Drug - PSNC
advertisement

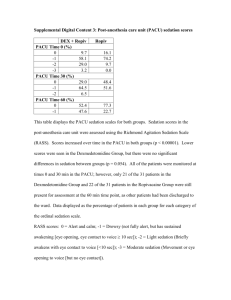
Drugs that can contribute to falls and confusion in the elderly Doncaster Central PCT Note: The effects of alcohol can increase the risk of falls and confusion in the elderly when taken with some medicines Drug Amitripytline Atropine (eye drops) Bromocriptine Chlorpheniramine Dantrolene Diazepam Dicycloverine Diphenydramine Dosulepin (dothiepin) Doxepin Hydroxyzine Imipramine Oxybutynin Procyclidine Promethazine Propantheline Tolterodine Trazadone Citalopram Co-beneldopa Co-careldopa Fluoxetine Indomethacin Paroxetine Sertraline Cimetidine Flupentixol Type of drug TCA* Antimuscarinic Anit-Parkinsons Antihistamine Muscle relaxant TCA* Anti-spasmodic Antihistamine TCA* Antidepressant Antihistamine TCA* Antimuscarinic Antimuscarinic Antihistamine Antispasmodic Antimuscarinic Antidepressant SSRI antidepressant* Anti- Parkinsons Anti-Parkinsons SSRI antidepressant* Analgesic SSRI antidepressant* SSRI antidepressant* Reduces stomach acid Antipsychotic Olanzapine Antipsychotic Quetiapine Antipsychotic Side-effect of drug Antimuscarinic Antimuscarinic Antimuscarinic Antimuscarinic Antimuscarinic Antimuscarinic Antimuscarinic Antimuscarinic Antimuscarinic Antimuscarinic Antimuscarinic Antimuscarinic Antimuscarinic Antimuscarinic Antimuscarinic Antimuscarinic Antimuscarinic Antimuscarinic Confusion Confusion Confusion Confusion Confusion Confusion Confusion Confusion (usually if kidney/liver impaired) Drug induced Parkinson’s Disease Drug induced Parkinson’s Disease, Drug induced Drug Type of drug Risperidone Antipsychotic Metoclopramide To treat nausea Prochlorperazine Nausea/dizziness Carbamazepine Anti-epileptic, Pain control Anti-epileptic Phenytoin Amlodipine Atenolol Bendroflumethazide Captopril Clonidine Diltiazem Dipyrimadole Doxazosin Enalapril Felodipine Furosemide(frusemide) Hydralazine Lisinopril Methyldopa Nifedipine Nitrates Pergolide Prazosin Propranolol Ramipril Selegilene Notes on the use of colour Red = drugs that have antimuscarinic effects (see notes at end) Blue = drugs that can lower the blood pressure Black = drugs which do not specifically fit in any of the above categories Ca channel blocker* Beta blocker Diuretic ACE inhibitor Antihypertensive, migraines Ca channel blocker* Anti-platelet Alpha blocker ACE Inhibitor ACE Inhibitor Diuretic Vasodilator ACE inhibitor Antihypertensive Ca channel blocker* Vasodilator Anti-Parkinsons Alpha blocker Beta blocker ACE Inhibitor Anti-Parkinsons Side-effect of drug Parkinson’s Disease, Drug induced Parkinson’s Disease, Drug induced Parkinsons Disease Drug induced Parkinsons Disease Lack of control of movements Lack of movement control Low BP Low BP Low BP Low BP Low BP Low BP Low BP Low BP Low BP Low BP Low BP Low BP Low BP Low BP Low BP Low BP Low BP Low BP Low BP Low BP Low BP Green = drugs that can cause sedation (see notes at end) Magenta = drugs which have a relatively high risk of causing confusion Thanks to© RUSHCLIFFE PRIMARY CARE TRUST This document is also available from http://medicinesmanagement.doncasterpct.nhs.uk/ Drugs that can contribute to falls and confusion in the elderly Doncaster Central PCT Note: The effects of alcohol can increase the risk of falls and confusion in the elderly when taken with some medicines Drug Timolol (inc eye drops) Verapamil Baclofen Type of drug Beta blocker Ca channel blocker* Muscle relaxant Fludrocortisone Prednisolone Chlordiazepoxide Chlormethiazole Chlorpromazine Co-codamol Codeine Co-proxamol Cyclizine Dihydrocodeine Nitrazepam Phenobarital Promazine Temazepam Tramadol Trifluoperazine Zopiclone Methocarbamol Steroid Steroid Benzodiazepine Sleeping tablet Antipsychotic Analgesic Analgesic Analgesic Nausea/dizziness Analgesic Benzodiazepine Anti-epileptic Antipsychotic Benzodiazepine Analgesic Antipsychotic Sleeping tablet Muscle relaxant Haloperidol Antipsychotic Morphine