Practical classes
advertisement

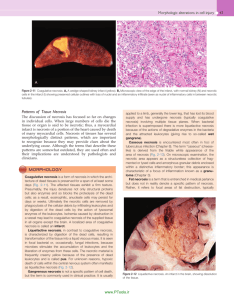
I. INTRODUCTION. NECROSIS, GANGRENE. ATROPHY. Coagulative necrosis 1. Recent myocardial infarction: An example of coagulative necrosis. Actually, this is not the most recent infarction. Judging from the lack of staining of the nuclei of cardiac muscle cells (with increased eosinophilia of the cytoplasm) and the diffuse neurotrophilic infiltrate in the interstitium, it has to be more than 24 hours old. Subendocardial layers survive (supplied through diffusion through the endocardium). Note the comcommitant endocarditis and pericarditis (leukocytes on the endocardial surface and in the subepicardial fat tissue) and thrombi in the arterial branches. Splenic infarction:Triangular shape with the base under the capsule, sometimes multiple. Result – retrcted fibrous scar, haemosiderin pigmentation. Ischaemic coagulation necrosis, most often caused by arterial embolism.Possibility of secondary ifection of the necrotic tissue. 2. Renal infarct: Coagulative necrosis of the kidney usually secondary to arterial occlusion, caused by a thrombotic embolus. Note preservation of the basic architercture of the necrotic renal parenchyma. Necrotic area is usually surrounded by a zone of leukocytic infiltration, haemorrhage and a zone of selective necrosi of epithelium of proximal tubules, which is most sensitive to hypoxia. In an older infarct, central necrosis is surrounded by a layer of fibrosing nonspecific granulation tissue. Liquefactive necrosis 3. Cerebral infarct (encephalomalacia): Ischamic colliquative necrosis, healing by formation of a pseudocyst. Cases: thrombosis, embolism. Haemorrhagic infarct (ussually caused by embolism, small, cortical) through reflux of blood into the necrotic focus. In our slides, we have an older infarction with disintegration of the necrotic center which has been mostly resorbed by activated microglia (enlarged cells with vacuolated cytoplasm) and a marked collateral oedema. Caseous necrosis 4. Caseous tbc lymphadenitis: Central necrosis in the lymph node is surrounded by a rim of the so-called epithelioid cells and large multinucleated giant cells of the Langhans type. Note the cheomatin dust from the destroyed nuclei in some areas of necrosis. Special forms of necrosis 5. Zenker's necrosis: in viral diseases (severe course of influenza), sepsis, typhoid fever etc. Segmental rupture of myofibrils in muscle fibers, hypercontraction of ruptured fibrils. 6. Lung tromboembolism and haemorrhagic infarct: Pyramidal shape, note a branch of pulmonary artery occluded by trombembolus. Develops only in congested lung. 7. Steaticytonecrosis (Balser's necrosis): Yellow-white foci under the peritoneal surface, remnants of mostly dissolved fatty (acid crystals). 8. Chronic peptic of stomach: Tissue defect with raised margins. Note three layers at the base of the ulcer – necrotic debris with leukocytes, fibrinoid necrosis, nonspecific granulation tissue with transition imto peripheral fibrosis. Modified forms of necrosis Atrophy 9. Atrophy of the heart muscle: Simple atrophy – cardiac muscle cells become smaller but their number does not decrease. Sudan B Black stain shows accumulation of the lipid pigment lipofuscin in the perinuclear lysosomes (“wear and tear pigment”), PAS-positive, insoluble pigment resulting from breakdown of cellular membranes. Elderly patients, chronic wasting diseases. 10. Fatty infiltration of the heart muscle: Fat cells dispersed in the myocardial interstitium. In obese patients, physiologically in the anterior wall of the right ventricle. No clinical significance. Do not confuse with fatty degeneration (see below). 11. Hydronefrosis: Severe pressure atrophy of the renal paranchyma caused by obstruction of the ourflow of urine (renal stones, uroteral obstruction by stones, tumours compressing the uritnary outflow tract, diseases of the urinary bladder, in males often hypertrophy of prostate). May be complicated by (usually ascending) infection – hydropyelonephritis. Numerous hyaline casts in the atrophic tubules, glomerular fibrosis, thickening of arterial walls. 12. Pancreatic atrophy and sclerosis: Often results from lithiasis (obstruction of a major pancreatic duct by stones).Frequently complicated by diabetes. Disappearing exocrine parenchme replaced by the newly formed connective tissue. Sometimes increased fat tissue – lipomatous atrophy. Islets of Langerhans often well preserved. II. CELLULAR AND TISSUE DYSTROPHIES A/ Protein dystrophy 1. Cytomegaloviral sialoadenitis: An example of predominantly alterative infiltration, mostly in small infants (cytomegaloviral infection in HIV patients usually involves other organs than the salivary glands). Typical basophilic intranuclear inclusions in the markedly enlarged ductal lining cells. 2. Follicular amyloidosis of spleen: AA amyloid, Congo-positive, apple green fluorescence in polarized light. Deposition mostly in the white pulp (in follicles). 3. Diffuse amyloidosis of spleen: Diffuse involvement of both red and white pulp. 4. Amyloid nephropathy: Deposition of amyloid in the walls of arteries and arterioles, less in the glomeruli and under the tubular epithelium. Both in the AA and AL amyloidosis, morphologically indistinguishable. 5. Erdheim's cystic medionecrosis: Multifocal necrosis of muscle cells with disappearance of elastic fibers (pale areas) and accumulation of acid mucopolysaccharides (small basophilic areas) (chondroitin-6-suplhate) in the aortic media. Note multifocal laminar splitting of aortic media, the origin of aortic dissection. 