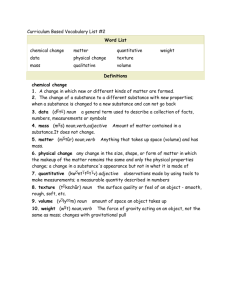
Grammatical Category
advertisement

Grammatical Category The term "grammatical category" refers to specific properties of a word that can cause that word and/or a related word to change in form for grammatical reasons (ensuring agreement between words). For example, the word "boy" is a noun. Nouns have a grammatical category called "number". The values of number are singular (one) and plural (two or more). 1. The boy is playing. 2. The boys are playing. In sentence 1, "boy" is in its basic form, giving its "number" the value of singular. There is one boy and the related auxiliary verb "to be" is in the singular form (is). In sentence 2, the form of "boy" has changed to "boys", giving its "number" the value of plural. There is more than one boy and the related "to be" is in the plural form (are). In the above example, the "number" of "boy" influences the form of boy, and also influences the form of a related word (be). "Number" is a "grammatical category". English has over twenty grammatical categories. Below we list the most common ones for English learners and summarise their main features. Number Number is a property of nouns and pronouns, and indicates quantity. Number has two values: singular: indicates one only plural: indicates two or more number singular plural noun boy pronoun I boys we Case Case is a property of pronouns and nouns, and expresses their relationship to the rest of the sentence. Case has three values (two of which do not apply to nouns): subjective (pronouns only): when the word is the subject objective (pronouns only): when the word is the object possessive (pronouns and nouns): when the word indicates possession (ownership) case subjective pronoun I boy noun objective possessive me mine boy boy's Gender Natural gender is a property of pronouns, and differentiates the sexes. Natural gender has three values: masculine: indicates male feminine: indicates female neuter: indicates everything else gender masculine pronoun he/him/his feminine neuter she/her/hers it/its Note that Old English had "grammatical gender" where words themselves had gender. Remnants of this are found in "natural gender", which is based on the sex of people rather than the gender of words. Person Person is a property of pronouns, and differentiates participants in a conversation. Person has three values: first person: refers to the speaker second person: refers to the hearer third person: refers to all other people or things person 1st pronoun I/me 2nd 3rd you he/him, she/her, it we/us they Tense Tense is a property of verbs, and most closely corresponds with location in time. Tense has two values: past: indicates before now present: indicates now (and sometimes before and after now) tense verb past present was did had worked ran am do have work run Note that "future tense" is not shown here because strictly-speaking it is not a tense but a structure to talk about the future (after now). Aspect Aspect is a property of verbs, and expresses our view of the time structure of an activity or state. Aspect has three values: simple: the time has no structure continuous: expresses ongoing action perfect: expresses completed action aspect verb simple continuous perfect they work they are working they have worked Mood Mood is a property of verbs, and relates to the speaker's feelings about the reality of what he is saying. Mood has three values: indicative: expresses simple statement of fact imperative: expresses command subjunctive: expresses something desired or imagined mood verb indicative imperative subjunctive James stood up. Stand up! We insist that he stand. Is it quiet enough? Be quiet! It is essential that you be quiet. Voice Voice is a property of transitive verbs*, and expresses the relationship of the subject to the action. Voice has two values: active: the subject does the action passive: the subject receives the action voice transitive verb active passive The cat ate the mouse. The mouse was eaten by the cat. * A transitive verb can have a direct object. Degree Degree is a property of gradable adjectives and adverbs, and indicates amount. Degree has three values: positive: indicates a basic quality comparative: indicates a greater quality superlative: indicates the maximum quality degree positive comparative superlative gradable adjective happy happier the happiest gradable adverb carefully more carefully the most carefully Grammatical Functions of English Nouns and Noun Phrases Noun phrases including nouns and pronouns perform eleven main grammatical functions within sentences in the English language. The eleven functions of nouns and noun phrases are: 1. Noun phrase head 2. Subject 3. Subject complement 4. Direct object 5. Object complement 6. Indirect object 7. Prepositional complement 8. Noun phrase modifier 9. Determinative 10. Appositive 11. Adjunct adverbial Nouns are traditionally defined as “persons, places, things, and ideas.” Noun phrase are defined as phrases that consist of a noun or pronoun and any number of constituents including adjectives, determiners, prepositional phrases, verb phrases, and adjective clauses. Noun Phrase Head The first grammatical function that nouns