November 9-13, Weathering and Erosion
advertisement

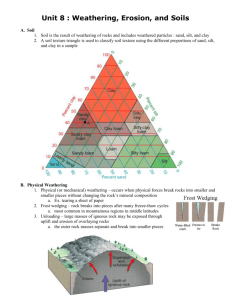
Science ------Chapter 4-Lesson 3---Weathering and Erosion Test --- Fri. Nov. 13, 2015 Vocabulary 1. Deposition- the process of dropping off bits of eroded rock. 2. Erosion- the process of carrying away soil or pieces of rocks. 3. Floodplain- land near a river that is likely to be under water during a flood. 4. Glacier- a large sheet of ice and snow that moves slowly over land. 5. Meander- a gentle loop that sometimes forms in slow moving water. 6. Sediment- the particles of soil or rock that may be eroded and deposited. 7. Weathering- the process through which rocks are broken down. Notes: 1. There are 2 kinds of weathering a. Physical weathering is caused by pushing, pulling, rubbing, or temperature changes. b. Chemical weathering occurs when chemicals break down rock. 2. In chemical weathering, rocks are worn down by the effect of chemicals such as acid rain, which is the product of gases from factories. 3. In physical weathering, rocks are worn over time by rubbing, gravity,and temperature changes, among other things. 4. A mudslide is the movement of a large amount of wet soil and rock down a slope. 5. Land can be eroded by gravity, glaciers, running water, waves, or wind. 6. A Landslide is the movement of a large amount of rock and soil down a slope. A landslide may occur after an earthquake or a volcanic eruption. 7. How does water force cracks in rocks further apart? As water freezes, it expands. This forces the cracks to become larger. 8. A headland is an area of land that has water on three sides. 9. A sandbar is a strip of sandy land. 10. Shoreline or the edge of a body of water. 11. When bits of rocks wear away the ground at the beginning of a glacier, a steep bowl-shaped hollow called a cirque (Surk) is formed. 12. If Kierra was creating a pamphlet on constructive processes that occur on Earth’s surface, she could include how a volcano forms islands in the Pacific Ocean. 13. Water is a significant factor in the physical weathering of rocks. 14. When waves pick up sand particles and move them along the shore, beach erosion can occur. 15. Plants can help prevent mudslides. 16. Evidence of chemical weathering is changes in color. 17. People can protect beaches from erosion by planting grasses. 18. Kelvin is creating a poster that shows rapid changes on Earth’s surface. He could show forest fires, earthquakes, or volcanic activity. 19. A flood forms when water collects on land that is normally dry. 20. Dunes are sand formations. They are formed when the wind blows sand into piles. 21. Breakwater is a long wall built out in the ocean parallel to the shore. 22.John placed a piece of limestone in a beaker filled with vinegar. John is studying the effect of chemical weathering. 23. Erosion can change mountains over many years by making the mountains shorter. 24. Pollution can also cause chemical weathering. 25. Erosion is caused by wind, gravity or running water.