History - Light Oaks Junior School
advertisement
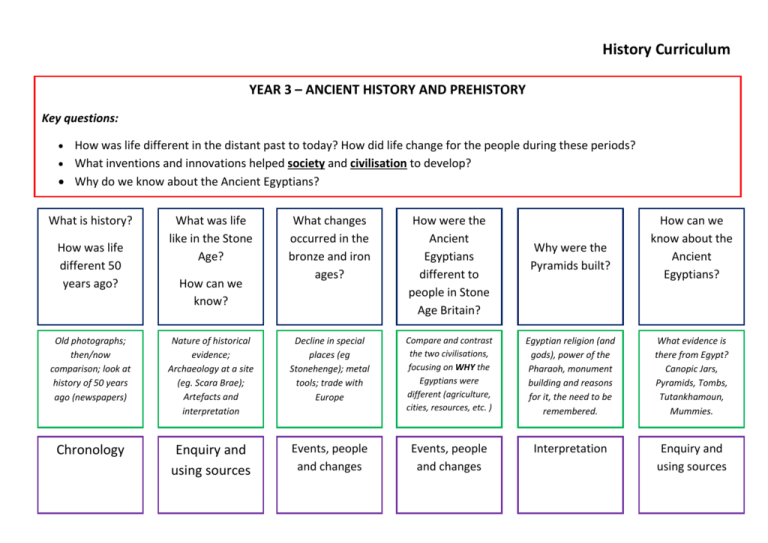
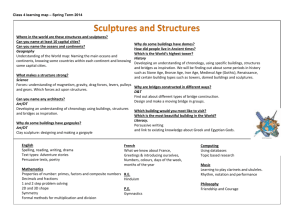
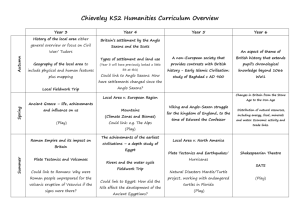
History Curriculum YEAR 3 – ANCIENT HISTORY AND PREHISTORY Key questions: How was life different in the distant past to today? How did life change for the people during these periods? What inventions and innovations helped society and civilisation to develop? Why do we know about the Ancient Egyptians? What is history? How was life different 50 years ago? What was life like in the Stone Age? How can we know? What changes occurred in the bronze and iron ages? How were the Ancient Egyptians different to people in Stone Age Britain? Why were the Pyramids built? How can we know about the Ancient Egyptians? Old photographs; then/now comparison; look at history of 50 years ago (newspapers) Nature of historical evidence; Archaeology at a site (eg. Scara Brae); Artefacts and interpretation Decline in special places (eg Stonehenge); metal tools; trade with Europe Compare and contrast the two civilisations, focusing on WHY the Egyptians were different (agriculture, cities, resources, etc. ) Egyptian religion (and gods), power of the Pharaoh, monument building and reasons for it, the need to be remembered. What evidence is there from Egypt? Canopic Jars, Pyramids, Tombs, Tutankhamoun, Mummies. Chronology Enquiry and using sources Events, people and changes Events, people and changes Interpretation Enquiry and using sources History Curriculum YEAR 4 – CLASSICAL HISTORY Key questions: Why are the Greeks remembered today? How did life change through the period? (City states, invasion, war, democracy, trade) Why were the Romans so successful at building an empire? How do we know about the Greeks? What was it like to live in a city state? How do we remember the Greeks? Who were the Romans? How were they different to the Greeks? Why and how did the Romans invade Britain? What did the Romans do for us? What evidence is there from Greece? Pots, buildings, histories, myths, names. Sparta vs. Athens, daily life, military duty and different styles; end of the system under Alexander. Democracy, philosophy, medicine, alphabet(s), buildings, Olympics. Famous Greeks Compare and contrast Greek/Roman systems: democracy vs dictatorship; belief systems; societies; city state vs. Empire. Reasons for the Roman invasion; Caesar and Claudius,; Boudicca; Hadrian’s wall. Life in Roman Britain: Celts and roundhouses; druidism; homes and frontier life; life in camps. Enquiry and using sources. Communication. Events, people and changes. Interpretation. Chronology Events, people and change. History Curriculum YEAR 5 – New Beginnings Key questions: What differences and similarities are there between the Anglo-Saxons and the Maya? How were the Anglo-Saxons and Maya different to what came before and after? (Romans/Vikings and Olmec/Aztecs respectively) What problems are there when studying the distant/unrecorded past? How did Britain under the AngloSaxons change from Britain under the Romans? How do we know about the Anglo Saxons? How did the Anglo Saxons live? How were the Maya different to the Anglo Saxons? What did a Mayan city look like? What did the Maya leave behind? Timeline work; Why did the Saxons come? (Why did the Romans leave?); Why did the Saxons stay? Written sources; Archaeology; Sutton Hoo; Coins and treasure; Offa’s dyke. Myths and mythology; Roundhouses; Warfare and warriors; trade. Differences in: location; buildings; people; culture; gods and goddesses; duration of