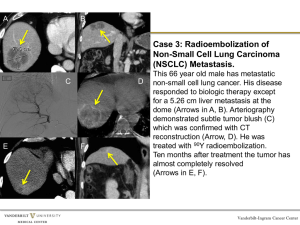
Supplementary Table 1 (docx 31K)
advertisement
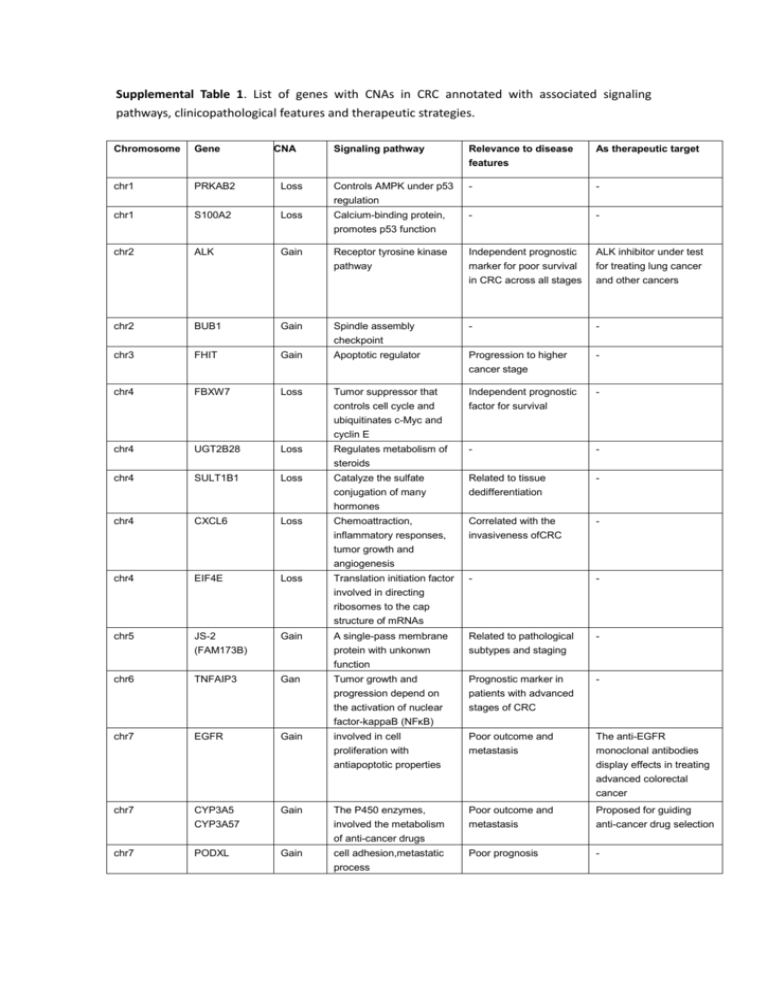
Supplemental Table 1. List of genes with CNAs in CRC annotated with associated signaling pathways, clinicopathological features and therapeutic strategies. Chromosome Gene chr1 PRKAB2 chr1 CNA Signaling pathway Relevance to disease features As therapeutic target Loss Controls AMPK under p53 regulation - - S100A2 Loss Calcium-binding protein, promotes p53 function - - chr2 ALK Gain Receptor tyrosine kinase pathway Independent prognostic marker for poor survival in CRC across all stages ALK inhibitor under test for treating lung cancer and other cancers chr2 BUB1 Gain Spindle assembly checkpoint - - chr3 FHIT Gain Apoptotic regulator Progression to higher cancer stage - chr4 FBXW7 Loss Tumor suppressor that controls cell cycle and ubiquitinates c-Myc and cyclin E Independent prognostic factor for survival - chr4 UGT2B28 Loss Regulates metabolism of steroids - - chr4 SULT1B1 Loss Catalyze the sulfate conjugation of many hormones Related to tissue dedifferentiation - chr4 CXCL6 Loss Chemoattraction, inflammatory responses, tumor growth and angiogenesis Correlated with the invasiveness ofCRC - chr4 EIF4E Loss Translation initiation factor involved in directing ribosomes to the cap structure of mRNAs - - chr5 JS-2 (FAM173B) Gain A single-pass membrane protein with unkonwn function Related to pathological subtypes and staging - chr6 TNFAIP3 Gan Tumor growth and progression depend on the activation of nuclear factor-kappaB (NFκB) Prognostic marker in patients with advanced stages of CRC - chr7 EGFR Gain involved in cell proliferation with antiapoptotic properties Poor outcome and metastasis The anti-EGFR monoclonal antibodies display effects in treating advanced colorectal cancer chr7 CYP3A5 CYP3A57 Gain The P450 enzymes, involved the metabolism of anti-cancer drugs Poor outcome and metastasis Proposed for guiding anti-cancer drug selection chr7 PODXL Gain cell adhesion,metastatic process Poor prognosis - chr7 RAPGEF5 Gain serves as a RAS activator by promoting the acquisition of GTP - - chr7 WNT2 Gain Promotes Wnt/β-Catenin pathway Contributes to initiation and progression of CRC Flavonoids proposed for treating CRCs with activated Wnt signaling chr7 MET Gain A growth factor receptor that promotes tumor growth, angiogenesis and metastasis Associates with invasivion and metastasis MET inhibitors such as ARQ197 under clinical trial for treating CRC, other inhibitors such as tivantinib, onartuzumab, and cabozantinib for treating other cancers chr8 MYC Gain Crucial oncogene that regulates transactivation of many cancer-related genes Overexpression associates with improved 5-year survival Myc inhibitors are studied in vitro and in animal models chr8 PPP2CB Loss A Ser/Thr phosphatases in negative control of cell growth and division - - chr8 MTUS1 Loss A tumor suppressor involved in AT2 signaling pathways