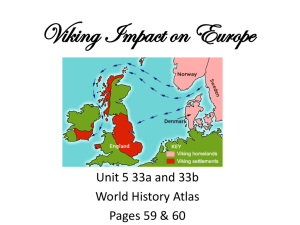
Anglo Saxons
advertisement

Anglo Saxons Social Studies Pd. 6 Izzy Durcan 2/20/13 History 1. Anglo-Saxons 2. Hadrian’s Wall 3. ‘Anglo-Saxon Chronicle’ Daily Life 1. Their houses were built of wood and had thatched roofs. Each family had one room, with a fire for cooking, heating, and light. 2. Loom 3. The smith made iron tools, knives and swords. Woodworkers made wooden bowls, furniture, carts and wheels. Potters made pottery. Shoemakers made leather shoes. Jewelers made metal brooches, beads and gold ornaments. Literature 1. Beowulf was a heroic prince in a famous story who kills a fierce man-eating monster Grendel, and Grendel’s mother. 2. Runes Government 1. Five kingdoms Northumbria, Mercia, Wessex, Kent, and East Anglia. 2. Sutton Hoo was the site of a kings ship burial possibly King Redwald. 3. King Offa was most powerful English king. He issued England’s first penny Coins in silver called ‘Offa’s pennies’, built a ditch and earth wall for defense along border with Whales. 4. Thanes and ceorls were the classes of freemen Alfred the Great 1. Vikings 2. They chose the next king 3. He built war ships to guard the coast from Viking raiders. He also built forts and walled towns known as burhs, split part time army (fryd) into two parts so half would stay home to farm while the other half went to fight the Vikings. Settlement 1. England got its name by the newcomers who spoke their own languages which became known as Anglo-Saxon or Old English. The Anglo-Saxons called it Englisc, when the country was taken over by new settlers it became England. Warfare 1. Battle axe 2. King would order local officials to provide so many men each in order to make sure he had enough soldiers. The more land you had to more men you had to provide. 3. It was a code that taught that a warrior must fight and die for his leader if he had to. 4. Vikings attacked monasteries to steal their gold and other treasures. Children 1. Thought girls and boys were equally important, but girls’ work centered on the home. Both girls and boys collected firewood and fetched water from wells. Only few learned to read and write. Girls learned to weave, cook, make cheese, and brew ale (housekeeping skills). Boys chopped down trees, ploughed in fields, fished, collected birds’ eggs, hunted, and learned to fight. Religion 1. The charms were believed to be lucky, protect them from evil spirits and sickness. 2. Belongings buried with a dead person were for use in the next life and materials used in their jobs. Men: spears and knives which suggest hunting. Women: sewing for weaving. Kings: treasures and weapons. 3. Augustine 4. He went to live with monks at age 7 and grew up to be a historian. He also wrote a book called ‘A History of the English Church and People’ The Crown 1. Cnut 2. King Edward spent most of his life in Normandy before becoming king. He was very religious and confessed his sins often. 3. Bayeux Tapestry was very important because it told the story of how the Normans conquered England. Normans 1. The Battle of Hastings 2. He built castles to provide a safe place for the soldiers to live and scare the Saxons. Also built castles to show the people who were in charge. 3. It was recorded to make sure landowners were paying the correct amount of tax so he would have enough money to equip his army.