File
advertisement
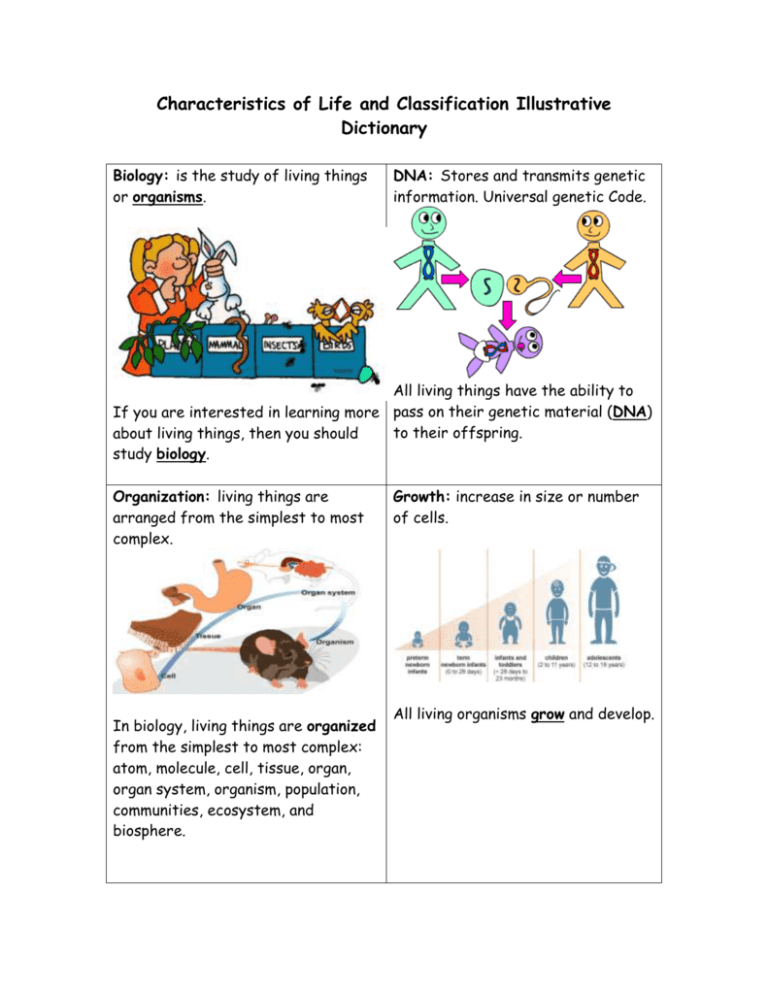
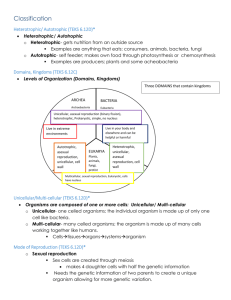
Characteristics of Life and Classification Illustrative Dictionary Biology: is the study of living things or organisms. DNA: Stores and transmits genetic information. Universal genetic Code. All living things have the ability to If you are interested in learning more pass on their genetic material (DNA) to their offspring. about living things, then you should study biology. Organization: living things are arranged from the simplest to most complex. In biology, living things are organized from the simplest to most complex: atom, molecule, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism, population, communities, ecosystem, and biosphere. Growth: increase in size or number of cells. All living organisms grow and develop. Stimulus Response: internal or external factor in the environment that causes a response: temperature, light, sound, pain, hunger…. When I was taking the cookies out of the oven my hand touched the hot oven accidently and I responded by pulling my hand away quickly. Sexual Reproduction: reproduction that involves an egg and a sperm. (2 parents) In sexual reproduction, two parents contribute genetic info (DNA) to produce a unique offspring. A population depends on reproduction to continue the species. Asexual Reproduction: reproduction which the offspring comes from a single organism; inherit traits from one parent. Metabolism (energy): The breakdown of molecules to obtain energy. Asexual reproduction is the primary form of reproduction for singlecelled organisms such as archaebacteria, eubacteria, and protists. When my body breaks down the cheeseburger I had for dinner, it will give me energy to study for my biology quiz. Adaptation (trait): a change in an organisms DNA that increases their chance of survival. A cactus has an adaptation that allows it to survive the hot desert heat by not losing water very easily. Unicellular: is an organism that consists of only one cell. Bacteria is an example of an organism that is made up of one cell, it is a unicellular organism. Multicellular: an organism that consists of more than one cell. Plants, animals, fungus, and most protists are multicellular, or manycelled. Homeostasis: is the ability to maintain internal stability in an organism to compensate for environmental changes. When I get too hot, my body will begin to sweat to help me maintain homeostasis. Autotroph: is an organism that produces its own food. I can make my own food!! Plants, cyanobacteria, and algae are autotrophs because they can use the sun to make their own food. Prokaryotes: organisms that DON’T have a nucleus. Heterotroph: cannot make their own food, they have to get their energy from an outside source. Organisms like this bear are heterotrophs, they cannot make their own food, they get energy from an external source. Eukaryotes: organisms that DO have a nucleus. NUCLEUS NUCLEUS Eubacteria and Archaebacteria are examples of prokaryotes. Animals, plants, fungi, and protest are examples of eukaryotes. Classification 3 Domains: Eukarya, Archaea, Bacteria 6 Kingdoms: Plantae, Fungi, Animalia, Protista, Eubacteria (everyday bacteria), Archaebacteria (ancient bacteria, live in extreme conditions) 7 levels of Taxonomy o Kingdom (Largest) o Phylum o Class o Order o Family o Genus o Species (Smallest)