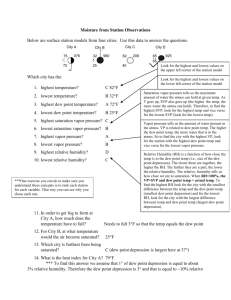
Topic I Notes - Central Square Central School District
advertisement

Name:_________________________ Earth Science Notes Topic 1: Weather Density/Rate of Change Observations/Inferences Interpreting Graphs Weather Variables Air Pressure Relative Humidity/Dew Point Winds Phase Changes of Water Air Masses and Fronts Mr. Argus Regents/Honors Earth Science Paul V. Moore High School Central Square Density: The amount of matter (mass) in a certain amount of space (volume). Calculating Density, Mass, and Volume: M D V Rate of Change: Measures the speed or rate at which an event happens. Formula: Rate of Change = Change in field value time Observations and Inferences Observation: Something you learn or know by using any of your senses. Inference: A guess or prediction that is based on your observations. Interpreting Graphs Direct Relationship: As X variable increases, it causes Y to also increase. Inverse Relationship: As X variable increases, it causes Y to decrease. Cyclic Change: As X variable increases, it causes Y to increase and decrease in a cycle. Topic 1 Vocabulary Air Mass: Anemometer: Atmosphere: Barometer: Cold Front: Warm Front: Greenhouse Effect: High Pressure: Low Pressure: Insolation: Latent Heat: Ozone Layer: Psychrometer: Saturation: Specific Heat: Weather Variables Variable Instrument used to measure Air Temperature Thermometer Air Pressure Barometer Relative Humidity Sling Psychrometer Dew Point Temperature Sling Psychrometer Wind Speed Anemometer Wind Direction Anemometer thermometer sling psychrometer barometer anemometer The Atmosphere The atmosphere is:______________________________________________ The atmosphere has layers (“spheres”): The “ozone layer” is part of the ________________________________ It’s important because ________________________________________ Composition of the atmosphere (see “troposphere”): Phase Changes of Water solid liquid gas From the Reference Tables, p. 1: Latent Heat: During melting, sublimation, and evaporation:________________________ Evaporation is a cooling process because:____________________________ During freezing, deposition, and condensation:_______________________ Condensation is a warming process because:_________________________ Station Models Used on weather maps to show weather data for one place Decode the station model to the left! temperature dew point precipitation present weather wind speed wind velocity air pressure visibility Heat Transfer Conduction: When heat energy is transferred between objects that are touching. Example: Burning your hand on a hot stove. Convection: Happens in liquids and gasses. Material circulates because of changes in temperature and density. Example: Lava lamp. Radiation: Energy moves through space. Example: Sunlight. Relative Humidity and Dew Point Temp. Relative Humidity:______________________________________ Two ways to change Relative Humidity: 1) _________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ Air Temp = 200 C RH=_______ RH=_______ RH=_______ RH=_______ 2) _________________________________________________ Temp = 200 C Temp = 15 C Temp = 12.50 C Temp = 100 C RH=_______ RH=_______ RH=_______ RH=_______ Dew Point Temperature:_________________________________ If air temp. and dew point temp. are the same: RH = _____________ and it _______________ *Dew Point Temperature depends on _______________________ Temp = 200 C Temp = 15 C Temp = 12.50 C Temp = 100 C RH=_______ RH=_______ RH=_______ RH=_______ Dew Point =_______________ Air Temp = 200 C RH=_______ RH=_______ Dew Point =_______________ RH=_______ RH=_______ Finding Relative Humidity and Dew Point Temperatures: Use Reference Tables p. 12- (use the correct chart!) Match up the dry bulb temp. and the difference between dry and wet bulb temps. Dewpoint Temp.: Practice finding the dew point by using these values: dry bulb (0C) wet bulb (0C) 14 12 22 18 6 3 Difference between wet and dry bulbs dewpoint temperature (0C) Relative Humidity: Practice finding the relative humidity by using these values: dry bulb (0C) wet bulb (0C) 16 12 4 23 3 18 Difference between wet and dry bulbs relative humidity (%) Precipitation Water coming from the air in some form (rain, snow, etc). How precipitation forms: Water vapor condenses and collects on “condensation nuclei” (dust, pollen, etc), makes cloud droplet. Cloud droplets collide and combine to make larger droplets. They can freeze now to make an ice crystal. When large enough, they fall to the ground. Precipitation forms: On hot, humid days (thunderstorms). At fronts. When air is forced over a mountain range (“Orographic Effect”). *In each of these situation, warm air rises and cools to its dew point temperature. Water vapor condenses, and makes precipitation. Air Pressure *See Reference Tables p. 13 for pressure conversion scale! Air pressure is:__________________________________________ High Pressure (“H”): Air ____________ because it is ___________ dense, because: _____________ _____________ Winds: H Weather associated with high pressure: Low Pressure (“L”): Air _________ ___ because it is ____________ dense, because: _____________ _____________ Winds: L Weather associated with low pressure: Wind Wind forms when:____________________________________ H L Wind moves in a curved path because:______________________ Isobars:_______________________________________________ Wind Speed/Pressure Gradient Heating of the Atmosphere The atmosphere is heated ________________________________ Insolation:_____________________________________________ Specific Heat:___________________________________________ *See p. 1 in Reference Tables for Specific Heats of Common Materials Table! “Greenhouse Effect”:____________________________________ Land: Water: Land and Sea Breezes In the daytime: At night: Air Masses and Source Regions An air mass is:__________________________________________________ Air Mass Source Regions:_________________________________________ Fronts Cold Fronts: Map Symbol: Weather: Warm Fronts: Map Symbol: Weather:______________________________________________________ Stationary Fronts: Map Symbol: Weather:______________________________________________________ Occluded Fronts: Map Symbol: Weather:______________________________________________________ Fronts, Continued… H C L A B The fronts and air pressure are causing the weather at these locations. Describe the weather at: Location A: Location B: Location C: