Refraction Worksheet: Physics Problems & Solutions
advertisement

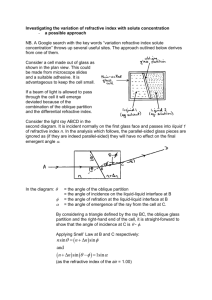
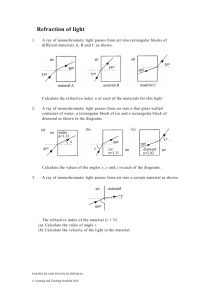
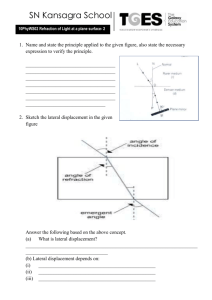
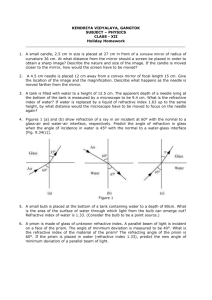
Refraction Worksheet For each question remember to draw a diagram and show all of your working, including the equation you are using. 1. A ray of light is incident in glass on a glass-water boundary. The angle of incidence is 50˚. Calculate the angle of refraction. (Refractive index of glass = 1.50, refractive index of water = 1.33) 2. A ray of light is incident in air on the surface of a glass block. The angle of incidence is 60˚. Calculate the angle of refraction. (Refractive index of glass with respect to air = 1.50.) 3. A ray of light is incident in water: a) on a plane water-air boundary at an angle of incidence 45˚, b) on a plane water-glass boundary at an angle of incidence of 30˚. Calculate the angle of refraction in each case. (Refractive index glass = 1.50, refractive index water = 1.33.) 4. A ray of light in incident in glass on a plane glass-air boundary and makes an angle of 30˚ with the normal to the boundary. Calculate the angle through which the ray is deviated on entering the air. (Refractive index of glass with respect to air = 1.5.) 5. A ray of light travelling through a liquid of absolute refractive index 1.4 is incident on the plane surface of a perspex block at an angle of 55˚. Calculate the angle of refraction in the perspex if it has an absolute refractive index of 1.5. Air n = 1.00 Glass n = 1.52 y x 50.0˚ 6. In the diagram a ray of light travelling through air is incident at A at an angle of 50.0˚ on to a glass surface which is coated with a layer of liquid. Use the information given in the table to find the angles x and y. Liquid n = 1.35 A Absolute refractive index of liquid Absolute refractive index of glass Assume parallel layers 1.35 1.52 7. A ray of light travelling through air is incident at an angle of 30.0˚ on to the first face of a perspex prism of angle 45.0˚. If the Perspex has refractive index 1.49, calculate the angle of the emergence at the second face. 30.0˚ 45.0˚