Interference, Diffraction, Refraction and Spectra
advertisement
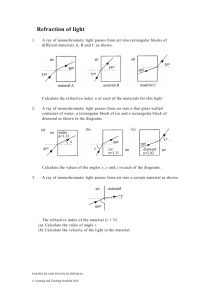
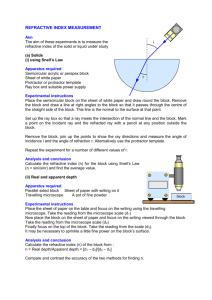
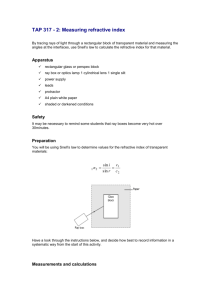
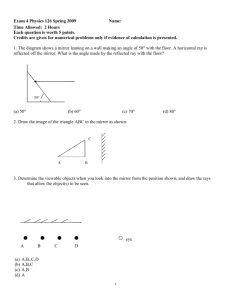
Arbroath High School Science Department Higher Physics Interference, Diffraction, Refraction and Spectra. Unit 2 Test 3 1. This pattern of maxima is produced by waves from two coherent sources, S1 and S2. S1 Central maximum S2 P Q R The second maximum occurs at Q, where S1Q = 18 cm and S2Q = 14 cm. The path difference for the 3rd minimum is A 30 cm B 37 cm C 40 cm D 47 cm E 50 cm 1 2. The refractive index of perspex varies, depending on the colour of the light passing through it. Which of the following statements is/are true? I Blue light incident on a perspex block gives it a higher refractive index than would red light. II Blue light incident on a perspex block gives it a lower refractive index than would red light. III Blue light travels more slowly through a perspex block than red light. A I only B II only C III only D I and III only E II and III only 1 3. Two speakers attached to a computer are placed on either side of it in a large room. A pure 1 kHz test tone is fed to both speakers. A pupil walks slowly across the floor in front of the speakers as shown. Speaker 1 Speaker 2 P Q 351 m 300 m R (a) (b) (i) State what the pupil hears as he walks across the room. 1 (ii) Explain carefully how the pattern of sound he hears is produced. 2 The pupil stops at R, where he is 351 m from speaker P and 300 m from speaker Q. (i) Assuming that the speed of sound in the room is 340 m s -1, calculate the wavelength of the tone. 1 (ii) What does the pupil hear at point R? Justify your answer with a calculation. 3 (c) What would happen to the sound pattern if a tone of a much higher frequency were played? 1 4. A violet light ray of frequency 746 1014 Hz is directed at an acrylic prism as shown. Violet light ray X 16° n θ n The refractive index of the acrylic is 153 for the violet light. (a) (b) (i) Calculate the value of the angle marked “θ”. 2 (ii) Calculate the wavelength of the light inside the prism. 3 The violet light ray is replaced by a red ray. This ray is directed at the prism at the same angle θ as in (a). Will the angle marked “X” be bigger than, the same size as or smaller than it `was for the violet light? You must justify your answer. 1 5. The energy levels in an atom are shown below. E3 -1·360 x 10-19 J E2 -1·415 x 10-19 J E1 -5·424 x 10-19 J E0 -21·76 x 10-19 J (a) State what is meant by: (i) The ionisation level. 1 (ii) The ground state. 1 (b) How many lines will be observed in the line spectrum of this atom? 1 (c) Which transition will give the emitted radiation of the : 6. (i) Highest frequency. 2 (ii) Longest wavelength. 2 This diagram represents some of the possible energy levels for the Hydrogen atom. E -136 10-19J 3 E -242 10-19J 2 E -545 10-19J 1 E -218 10-19J 0 (a) (b) How many spectral lines would these four energy levels produce? 1 Which transition for these levels would give the longest wavelength of emitted radiation? Explain your answer. 2 7. Light of wavelength 500 nm is passed through a grating of 400 lines per mm. A pattern of bright fringes is produced. The angle between the zero and second order maxima is 8. A 040 ° B 115 ° C 236 ° D 664 ° E 785° 1 The effect that a transparent block has on a laser beam is being studied. This diagram shows the apparatus in use. P light meter C θ Q laser The light meter is used to measure the irradiance of ray P as angle θ is varied. (a) (b) Explain why a laser is used rather than a ‘white’ light ray box fitted with a single slit. 2 What is meant by the “irradiance” of an electromagnetic radiation? 1