Analgesic Digoxin (usually associated with toxicity) Benzhexol To treat heart failure Antimuscarinic Side-effect of drug Low BP Low BP Muscle spasticity, dizziness Osteoporosis Osteoporosis Sedation Sedation Sedation Sedation Sedation Sedation Sedation Sedation Sedation Sedation Sedation Sedation Sedation Sedation Sedation Sedation, confusion, dizziness Sedation, Drug Induced Parkinson’s Disease Sedation, low BP, muscle rigidity Visual disturbances, Drowsiness, confusion, dizziness Visual impairment TCA* – Tricyclic Antidepressant Ca channel blocker* – Calcium Channel blocker used to treat cardiovascular problems SSRI* - Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor (a type of antidepressant) Notes on the chart This is a general guide; the list is not comprehensive and shows examples only. Many drugs will have a number of side effects, only the main ones have been listed. Further information should always be sought. Brand names have not been included. The drug name is usually apparent on the box or strip of medication. The chart contains information derived from the BNF, studies on the relationship between drugs and falling, the “Beer Criteria” and North-East Derbyshire Primary Care Trust. Drugs that cause sedation Any drug which cause sedation can worsen a pre-existing or create a new state of confusion in the elderly. It is one of the most common causes of drug-induced falls. However, almost any of the commonly used drugs can cause confusion in the elderly as adverse effects in these people tend to present with confusion as the main symptom. Drugs with antimuscarinic effects These are drugs which block muscarinic receptors in the nervous system. Actions of these drugs include relaxation of smooth muscle, decreased secretion of saliva, sweat and digestive juices and dilation of the pupil of the eye. Side-effects include drowsiness and blurred vision. Toxicity is common and can result in confusion. Toxicity is often the cumulative effect of several medicines with antimuscarinic effects. Drugs which affect the central nervous system These include antipsychotics, antidepressants, sleeping tablets and benzodiazepines. They can cause confusion, sedation, impaired balance and low BP, especially on standing and often also have antimuscarinic Notes on the use of colour Red = drugs that have antimuscarinic effects (see notes at end) Blue = drugs that can lower the blood pressure Black = drugs which do not specifically fit in any of the above categories Green = drugs that can cause sedation (see notes at end) Magenta = drugs which have a relatively high risk of causing confusion Thanks to© RUSHCLIFFE PRIMARY CARE TRUST This document is also available from http://medicinesmanagement.doncasterpct.nhs.uk/ Doncaster Central PCT Drugs that can contribute to falls and confusion in the elderly Note: The effects of alcohol can increase the risk of falls and confusion in the elderly when taken with some medicines effects. Some drugs can also cause symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease such as tremor and abnormal body movements. It should be remembered that these drugs are often prescribed for conditions which in themselves can cause confusion and sedation such as depression. Multiple drugs The greater the number of drugs an older person takes, the greater the likelihood is of then falling, especially if these drugs affect the central nervous or cardiovascular systems. Notes on the use of colour Red = drugs that have antimuscarinic effects (see notes at end) Blue = drugs that can lower the blood pressure Black = drugs which do not specifically fit in any of the above categories Green = drugs that can cause sedation (see notes at end) Magenta = drugs which have a relatively high risk of causing confusion Thanks to© RUSHCLIFFE PRIMARY CARE TRUST This document is also available from http://medicinesmanagement.doncasterpct.nhs.uk/