stay. (Contrast with Aztecs) – ball games; temples [El Castillo]; Mayan glyphs (writing system); houses and dwellings. Maya today: language and people; Temples and ruins (and problems with these being in jungle); writing; folk stories. Chronology Enquiry and use of sources Events, people and changes. Events, people and changes. Interpretation Communication History Curriculum YEAR 6 – New Frontiers Key questions: What evidence is there that Britain was once settled by the Vikings? Why might Historians now believe that Vikings were settlers and not invaders? What technological advances occurred to allow things to happen? Who were the Vikings? Where did the Vikings settle? Why? How was Britain different under the Vikings? What was life like in Baghdad in 900? What was the House of Wisdom? What happened there? What would life be like without the House of Wisdom? Where did they come from? What did they look like? What did they believe? Nature of historical evidence. Britain; Iceland; America; France (Normandy); Jerusalem. Comparison of life under Vikings and AngloSaxons/Romans (/Normans?) Danelaw; Language Life in 10th Century Baghdad. Political structure – Caliphate and caliphs; Baghdad as a seat of learning; differences between modern and medieval middle-east. Case study on thinkers from the house of wisdom (EG): Al-Jazari (Medicine) ; AlKhwarizmi (Alegbra); Musa (Physics); Al-Idrisi (Maps) Technological advances led by house of wisdom and their effect on modern society. Events, people and changes. Interpretation/ Events, people and changes. Enquiry and use of sources. Why did the Vikings leave their homes? Communication Events, people and changes. Chronology History Curriculum – Local History LOCAL HISTORY WEEK – Thematic British History Key questions: -How do we know about the past? -How does the past compare to the present? - How have we got to where we are today? Year 3 – Transport Year 4 – Work Year 5 – Buildings Year 6 – My Local Area Why do we move around? How do we move around? How has travel changed? What has been the impact in our local area? Farming & subsistence, the How can we tell the age of buildings? How have buildings changed and why? What types of buildings characterise different historical eras and why? What do our local buildings tell us about the history of this place? The history of the school and its locality. How is history recorded? Looking at sources and how these are different for different eras. How are buildings from different periods different? Why? (Styles, technology, materials.) What types of buildings are around? (Learning walk) Can we date an area from its buildings? Nature of history – using sources (written, pictorial, artefacts). What was here before the school? How has technology changed the way that history can be recorded? (Internet, publishing, photos). Roads, horses and carts. What were the roads like? (Clues in road names to where the used to lead.) Canals, waterways, Ship canal. Motorways, cars, modern ways of moving. development of labour and industrialisation. How this has impacted on our local community – focus on child labour & women’s role (Suffragettes). What jobs have people done? (Farming, subsistence work, soldiers, miners, factory hands). What jobs have children had? (Chimney sweeps, labourers, mines, etc.) Women and work. Events, people and changes Events, people and changes Events, people and changes Events, people and changes Chronology Chronology Chronology Chronology Enquiry and using sources Enquiry and using sources Enquiry and using sources Enquiry and using sources