6. Rheumatismus nodosum: Central eosinophilic (fibrinoid) necrosis with a rim of palisading histiocytes. Disperse lymphocytic infiltrate can also be seen. 7. Fibrocartilaginous perisplenitis: The splenic capsule is thickened by the newly formed, relatively acellular hyaline eosinophilic mass, grossly resembling cartilage. B/ Fatty dystrophy, steatosis Myocardial steatosis 8. Fatty change of the liver: Intracellular accumulation of neutral triglycerides in large vacuoles in the liver cells. Various causes: hypoxia, toxic effects (mushroom poisoning, carbon tetrachloride), starvation etc. 9. Atherosclerosis: Principal morphological envents: fatty streaks, fibrous plaques, atheromas, ulceration, dystrophic calcification. Mostly intimal involvement. The section shows popliteal artery with a large atheromatous plaque. The lumen is partly filled with red thrombus (amputation spcimen, gangrene of the leg caused by arterial obstuction). Fatty infiltration of the heart muscle: Fat cells dispersed in the myocardial interstitium. In obese patients, physiologically in the anterior wall of the right ventricle. No clinical significance. Do not confuse with fatty degeneration (see below). C/ Glycogen dystrophy 10. Armani's cells: In pars recta of proximal tubules, deposition of glycogen in the water-clear cytoplasm, Glycogen is PAS-positive, amylase-digestible. 11. Renal cell carcinoma (tumor of Grawitz): Assesment of malignancy is unreliable on morphological grounds, since malignant tumours may appear differentiated and encepsulated. Small tumours (under 2cm in diameter) considered benign (clear cell adenoma). Vascular, sometimes cystic, consisting mostly of celar cells containing glycogen. Sometimes with oxyphilic cells, sarcomatoid variant. III. METABOLIC DISEASES, CALCIFICATION, PIGMENTATION Calcification 1. Atherosclerosis: Principal morphological events: fatty streaks, fibrous plaques, atheromas, ulceration, dystrophic calcification. Mostly intimal involvement. The section shows popliteal artery with a large atheromatous plaque. The lumen is partly filled with a thrombus (amputaton specimen, gangrene of the leg caused by arterial obstruction). 2. Miliary tuberculosis: This lung tissue section shows multiple microscopic granulomas consisting of epithelioid and scattered multinucleated Langhans cells, surrounded by a thin layer of lymphocytes. Note accumulation of anthracotic pigment in the perivascular and peribronchial lymphatics. Pigmentation 3. Intradermal naevocellular naevus: Clinically small, variably pigmeted, slightly elevated lesion in the skin. Histological types: junctional (with nests of naevus cells in the dermo-epidermal junction. Compound naevus – with more pronouced dermal component. Dermal naevus – no junctional activity, naevus cells are only in the dermis. 4. Malignant melanoma: Increasing in frequency, relation to sunlight. Often developing on the basis of a naevocellular naevus. Variable histological composition, differences in amount of melanin. In nonpigmented variants, Fontana's silver stain for melanin and immunohistology (S100 protein, HMB45 antibody) help in establishing correct diagnosis. Superficial spreading, nodular type. Prognostic assessment according to the depth of infiltation on the dermis (Clark, Breslow grading). 5. Atrophy of the heart muscle: Simple atrophy – cardiac muscle cells become smaller but their number does not decrease. Sudan B Black stain shows accumulation of the lipid pigment lipofuscin in the perinuclear lysosomes (“wear and tear”, PAS-positive, insoluble pigment resulting from breakdown of membranes. Elderly persons, chronic wasting diseases. 6. Haemosiderosis and haemochromatosis of the liver: The section of the liver tissue shows micronodular cirrhosis and severe deposition of the coarsely granular greensh-brown haemosiderin mostly in the lever cells. In some areas pigmentation can be located to lysosomes on the biliary pole of hepatocytes. There is no pigmentation of Kupffer cells and of the macrophages in the fibrous septa, which show proliferation of bile ducts and mononuclear infiltrate. Haemosiderosis – from excessive destruction of erythrocytes in the RES (e.g.after multiple blood transfudions). Haemochromatosis – from excessive absortion of iron in the intestine. Haemochromatosis of pancreas: In haemochromatosis, pigment is deposited in varius organs (liver, skin, heart muscle, kidney etc.). Pigmentation of pancreas is accompanied by fibrosis with destruction of the Langerhans islets, leading to diabetes (bronze diabetes). Pearls stain (blue coloration of haemosiderin). 7. Biliary cirrhosis: This lesion is often called biliary fibrosis (there is no nodular transformation of the liver tissue), it appears with severe long-lasting intrahepatic bile stasis. Bile plugs in biliary capillaries between the hepatocytes in liver cell cords, bile stasis in interlobular bile ducts, formation of bile lakes. Staining of bilirubin with the Fouchet's reagent (oxidation to dark green biliverdin – sections bleache out, the staining is not permanent). 8. Biliary nephrosis: Secondary to severe obstructive jaundice (conjugated bilirubin excreted in the urine). Look for pigmented casts in the renal tubules, pigmentation of epithelium of the proximal tubules. 9. Antracosis of the lungs: Many macrophages filled with black pigment in the area of lymphatics (periarterial, peribronchial location), intraalveolar pigmented macrophages. 10. Silicosis of the lungs: Coniofibrosis with three stages: 1-stigmatization with SiO2 crystals in similar location as antracotic pigment. 2-formation of silicotic nodules, 3-massive fibrosis. Silica crystals can be observed as fine needles in polarized light.