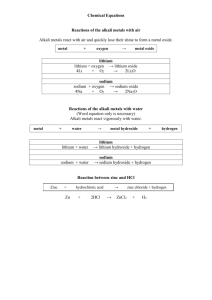
SLIDES FROM SEMINAR Antidepressants Side effects: Dry mouth
advertisement

SLIDES FROM SEMINAR • • Antidepressants • Side effects: Dry mouth and other anticholenergics ( hard candy, sips, oral hygiene) • Sedation ( bedtime) • Nausea (take with food) • Discontinuation syndromes: abrupt stopping may result in dizziness, headache, , worsening of symptoms,etc. (taper) • Patho/ Pharm • Psychopharmocology Depression • 1.Tricyclic Antidepressants /TCA: up to 4 weeks to see action; selection of medication is based on symptoms: side effects: sedation, tachycardia, dry mouth, constipation, urinary retention, low b/p and seizure threshold; caution in use with elders and glaucoma and heart disease • Blocks reuptakes of neurotransmitters • Be alert to suicidality as medication begin to work • Fatal if overdose! • HYPERTENSIVE CRISIS, hyperpyretic crisis. Severe seizures, tachycardia when used with MAOI’s. • Tricyclic PrototypeAmitriptyline(Elavil)50-300mg/D(usually starts with 25 TID or 50 QHS) Depression; blocks reuptake of norepi, serotonin Adjunct to chronic pain control .Hypertensive crisis if used with MAOI. Need a 2 week wash out; Check B/P; Cardiac workup prior; SE dizziness, drowsiness, constipation, urinary retention, EKG changes, hypotension; Suicide precautions; increased risk of agranulocytosis – Complete blood studies • 2.MAO Inhibitors /MAOI’s • Blocks reuptake of neurotransmitters when the enzyme, MAO is inhibited at various site in the nervous system • HPERTENSIVE CRISIS OCCURS if the patient is using amphetamines, methyldopa, resperpine, epinephrine, norephinepherine, OR ingests any food with tyramine • Tyramine: 2 hours- pounding headache, photophobia, choking, neck stiffness, marked hypertension • BE ALERT TO TYRAMINE • What is tyramine? • Amino acid found in aged cheese, other aged, overripe, fermented foods • Get a list from the Nutrition department/Pharmacy • TEXT 160 !!! • Aged cheese, wine Esp. Chianti, road beans, pickled herring, beef or chicken liver, preserved lunch meats/sausages, beer and wine, yeast products, chocolate, caffeinated drinks, canned figs, sour cream, coffee, tea, yogurt, soy sauce, some over the counter cold medications, , diet pills MAOI Prototype:Tranylcypromine(Parnate)30-60mg/DStart 10 BID; Depression; increase concentration of endogenous epinephrine, norepi, serotonin, dopamine in CNS by inhibiting MAO ; Hypertensive crisis if consume food with tyramine or select medications; d/c drug immediately, antihypertensive medications; serotonin syndrome; SE dizziness, drowsiness, anorexia, orthostatic hypotension; monitor B/P; Suicide precautions****** • List of MAOI on page 159 3. Heterocyclics “Other”or Misc Bupropion (Wellbutrin)200-450mg/DStarts with 100 BID;Slow increase of dose; Depression ,Smoking Cessation; inhibits reuptake of dopamine, norepi, serotonin ;Precaution if seizure or head injury as it lowers seizure threshold; complete AV block; SE headache, agitation, n, v, rash, impotence; 2-4 weeks to see effect 4. SSRI Selective Serotonin reuptake inhibitors/ Nonselective reuptake inhibitors • Prozac, Paxil, Zoloft,Luvox, Celexa, Lexapro • Fewer anticholenergic side effects, faster acting, good efficiency, headache, insomnia, weight loss • SE profile is more manageable • Action: inhibits the reuptake of serotonin at the brain synapse thus increasing the amount available at the serotonin sensitive receptor sites • Serotonin norephenerine reuptake inhibitors • Act on both serotonin and NE to relieve depression, OCD, pain often accompanying depression • Serotonin syndrome • Effexor, Cymbalta • SSRI Prototype: Fluoxetine (Prozac)20-80mg/D • Starts 20 qD; Depression’ OCD’ Bulimia nervosa’ PMS Insomnia, headache; serotonin syndrome when 2 drugs potentiate serotonergic neurotransmission- block serotonin immediately; may be fatal; do not use with any other medications that increase serotonin or MAOIs. Potentiate many other