Necrosis
advertisement

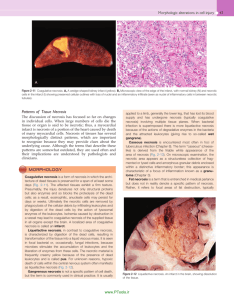
Necrosis TAMMY DO TRAUMA RESEARCH ASSOCIATES PROGRAM 8.24.2012 Necrosis Premature death of cells/death of body tissue Apoptosis vs. Necrosis Caused by: Infections Toxins Trauma Ischemia Causes Ischemia Thrombosis/embolism Infection/Disease Fungal/bacterial Diabetes Chemicals Poisons/toxins venom Trauma Necrotic Wound from Spider Bite Types of Necrosis Coagulative Liquefactive Caseous Fatty Fibrinoid Gangrenous Aseptic Coagulative Necrosis Caused by ischemia Denaturation of structural proteins Enzymatic digestion of cells Architecture of tissue preserved Occurs in organs like heart, spleen, kidney Does not occur in brain Liquefactive Necrosis Necrotic tissue digested by enzymes into liquid Associated with abscess formation Commonly seen in brain ischemia Fungal or bacterial infection Not in brain Caseous Necrosis Necrotic tissue is crumbly and cheese-like Typically caused by tuberculosis Syphilis fungal Fat Necrosis In response to trauma Lipases break down fats React with calcium: saponification Chalky white deposits Most commonly seen in pancreas and breasts Acute pancreatitis Fibrinoid Necrosis Caused by deposition of fibrin or fibrin-like materials Vasculitis Gangrenous Necrosis Considerable mass of necrosis Types of gangrene Dry Wet Gas Dry Necrosis Form of coagulative Caused by ischemia Autoamputation Distal parts of limbs Dry, shrunken, black Gangrenous Cont. Wet Moist tissue and organs Characterized by bacterial infection Dark, swollen, foul odor Gas Bacterial infection that produces gas within tissue Deadly Gangrenous Cont. Aseptic Necrosis Avascular necrosis or osteonecrosis Necrosis of bone Lack of blood supply to bone Medications, trauma, ischemia, hypercoagulable blood, alcoholism Treatment Depends on the extent of damage Restoration of blood flow Maggot Therapy Debridement Amputation Sources http://onlinemedicinefacts.com/pathology/caseous necrosis-liquefactive-necrosis-and-fibrinoid-necrosis http://www.symptomsbook.com/Facts-Therapy-PicturesDiagnosed-Information-Diagnosis-Herceptin-Treatednecrosis-Diagnosed-Diagnosis.htm http://www.medicinenet.com/aseptic_necrosis/article.htm http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/00226 6.htm http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/avascularnecrosis/DS00650 http://library.med.utah.edu/WebPath/CINJHTML/CINJ0 29.html