Downregulation associates with poor overall and disease-free survival - chr8 CSMD1 Loss A potential tumor suppressor with deletions promoting cancer aggressiveness Associates with poor prognosis of CRC - chr10 CASP7 Loss apoptosis effector caspase gene - - chr10 PTEN Loss Tumor suppressor in regulation of the PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway Not a predictive factor for anti-VEGF therapy in mCRC. - chr11 IGF2 Gain PI3K pathway - - chr11 miR-483 Gain May suppresses the expression of DPC4/Smad4 - - chr11 91H (antisense RNA of H19) Gain (TCGA) LncRNA, upregulation of IGF2 expression development and progression of CRC poorer prognosis chr12 WNK1 Gain a member of the WNK family of serine/threonine kinases which affect MAPK signaling evasion of apoptosis, invasion and metastasis, and metabolic adaptation - chr12 ARHGDIB Loss Regulates COX2 and inhibit RhoGTPase, which inhibits cancer invasion Associates with distant metastasis of CRC - chr12 KRAS Gain Oncogene, a small GTPase with malignant transforming function in multiple tumors KRAS CNA associates with responses to anti-EGFR therapy Proposed inhibition of KRAS signal by MEK1/2 inhibitors chr12 RERGL Gain Ras-Related And Estrogen-Regulated Growth Inhibitor-Like Protein - - chr13 GPC5 Gain Glypican-related integral membrane proteoglycan, control of cell division and growth regulation Associates with tumor recurrence and shorter disease-free survival - chr13 IRS2 Gain IGF2–IGF1R–IRS2 axis signals to PI3K - - chr15 BLM Loss RecQ helicase family - - chr16 WWOX Loss WNT/betacatenin pathway tumor suppressor - chr16 AXIN1 Loss Induce apoptosis prognostic - chr17 ERBB2 (HER2) Gain Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase regulating MAPK, PI3K/Akt, PKC, STAT signals Overexpression is not a predictor of outcome but may indicate respond to Herceptin therapy anti-ERBB2 antibody trastuzumab chr17 TP53 Loss Tumor suppressor as a master regulator of cell apoptosis Loss of TP53 gene may associate with CRC outcome MDM2 inhibitor proposed for treating tumors with loss of p53 chr17 WDR16 Loss signaltransduction, RNA processing, cytoskeleton remodeling, the regulation of vesicular traffic, and cell division involved in tumorigenesis, - chr18 DCC Loss A cell adhesion protein partially localized in lipid rafts, involved in induction of apoptosis without ligand genetic biomarkers of sCRC and typicallyare associated with advanced disease - chr18 SMAD4 Loss Regulates the transcription of target genes in TGF-β pathway An independent diagnostic biomarker for CRC - chr18 CABLES1 Loss Catalyze tyrosine phosphorylation of cyclin-dependent kinases CABLES1-deficient mice had more DMH-induced tumors and shorter survival - chr18 DNAM-1 Loss Suppressor of cytokine signaling 6 (SOCS6)and a-7 nictonic receptor(ACHR-7) Worse prognosis among patients with sporadic CRC - chr18 BRUNOL4 Loss Regulates pre-mRNA alternative splicing, mRNA editing, and translation