Changes in temperature can cause rocks to crack and flake. When
advertisement

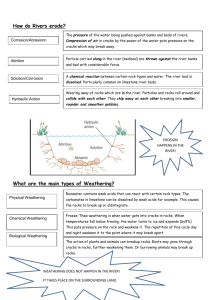
Weathering and Erosion Focus Questions 1. What is weathering? - The breakdown of rocks and other materials into smaller pieces. 2. What is physical (mechanical) weathering? - Cracking, breaking up, and grinding down of rocks into smaller pieces while maintaining the same mineral composition. 3. What is chemical weathering? - The breakdown of rocks as a result of change in their composition. 4. Explain how changing temperatures are responsible for weathering of rock surfaces. - Heat makes things expand. Cold makes things contract. Changing temperatures cause rocks to crack and flake. Ice splits rocks open. 5. How can animals function as agents of weathering? - Living things dig or pry open rocks. 6. How do plants cause physical weathering? - Plant roots can grow into cracks of rocks. 7. Explain abrasion and give examples of the process. - Abrasion breaks down rocks with solid particles like sand. 8. What are the many ways in which water is responsible for weathering? - Water can dissolve minerals that hold rocks together by chemically changing the rock and causing it to crumble. 9. What is erosion? - The removal and relocation of rocks and soil from their original location. 10. What is deposition? - The process of dropping off or depositing weathered materials in a new location. 11. What is acid rain, carbonation, and oxidation? - Acid rain- rain, snow, sleet, or hail that has a heavy concentration of sulfuric and nitric acids. Acid rain forms when pollutants from burning fossil fuels combine with moisture in the air. - Carbonation – the process in which weak carbonic acid created by the combination of water and carbon dioxide interacts with another substance. Carbonation dissolves rocks and minerals. - Oxidation – The process in which oxygen in the air combines with minerals to weaken rock. The oxidation of iron causes rust. Discussion Questions 1.) How can changes in temperature cause weathering? Changes in temperature can cause rocks to crack and flake. When the temperature drops below the freezing point of water (0 degrees Celsius), water in cracks turns to ice. Water expands as it freezes, pushing apart the walls of the crack. 2.) Describe what abrasion does to rocks. Moving water and air (wind) can carry sand and other particles. When these particles strike rocks, they chip away at the surface, much as you would if you rubbed a rock with sand paper. 3.) What process changed the color of these rocks? Oxidation- the red brown crust called rust is iron oxide. It forms when oxygen in the air combines with iron. Oxidation can weaken and crumble rocks. 4.) Which sample eroded the most in the investigation? Which sample eroded the least? Explain why. The soil in the sod sample eroded the least. The roots of the grass keep the soil in place. The loose soil with the rocks eroded the most. Has no protective covering of plants to keep the soil in place. 5.) Name some ways people can prevent erosion. Construction of levies, jetties, and dams. Plants keep soil in place and prevent erosion.