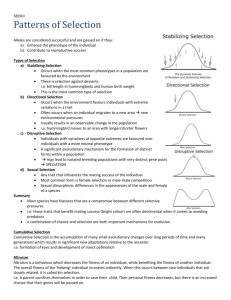
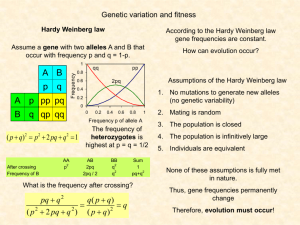
Variable names
advertisement

Common variable names, as used in L567 Theoretical population genetics (one locus with two alleles: 1 and 2) p q The frequency of allele one The frequency of allele two. Equal to 1 – p. W11 W12 W22 The fitness of the 11 homozygote. W11 = 1. The fitness of the 12 heterozygote. W12 = 1 - hs. The fitness of the 22 homozygote. W22 = 1 - s. Mean fitness of the populations. s h Little s. The selection coefficient. The dominance coefficient. Note: the dominance coefficient is not the square root of heritability. The rate of mutation u Quantitative genetics h2 H2 narrow sense heritability. h2 = (VA/VP) Broad sense heritability. H2 = (VG/VP) S R The selection differential. Capital S. Equal to cov(w, z) The response to selection (also equal to ) VA VG VP VE Additive genetic variance Total genetic variance (VA is a proportion of VG) Total phenotypic variation Total variation due to the environment. The variance in mid-parent values Vz Total phenotypic variation in trait z. This is the same as VP var(z) Total phenotypic variation in trait z. This is just another way to write the same thing cov(w, z) Covariance between fitness and trait value. Slope of the regression of w (fitness) on z (the trait value). d a -a The dominance deviation, as used for calculating breeding values The phenotype of the 11 homozygote, as used for calculating breeding values The phenotype of the 22 homozygote, as used for calculating breeding values The average effect of allele 1 The average effect of allele 2