Independent adverse prognostic factor - chr18 PHLPP1 Loss Negative regulator of Akt - therapeutic or diagnostic tool chr18 RALBP1 Loss Anti-apoptosis function and protection from stress by glutathione conjugation - transportation of chemical anti-cancer compounds chr18 TYMS Loss Maintains the dTMP pool critical for DNA replication and repair Overexpression associates with poorer overall survival in CRC Target for the anti-cancer drug 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) chr18 MAPRE2, ZNF24, DNAM-1, SOCS6, ACHR-7, CCDC68, TCF4, RAX Loss Transcription factor activity and DNA binding (DAVID annotation) Associates with metastasis and shorter overall survival in CRC - chr19 LTBP4 Gain TGFβ-pathway, prevent tumor suppressive downstream reactions such as apoptosis, and growth arrest chr19 BAX Loss pro-apoptotic gene Associates with shorter disease-free survival in CRC 5-FU-based treatment resistance chr19 POLD1 - impaired DNA replication generating breaks - - chr20 BCL2L1 Gain Mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis Increased BCL2L1 expression indicates poor prognosis in CRC overexpression of BCL2L1 associates with chemotherapy resistance chr20 POFUT1 Gain Addition of O-linked fucose to the EGF domains of the Notch receptor - - chr20 SNAI1 Gain through Axin and GSK-3beta for degradation of beta-catenin in proteasomes in the Wnt-signaling pathway - - chr20 AURKA Gain Phosphorylates TP53 and regulates cell proliferation - - chr20 WISP2 Gain Transforming growth factor signaling pathway - - chr20 CDC25B Gain Proceed through the S-phase checkpoint and prematurelyenter mitosis - - chr20 AHCY Gain MYC-target gene - - - chr20 PCNA Gain DNA synthesis and cell cycle progression - PCNA inhibitors under study in vitro chr20 RPN2 Gain Inhibits Bcl-mediated apoptosis - - chr20 TH1L Gain Belongs to negative elongation factor complex - - chr20 PRPF6 Gain Maintaining cell viability - - chr20 SNAI1 Gain Cell adhesion Wnt-signaling - - chr20 BMP7 Gain Transforming growth factor pathway Independent prognostic factor of liver metastasis and overall survival - chr20 TOP1 Gain Catalyzes the unwinding of DNA and creates single-strand molecules Associates with CRC stage - chr20 PLCG1 Gain Response to growth factor stimulation and regulates cell invasion and metastasis - - chr20 PTPRT Gain Regulation of cell adhesion - - chr20 EEF1A2 Gain Encodes a subunit of the elongation factor-1 complex Prognostic of a poor response to taxol - chr22 ApoL6 Loss With BH3 domain, regulation of mitochondrial apoptosis - proposing a new strategy for chemotherapy SEX X,Y, multiple genes Gain (X), Loss (Y) "Feminization" associates with microsatellite stability and BRAF status No significant association with clinicopathological features including disease-free survival - mtDNA Multiple genes Gain, loss Cell metabolism and ATP generation Gain in early stage tumors, and loss in invasive tumors Proposed as biomarker in early diagnosis of CRC