Standard 4A: DNA and Protein Synthesis Describe the chemical
advertisement
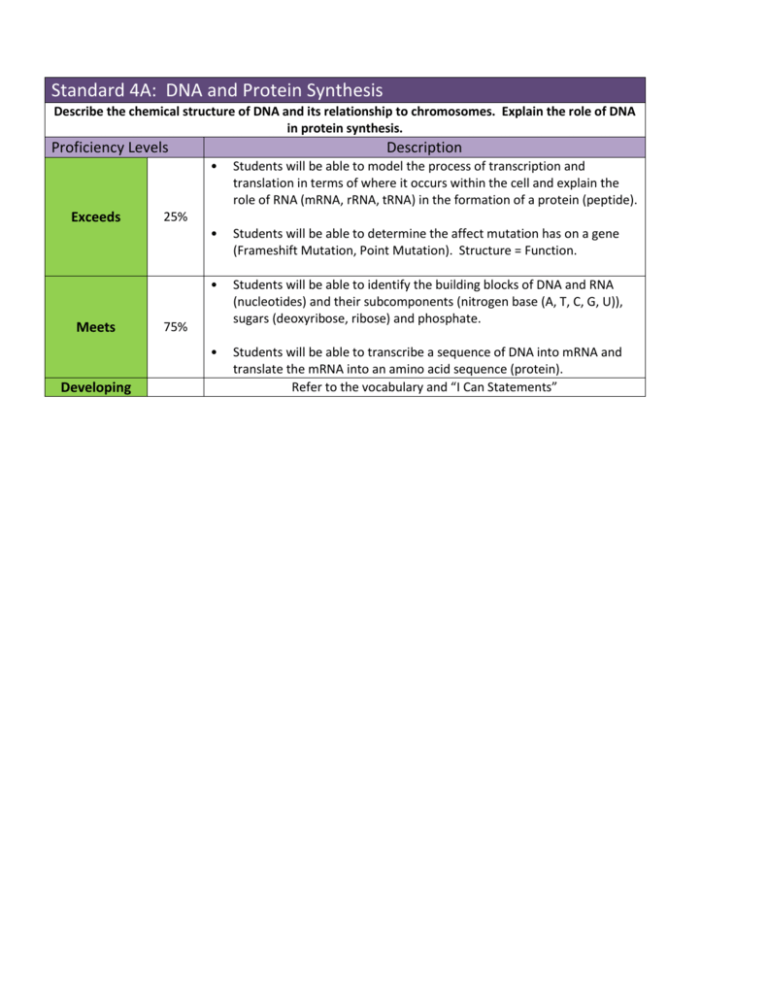
Standard 4A: DNA and Protein Synthesis Describe the chemical structure of DNA and its relationship to chromosomes. Explain the role of DNA in protein synthesis. Proficiency Levels Exceeds Meets Developing Description • Students will be able to model the process of transcription and translation in terms of where it occurs within the cell and explain the role of RNA (mRNA, rRNA, tRNA) in the formation of a protein (peptide). • Students will be able to determine the affect mutation has on a gene (Frameshift Mutation, Point Mutation). Structure = Function. • Students will be able to identify the building blocks of DNA and RNA (nucleotides) and their subcomponents (nitrogen base (A, T, C, G, U)), sugars (deoxyribose, ribose) and phosphate. • Students will be able to transcribe a sequence of DNA into mRNA and translate the mRNA into an amino acid sequence (protein). Refer to the vocabulary and “I Can Statements” 25% 75% UNIT 6: DNA and Protein Synthesis, Biotechnology VOCABULARY Adenine Double-Helix Phosphate Template Amino Acid Frameshift Mutation Point Mutation Thymine Anticodon Guanine Protein Transcription Codon mRNA Ribose Translation Cytosine Mutation Ribosome tRNA Deoxyribose Nucleus rRNA Uracil DNA Peptide Single-Helix Restriction enzyme Clone Stem cell DNA fingerprint genomics 1. I can explain the attributes of DNA in terms of its four nitrogen bases, type of sugar, helical form and function. 13.1 Quiz 1 2. I can identify the complete nucleotide for any DNA molecule. 13.1 3. I can describe how DNA is replicated (copied). 13.2 4. I can explain the attributes of RNA in terms of its four nitrogen bases, type of sugar, helical form and function. 13.3 5. I can identify the complete nucleotide for any RNA molecule. 13.3 6. I can define the term transcription in my own words. 13.3 7. I can define the term translation in my own words. 13.3 Quiz 2 8. I can determine the cellular location of where transcription occurs. 13.3 9. I can determine the cellular location of where translation occurs. 13.3 10. I can take a strand of DNA and convert it into a complementary strand of mRNA. 13.3 11. I can take a strand of mRNA, allocate it into codons and determine its correct amino acid sequence. 13.3 12. I can draw a picture of a cell and show how the steps of transcription and translation in their appropriate location, labeling the appropriate components necessary to produce a peptide (Nucleus, DNA, Ribosome, tRNA, rRNA, mRNA, amino acids, peptide). 13.3 13. I can look at a strand of mRNA that has been mutated from the original strand of DNA and determine if a Quiz 3 frameshift or point mutation has occurred. 14.1 14. I can look at mutated strands of mRNA and determine which one would affect the function of the peptide the most, by translating the mutated strand into the amino acid sequence and comparing it to the un-mutated strand. 14.1 15. I can describe DNA fingerprinting and its practical applications. 15.1 16. I can explain how a stem cell is different from other cells. 15.2 17. I can explain how large animals (such as a mouse) can be cloned and describe the biological relationship between the clone and it’s surrogate, somatic cell donor, and egg donor. 15.2 18. I can explain how a restriction enzyme functions, and demonstrate with a given sequence of DNA where the enzyme will cut the DNA. 15.3 Quiz 4










