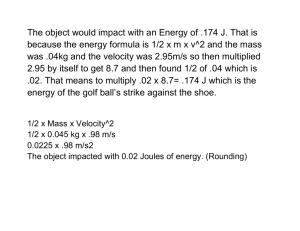Physics Holiday Test
advertisement

KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA ANDAL HOLIDAY TEST CLASS – XII SUBJECT – PHYSICS TIME : 2 Hr. MARKS : 50 General Instructions: a) All the questions are compulsory. b) There are 19 questions in total. c) Questions 1 to 5 are very short answer type questions and carry one mark each. d) Questions 6 to 10 carry two marks each. e) Questions 11 to 15 carry three marks each. f) Questions 16 to 19 carry five marks each. ______________________________________________________________________________________________ 1. Can two equipotential surfaces intersect each other? Justify your answer. 2. What is the direction of the force acting on a charged particle q, moving with a velocity v in a uniform magnetic field B? 3. Why does the bluish colour predominate in a clear sky? 4. At what angle of incidence should a light beam strike a glass slab of refractive index √3, such that the reflected and refracted rays are perpendicular to each other? 5. Two different wires X and Y of same diameter but different materials are joined in series across a battery. If the number of density of electrons in X is twice that in Y, find the ratio of drift velocity of electrons in the two wires. 6. Calculate the amount of work done in turning an electric dipole of dipole moment 2 X 10-8 Cm from its position of unstable equilibrium to the position of stable equilibrium, in a uniform electric field of intensity 103 NC-1. 7. Derive an expression for drift velocity of free electrons in a conductor in terms of relaxation time. 8. Write down the two condition for phenomenon of total internal reflection. 9. Two long and parallel straight wires A and B carrying currents of 8.0A and 5.0A in the same direction are separated by a distance of 4.0cm. Estimate the force on a 10cm section of wire A. 10. In a single slit diffraction experiment, the width of the slit is made double the original width. How does this affect the size and intensity of the central diffraction band? 11. On what principle does a meter bridge work? Draw a circuit diagram and explain how this derive can be used for determination of an unknown resistance. 12. Deduce an expression for the electric potential due to an electric dipole at any point on its axis. 13. Draw a schematic sketch of the cyclotron. State its working principle. Show that the cyclotron frequency is independent of the velocity of the charged particles. 14. What is an unpolarized light? Explain with the help of suitable ray diagram how an unpolarized light can be polarized by reflection from a transparent medium. Write the expression for Brewster angle in term of refractive index of denser medium. 15. A convex lens of refractive index 1.5 has a focal length of 20cm in air. Calculate the change in its focal length when it is immersed in water of refractive index 1.35. 16. (i)State Biot-Savart law, giving the mathematical expression for it. (ii)Use this law to derive the expression for the magnetic field due to circular coil carrying current at a point along its axis.(iii) How does a circular loop carrying current behave as a magnet? 17. (i) State the conditions for obtaining sustained interference of light from different sources. (ii) State the reason, why two independent sources of light cannot be considered as coherent sources. (iii) In Young’s double slit experiment, two slits are separated by 3mm distance and illuminated by light of wavelength 480mm. the screen is at 2m from the plane of slits. Calculate the distance between central bright fringe and 3rd dark fringe. 18. Draw a ray diagram for the formation of image by a compound microscope. Define its magnifying power. Deduce the expression for magnifying power of the microscope. Write down the expression of resolving power of telescope. 19. Explain the underlying principle of working of a parallel plate capacitor. If two similar plates, each of area A having surface area A having surface charge densities +σ and –σ are separated by a distance d in air, write expression for (i) the electric field at points between the two plates, (ii) the potential difference between the plates, (iii) the capacitance of the capacitor so formed.