perform is the noun phrase head. A noun phrase consists of a noun including a pronoun plus any determiners, modifiers, and complements. For example, the following italicized nouns function as noun phrase heads: the big blue ball someone to love an old woman who lived in a shoe Subjects The second grammatical function that noun phrases perform is the subject. A subject is a word, phrase, or clause that performs the action of or acts upon the verb. For example, the following italicized noun phrases function as subjects: The baby cried. Dogs and cats make excellent pets. I will have extensively studied English grammar. Subject Complements The third grammatical function that noun phrases perform is the subject complement. A subject complement is a word, phrase, or clause that follows a copular, or linking, verb and describes the subject of a clause. The terms predicate nominative and predicate noun are also used for noun phrases that function as subject complements. For example, the following italicized noun phrases function as predicate nominatives: My grandfather is a farmer. Our favorite pets are dogs with short hair. The woman whom you are looking for is she. Direct Objects The fourth grammatical function that noun phrases perform is the direct object. A direct object is a word, phrase, or clause that follows a transitive verb and answers the question “who?” or “what?” receives the action of the verb. For example, the following italicized noun phrases function as direct objects: The children ate all the cookies. My professor recommended an extremely captivating book. The woman has always hated mice and rats. Object Complements The fifth grammatical function that noun phrases perform is the object complement. Object complements are defined as nouns, pronouns, noun phrases, adjectives, and adjective phrases that directly follow and modify the direct object. For example, the following italicized noun phrases function as object complements: We consider our puppy our baby. My aunt calls my uncle sweetheart. America recently elected Barack Obama president. Indirect Objects The sixth grammatical function that noun phrases perform is the indirect object. An indirect object is word, phrase, or clause that indicates to or for whom or what the action of a ditransitive verb is performed. For example, the following italicized noun phrases function as indirect objects: My husband bought me flowers. The child drew his mother a picture. The salesman sold the company suffering from the scandal new computers. Prepositional Complements The seventh grammatical function that noun phrases perform is the prepositional complement. A prepositional complement is a word, phrase, or clause that directly follows a preposition and completes the meaning of the prepositional phrase. For example, the following italicized noun phrases function as prepositional complements: My husband bought flowers for me. The students studied during their spring break. Because of the lengthy delay, we missed our flight. Noun Phrase Modifiers The eighth grammatical function that noun phrases perform is the noun phrase modifier. A noun phrase modifier is a word, phrase, or clause that modifies or describes a noun including a pronoun or a noun phrase. For example, the following italicized noun phrases function as noun phrase modifiers: The child actor won an award. The carpenter fixed the broken table leg. We reserved twenty hotel rooms. Determinatives The ninth grammatical function that noun phrases can perform is the determinative. Determinatives provide information such as familiarity, location, quantity, and number. Possessive nouns — which are a noun, pronoun, or noun phrase and the possessive clitic (apostrophe s or s apostrophe) — function as determinatives. Possessive nouns indicate possession of or some other relationship to another noun or noun phrase. For example, the following italicized noun phrases function as possessive modifiers: My brother’s apartment is small. I found everyone’s reports informative. The man who stole my purse’s car has been towed. Appositives The tenth grammatical function that noun phrases perform is the appositive. An appositive is a word, phrase, or clause that modifies or explains another noun phrase. For example, the following italicized noun phrases function as appositives: My grandfather, the farmer, bought more farm land. The teacher, my uncle, assigns a lot of homework. The musician Stevie Nicks is a singer in the band Fleetwood Mac. Adjunct Adverbials The eleventh grammatical function that noun phrases perform is the adjunct adverbial. An adjunct adverbial is a word, phrase, or clause that modifies an entire clause by providing additional information about time, place, manner, condition, purpose, reason, result, and concession. For example, the following italicized noun phrases function as adjunct adverbials: Today the children woke up early. Yesterday the children slept in late. We decided to go home. The eleven functions of noun phrases are noun phrase head, subject, subject complement, direct object, object complement, indirect object, prepositional complement, noun phrase modifier, determinative, appositive, and adjunct adverbial.