Mutation - Iowa State University
advertisement

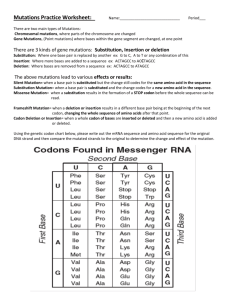
Mutation Supplemental Instruction Iowa State University Leader: Course: Instructor: Date: Lilli Howard BIOL/GEN 313 Dr. Vollbrecht 04/08/14 Types of Mutations Germline Mutations/Somatic Mutations Base Substitutions Transition and Transversion Single Base Substitutions Insertions/ Deletions Intra/Intergenic Suppressors Effects of Mutations Neutral Loss of Function/Gain of Function Causes of Mutations Tautomeric Shifts Depurination Deamination Chemical Mutagenesis UV Light 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 515-294-6624 sistaff@iastate.edu http://www.si.iastate.edu 1. Which of the following types of gene mutation in a protein-coding gene usually have the least severe effects? a. Missense mutations b. Nonsense mutations c. Single base deletions d. Expansion of a dinucleotide repeat e. ‘all of the above generate equally severe phenotypes 2. Which of the following is not a reason that understanding mutations is important? a. Mutations provide stability to genomes b. Mutations cause inherited diseases c. Mutations provide variability that is the basis of evolutionary selection d. Mutations provide information about biological mechanisms e. Mutations can cause cancer in somatic tissue 3. Which type of mutation is likely to lead to an intragenic suppressor of a forward mutation that was caused by insertion of a single base pair? a. Insertion of one additional base pair b. Insertion of two additional base pairs c. Deletion of two additional base pairs d. Transition mutation elsewhere in the gene e. Transversion mutation elsewhere in the gene 4. Which kind of mutation is most likely to cause loss-of-function of the protein product of the gene? a) Transition b) Transversion c) Frame shift d) Missense e) Spontaneous 5. Which of the following is a defining characteristic of a germ line mutation? a) A stop codon is abnormally placed within the coding region of gene b) Abnormal extra nucleotides are found within the coding region of gene c) The mutation causes cancer in a clonal population of cells within an organism d) The mutation is found in the progeny of the individual in which it arose e) The mutation arose in an individual early in its lifespan 6. What is the basis for induction of mutations by ultraviolet light? a) UV light causes formation of dimers between two adjacent T bases stacked in the double helix b) UV light causes spontaneous depurination c) UV light causes spontaneous deamination of cytosine bases d) UV light causes DNA polymerase to become error prone e) UV light cleaves the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 515-294-6624 sistaff@iastate.edu http://www.si.iastate.edu