Study/Note taking guide 1
advertisement

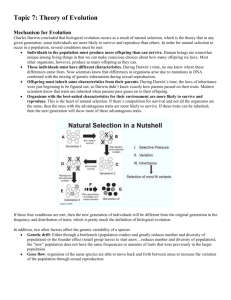
Study/Note taking guide 1 Notes: There will be three midterms, each worth 100 points. 50 of these points will be short answer questions, directly from the study guide questions and the associated vocabulary. The points next to the questions give you an indication of the detail I expect. On exams, I use the following grading scheme: Technical term listed, correctly spelled Concept explained, term defined Correct example (if asked) 1 2 2 I have partially filled out this study guide to give you an idea of what I am looking for in terms of depth. I. The evolutionary framework Application 0. Explain what led to the Indian Leaf butterfly depicted to the right looking like a dead leaf. Image: Magic of Life Trust 2007 Biology is the scientific study of life. What does it take to be alive? What strategies have evolved? What can go wrong? I find it useful to think in terms of challenges and solutions. 1. What challenges does life pose (see Key Concept I and page 2 in Hillis)? 4 Living things (organisms) must 2. Name some solutions to the challenge of being alive that are common to all life forms as we know them (the common characteristics of life). All organisms… (see remaining points in bulleted list on page 2 of Hillis) are composed of… contain… share… evolve… 3. Describe the common ancestor of life (a prokaryote) and its habitat. 6 H1_Introduction© Crima Pogge, CCSF, page 1 4. 5. 6. Define biological evolution, the evolution of the diversity of life forms. 4 Genetic and resulting phenotypic change of populations from generation to generation. What evidence points to a common ancestry of life? 4 Evolution is often simplified as the survival of the fittest. Major steps in evolution were the appearance of highly efficient eukaryotic cells (rather than prokaryotic cells) with organelles specialized for energy transformation and the evolution of multicellular organisms that allowed for more sophisticated behaviors. Explain what role cooperation plays in evolution. 8 The endosymbiosis theory postulates that chloroplasts and mitochondria originated when a cell engulfed another cell. Rather than one cell digesting the other, the two cells set up a partnership and divided labor (cooperate). Similarly, cooperation of cells in a multicellular organisms allows more sophisticated lifestyles and behaviors by having different cells specializing for different tasks. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Don’t forget to learn relevant vocabulary! gene evolution eukaryote prokaryote organelle multicellular species mutation etc. Describe the (2) observations and (2) inferences that led Charles Darwin to his theory of evolution by natural selection. Observations: - Any population of organisms displays heritable variation. - Only a small percentage of a population survives to reproduce. Inferences: - Variation leads to differential reproductive success. - Adaptations evolve in the population. Key concept II states: Adaptive responses (solutions) to the challenges of life arise randomly by mutation and are sustained by natural selection. Give an example that illustrates this key concept (e.g., the Indian leaf butterfly story). In your story, identify the selective pressure and the adaptive advantage of what has evolved. Explain the evolution of different species and give an example. Random changes in the genetic sequence (mutations) can give rise to structural and functional differences (phenotype) between descendants of a common ancestor. These changes, when not selected against, can accumulate in isolated populations over time to a point were the members of these different populations can no longer reproduce with each other. Key concept III states: The responses that evolve are constrained by (a) the laws of chemistry and physics, and (b) present and historical abiotic and biotic factors (internal and external). Can you explain this using plain language and examples? Following are three common misconceptions about evolution. What is wrong about the following statements? H1_Introduction© Crima Pogge, CCSF, page 2 8 8 6 a) evolution favors the fit, and fit equals perfect b) evolution states that humans descended from apes c) evolution is driven by competition, the survival of the fittest On your own: 12. Why is natural selection called a theory? See page 10 in Hillis. 13. Study the phylogenetic tree in Fig. 1.4. and answer the following questions: a. Are eukaryotes more closely related to archaea or to bacteria? How do you know? b. What structure is present in the common ancestor of all eukaryotes, but not in the common ancestor of all three domains of life? c. What structure is present in the common ancestor of plants and some protists, but not in the common ancestor of all eukaryotes? d. Which group evolved earlier, animals or fungi? How do you know? Note: As stated above, exams consist of short answer and multiple choice questions. All questions are derived from study guides which you’ll find for all chapters on my website at http://fog.ccsf.edu/~cpogge. Print study guides and fill them in as you are first reading the chapter BEFORE CLASS. Fill in the remaining answers during lecture. Study guides will help you organize your lecture notes, focus your reading and deepen your understanding of the concepts discussed. Understanding the answers will help you commit the ideas to your memory and draw connections between the concepts discussed throughout the course. If you are not sure about what a question is getting at, please ask for feedback in the discussion section. There are multiple choice practice quizzes online at BioPortal. Ignore questions that do not refer to study guide questions and use the practice quizzes to further commit concepts to your memory. Most important: if you get a question wrong, analyze why you got it wrong. Did you not study this concept? Did you misunderstand it? Or did the wording “trick” you? Please, always feel free to ask me for clarification! After today: Check out the links on the study guides website if you are interested in learning more about anything we discuss. Read pages 1-10 (for lecture) and 10-13 (for lab). Read and bring the file Biological Key Concepts. Make note of any questions you have about the reading. Bring those questions to your discussion section. Essay question (one essay question from the first three quarters of the course will be part of your final examination) Explain how the Indian Leaf butterfly came to look like an old leaf. Your essay should illustrate the theory of natural selection and discuss why evolution is still controversial in the US. H1_Introduction© Crima Pogge, CCSF, page 3 4 10