MODEL-EXAM-chem - Students vs Teachers
advertisement

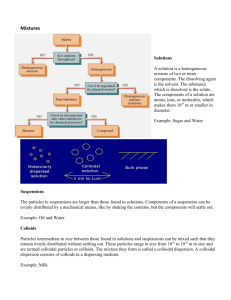
MODEL EXAM -2013 CHEMISTRY -150 Mark 1 X 30 =30 1. The oxidation number of Nickel in the complex ion, [NiCl4]2- is a) +1 b) -1 c) +2 d) -2 2. Which is not an anionic complex? a) [Cu(NH3)4]Cl2 b) K4[Fe(CN)6] c) K3[Fe(CN)6] d) [NiCl4]23. The geometry of [Ni(CN)4]2- is a) Tetrahedral b) Square planar c) Triangular d) Octahedral 4. An example of an ambidentate ligand is a) CN- b) Cl- c) NO2 d) I5. The name of [PtIV(NH3)2Cl2]2+ is a) Diamminedichloroplatinum(IV) ion b) Diamminedichloroplanitate(IV) c) Diamminedichloroplatinum d) Dichlorodiammineplatinum(IV) ion 6. The type of isomerism found in the complexes [Co(NO2)(NH3)5]SO4 and [Co(SO4)(NH3)5] NO2 a) Hydrate isomerism b) Coordination isomerism c) Linkage isomerism d) Ionisation -- 11. 12. 13. The migration of colloidal particles under the influence of an electric field is known as (a) electroosmosis (b) cataphoresis (c) electrodialysis (d) electrophoresis 14.Which one is the correct factor that explains the increase of rate of reaction by a catalyst (a) shape selectivity (b) particle size (c) increase of free energy (d) lowering of activation energy 15. Fog is a colloidal solution of (a) gas in liquid (b) liquid in gas (c) gas in solid (d) solid in gas. 16. The phenomenon of Tyndall’s effect is not observed in (a) emulsion (b) colloidal solution (c) true solution (d) None 17. The Tyndall’s effect associated with colloidal particles is due to (a) presence of charge (b) scattering of light (c) absorption of light (d) reflection of light 18. In case of physical adsorption, there is desorption when (a) temperature increases (b) temperature decreases (c) pressure increases (d) concentration increases 19. Colloidal medicines are more effective because (a) they are clean (b) they are easy to prepare (c) the germs more towards, them (d) they are easily assimilated and adsorbed 20. Oil soluble dye is mixed with emulsion and emulsion remains colourless then, the emulsion is (a) O/W (b) W/O (c) O/O (d) W/W 21. The specific conductance of a 0.01 M solution of KCl is 0.0014 ohm-1 cm-1 at 25oC. Its equivalent conductance is ............... (a) 14 ohm–1 cm2 eq–1 (b) 140 ohm–1 cm2 eq–1 (c) 1.4 ohm–1 cm2 eq–1 (d) 0.14 ohm–1 cm2 eq–1 22. The equivalent conductivity of CH3COOH at 25oC is 80 ohm-1 cm2 eq-1 and at infinite dilution 400 ohm-1 cm2 eq-1. The degree of dissociation of CH3COOH is ............... (a) 1 (b) 0.2 (c) 0.1 (d) 0.3 23. When sodium acetate is added to acetic acid, the degree of ionisation of acetic acid ............... (a) increases (b) decreases (c) does not change (d) becomes zero 24. NH4OH is a weak base because ............... (a) it has low vapour pressure (b) it is only partially ionised (c) it is completely ionised (d) it has low density 25. Ostwald’s dilution law is applicable in the case of the solution of ............... (a) CH3COOH (b) NaCl (c) NaOH (d) H2SO4 26. The potential of a single electrode is a half cell is called the (a) Reduction potential (b) Half-wave potential (c) Single electrode potential (d) cell potential 27. The relationship between free energy change and e.m.f. of a cell is (a) G = –nFE (b) H = –nFE (c) E = nFG (d) F = nEG 28. The feasibility of a redox reaction can be predicted with the help of (a) Electronegativity (b) Electrochemical series (c) Electron affinity (d) Equivalent conductance 29. The metals near the bottom of the electrochemical series are (a) strong reducing agents (b) strong oxidising agents (c) weak reducing agents (d) weak oxidising agents 30. The emf of a cell with 1 M solutions of reactants and products in solution at 25o C is called (a) Half cell potential (b) Standard emf (c) Single electrode potential (d) Redox potential 3 Mark 15 X 3 = 45 1.what are ligands and coordination numbers? 2.In what way complex salt differs from double salt? 3.Give one examples for a monodentate ligand ,a bidentate ligand and a chelating ligand? 4.what are chelates? Give one examples? 5.Define radioactivity. 6.what is half life period? 7.write any three difference between chemical and nuclear reaction? 8.what is Q value of a nuclear reaction? 9.what is radiocarbon dating? 10.Define colloidal solution? 11. what is catalysis? 12.what is tyndall effect? 13.Define faraday. 14.state ostwald’s dilution law. 15.what is Henderson equation? 16.what is common ion effect. Give examples. 17.Define standard emf of cell 18.what is single electrode potential? 19.write the Nernst equation? 20.How to predict the feasibility of cell reaction? 5Mark 7 X 5 =35 1.Application of valence bond theory in Octahedral complexes 1.Fe atom 2.Fe +2 ion 2.Uses of coordination compounds 3.The half life of cobalt-60 is 5.26 years. Calculate the % activity remaining after 4 years? 4.Uses of Radioactive isotopes 5.Difference between the physical and chemical adsorption ? 6.Theories of Catalysis 7.Explain the N-type and p-type semiconductor 8.Application of Kohlraush’s Law. 9.Determination of emf of a half cell. 10. The standard electrode potentials of the half cells Ag+ / Ag and Fe3+, Fe2+ / Pt are 0.7991 V and 0.771 V respectively. Calculate the equilibrium constant of the reaction : 10marks 4 x 10=40 1.a.Explain the Daniel cell: b. Relation between EMF add free energy 2.a.Significance of the Henderson Hasselbalch equation. b. Find the pH of a buffer solution containing 0.20 mole per litre CH3COONa and 0.15 mole per litre CH3COOH, Ka for acetic acid is 1.8 10-5 3. i)Variation of equivalent conductance with concentration ii) Importance of the First law of electrolysis. 4.Electrical properties i) Charge on colloidal particles ii)Electrophoresis 5.Explain the Electrodialysis and ultrafiltration 6.Explain the dispersion methods: a) Mechanical b) Electro c) ultra sonic and peptisation 7. a) Half-life period of a radioactive element is 100 seconds. Calculate the disintegration constant and average life period. How much time will it take for 90% decay? b)Explain the geometrical and optical isomerism.