drugs, inc St Johns Wort. SE nervousness, insomnia, headache, seizures, tachycardia; Suicide precautions • ALERTS FOR SSRI’s • Serotonin Syndrome: when 2 drugs that potentiate serotonergic transmission are used concurrently( St johns Wort, MAOIs, pg 159) • Labile blood pressure, mental status changes, myclonus, hyperreflexia, shivering, tremors • STOP medications immediately. MD will prescribe medication to block the serotonin receptors. Artificial ventilation may be needed • May be fatal • Types of Antidepressants Table 10-2 • Interactions • Planning/Implementation Table 10-4 All Antidepressants • Dry mouth • Sedation • Nausea • Discontinuation Syndromes • Offer sugarless candy, gum ice chips, water, oral hygiene Administer at bedtime; Advise not to use dangerous equipment when experiencing sedation Take with food to minimize effect Must taper gradually all antidepressants Abrupt withdrawal SSRI-dizziness, headache, lethargy, headache; TCA-hypomania, cardiac arrhythmias, panic attacks; MAOI;s- confusion, hypomania, worsening of symptoms • Planning/Implementation Tricyclics and Wellbutrin • Reduces seizure threshold • Weight gain • Constipation • Blurred vision • Urinary retention • Orthostatic hypotension • Photosensitivity • Observe client with seizure disorder closely; Give no more than 150 mg per dose and nor closer than 8 hours apart • Encourage increased activity. Nutritional instruction • High fiber food, increased water • Should subside after a few weeks; do not drive while blurred • Monitor any difficulties • Advise to Rise slowly; avoid hot long showers or baths • Ensure the use of sunscreen, sunglasses, protective clothing • Planning/Implementation SSRI’s • Insomnia, agitation • Headache • Weight loss • Sexual dysfunction • Serotonin Syndrome – Myclonus, restlessness – • Hyperreflexia, tachycardia, shivering, tremors, tremors Instruct take early in the day, avoid caffeine, teach relaxation prior bedtime Administer analgesic Initial loss, instruct maintain caloric intake, daily weights Men- abnormal ejaculation, impotence; women- delayed or loss of orgasm Discontinue drug immediately; MD will order a serotonin blocking agent; artificial ventilation may be required; if med is not discontinued, it may become serious and fatal • Planning/Implementation MAOI’s • Hypertensive Crisis if consumes re occipital headache tyramine – Severe occipital headache – Palpitations – Nausea/vomiting – Nuchal rigidity – Fever, sweating – Increased B/P – Chest pain – Coma • Discontinue drug immediately • Monitor vital signs, administer antihypertensive agent, use cooling measures • Mood Stabilizers • 10-5 in text • Anti manic and anticonvulsant medications; are others • Action is treatment of bipolar illness is unclear • Lithium: • Common side effects include drowsiness, dizziness, dry mouth, GI upset, fine hand tremors, weight gain. • Therapeutic Blood levels 1.-1.5 mEq/L for mania; • For maintenance: 0.6-1.2 mEq/L • Page 167 in text • AntimanicLithium(Eskalith)300-600mg TID*Blood levels;Ind to blood levels; May balance biogenic amines of norepi and serotonin ; alters sodium and potassium transport; decreased sodium intake and water intake leads to lithium toxicity; increased sodium and water intake leads to decreased lithium retention SE: Headache, drowsiness, seizure, dry mouth, polyuria, glycouria, proteinuria, albuminuria, hypotension, leukocytosis; contr liver disease, pregt, OBS, Many precautions, Excreted by kidney: Many toxic interactions; Teach toxicity symptoms ( V,D, tremors) BLOOD LevelS weekly then monthly-0.5-1.5 mEq/LMust balance use of sodium and water intake; initially 2-3 L/D then 1-2 L/D; Embryotoxic • Lithium Toxicity Blood levels • Warning Signs • Anorexia • N,V • Tremor • Muscle twitching • Tinnitus • Vertigo • Weakness, drowsiness • Signs • Fever • Decreased urine output • Decreased blood pressure • Irregular pulse • EKG changes • Altered consciousness • Seizures • Coma • Death • Planning/Implementation: Side effects and intervention Lithium: 10-6 • Lithium toxicity • Margin between therapeutic and nontherapeutic are narrow • Usual ranges: • Acute mania:1.0-1.5mEq/L • Maintence0.06-1.2 mEq/L • Toxicity appears at 1.5 or greater and are dosage determinant – 1.5-2.0 Blurred vision, ataxia, tinnitus, N,V,D – 2.0-3.5 Excess output of urine, tremors, muscular irritability, giddiness, confusion – 3.5 or greater impaired consciousness, nystagmus, seizure, coma oliguria, cardiac collapse • Monitor levels weekly until levels are stable then monthly • Blood draw 12 hours after last dose • If high or symptoms: Hold dose, notify MD • Li is similar chemical structure to sodium and competes with sodium in the body; if sodium intake is reduced or the body is depleted of sodium lithium is reabsorbed by the kidneys increasing the chance for toxicity • Patients should consume a diet adequate in sodium and 2,5000-3,000 of fluid each day. • Adequate intake and output records • Planning/Implementation: Side effects and intervention Lithium: 10-6 • Lithium toxicity • Margin between therapeutic and nontherapeutic are narrow • Usual ranges: • Acute mania:1.0-1.5mEq/L • Maintence0.06-1.2 mEq/L • Toxicity appears at 1.5 or greater and are dosage determinant – 1.5-2.0 Blurred vision, ataxia, tinnitus, N,V,D – 2.0-3.5 Excess output of urine, tremors, muscular irritability, giddiness, confusion – 3.5 or greater impaired consciousness, nystagmus, seizure, coma oliguria, cardiac collapse • Monitor levels weekly until levels are stable then monthly • Blood draw 12 hours after last dose • If high or symptoms: Hold dose, notify MD • Li is similar chemical structure to sodium and competes with sodium in the body; if sodium intake is reduced or the body is depleted of sodium lithium is reabsorbed by the kidneys increasing the chance for toxicity • Patients should consume a diet adequate in sodium and 2,5000-3,000 of fluid each day. • Adequate intake and output records • Planning/Intervention Lithium • Drowsiness, dizziness • Dry mouth • GI upset, N,V • Hand tremors • Hypotension • Polyuria, dehydration • Weight gain • Teach client must not participate in activities that require alertness • Hard candy, sips, oral hygiene • Take medication with food • Report tremors to MD, observe severity • Monitor vital signs • Daily weight,intake,output,skin turgor • Instruct keep adequate intake of sodium; instruct reduced calorie diet if gain weight • Planning/Interventions Lithium con’t • Med noncompliance • Dietary teaching • Risk of fetal malformation • Toxicity • Instruct to take ,even when feeling well • Do not skimp on dietary sodium intake, drink 6-8 glasses of water daily • Avoid caffeine which increases urinary output • Notify MD if N,V occurs (sodium loss) • Carry a card regarding Li • Discuss with MD the desire to become or realization of pregnancy • As previous, instruct patient on bloodwork, dietary teachings and signs and interventions • Planning/Intervention Valproic Acid • N,V • Drowsiness, dizziness • Blood dyscrasias • Prolonged bleeding time • Severe rash • Decreased efficacy of BCP • Do not discontinue • Do not mix with alcohol • Take with food • Do not operate machinery • Report bleeding ( gums, bruising) • Regular bloodwork for therapeutic levels and platelet count • Instruct to inform of rash • Make client aware of BCP risks • Instruct to not abruptly withdrawal , MD will taper • Carry a card • Anticonvulsants • Quicker action • Can be used with lithium • Action unknown ( Do you use antidepressants in mania?) • Anticonvulsant Valproic Acid (Depakote)Psych purposes750 mg QD, max 60mg/kg/dBlood levelsIncrease GABA in the brain;Manic episodes, adjunctive to schizophrenia, tardive dyskinesia ( Mental health Purposes)Thrombocytopenia, sedation, drowsiness, dizziness, N,V,C,D ,hepatic failure Valproic acid levels to prevent toxicity 50-100mcg/mlMust wean slowly to prevent seizuresPhysical dependency may result