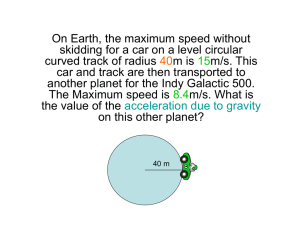
Circular Conceptual Review
advertisement

2) When a car goes around a circular curve on a horizontal road at constant speed, what force causes it to follow the circular path? A) the normal force from the road B) the friction force from the road C) gravity D) No force causes the car to do this because the car is traveling at constant speed and therefore has no acceleration. 3) A car goes around a circular curve on a horizontal road at constant speed. What is the direction of the friction force on the car due to the road? A) tangent to the curve in the forward direction B) tangent to the curve opposite to the direction of the car's motion C) perpendicular to the curve outward D) perpendicular to the curve inward E) There is no friction on the car because its speed is constant. 4) When an object moves in uniform circular motion, the direction of its acceleration is A) in the same direction as its velocity vector. B) in the opposite direction of its velocity vector. C) is directed toward the center of its circular path. D) is directed away from the center of its circular path. E) depends on the speed of the object. 8) Two small balls, A and B, attract each other gravitationally with a force of magnitude F. If we now double both masses and the separation of the balls, what will now be the magnitude of the attractive force on each one? A) 16F B) 8F C) 4F D) F E) F/4 9) Two small objects, with masses m and M, are originally a distance r apart, and the magnitude of the gravitational force on each one is F. The masses are changed to 2m and 2M, and the distance is changed to 4r. What is the magnitude of the new gravitational force? A) F/16 B) F/4 C) 16F D) 4F E) F/2 10) Two small objects, with masses m and M, are originally a distance r apart, and the gravitational force on each one has magnitude F. The second object has its mass changed to 2M, and the distance is changed to r/4. What is the magnitude of the new gravitational force? A) F/32 B) F/16 C) 16F D) 32F E) 2F 15) A hypothetical planet has a mass of one-half that of the earth and a radius of twice that of the earth. What is the acceleration due to gravity on the planet in terms of g, the acceleration due to gravity at the surface of the earth? A) g B) g/2 C) g/4 D) g/8 E) g/16 16) The acceleration due to gravity on Planet A is one-sixth what it is on Planet B, and the radius of the Planet A is one-fourth that of Planet B. The mass of Planet A is what fraction of the mass of Planet B? A) 1/6 B) 1/16 C) 1/24 D) 1/96 E) 1/12 2) Answer: B 3) Answer: D 4) Answer: C 8) Answer: D 9) Answer: B 10) Answer: D 15) Answer: D 16) Answer: D 22) Satellite A has twice the mass of satellite B, and moves at the same orbital distance from Earth as satellite B. Compare the speeds of the two satellites. A) The speed of B is twice the speed of A. B) The speed of B is one-half the speed of A. C) The speed of B is one-fourth the speed of A. D) The speed of B is equal to the speed of A. E) The speed of B is four times the speed of A. TRUE/FALSE 1) Satellites in orbit are accelerated toward Earth, so they must be getting closer and closer to our planet. 3) If a highway curve is properly banked and posted at 45 mph, it is a good idea to drive somewhat below this speed if your tires are bald or if the road is icy. 4) An ordinary car would not be able to go around an unbanked curve of a perfectly smooth road, no matter how the driver turned the wheels. 5) If you swing a ball in a vertical circle using a thin string, at the bottom of the circle the tension in the string must be greater than the ball's weight. 13) If Earth had twice as much mass as it now does but were also twice its present diameter, the acceleration due to gravity at its surface would be the same as it is now. 14) If the mass of Earth and all objects on it were suddenly doubled, the acceleration due to gravity at the surface would become 4 times what it is now. 3) A person ties a rock to a string and whirls it around in a vertical circle such that sometimes the rock is going straight upward and sometimes the rock is going straight down. She whirls the rock at the minimum speed (constant in time) such that the string is always taut (no sag). When is the tension the highest? A) It is highest when the rock is at the lowest elevation. B) It is highest when the rock is at the highest elevation. C) The tension is constant as the rock moves around in a circle. 4) A merry-go-round is spinning at a fixed rate. As a person is walking toward the edge, A) the force of static friction must increase in order for the person not to slide off. B) the force of static friction must decrease in order for the person not to slide off. C) the force of static friction such that the person does not slide off remains the same. 13) If you stood on a planet having a mass four times higher than Earth's mass, and a radius two times longer than Earth's radius, you would weigh A) the same as you do on Earth. B) two times more than you do on Earth. C) two times less than you do on Earth. D) four times more than you do on Earth. 17) If an astronaut were exactly half way between Earth and the Moon, the net gravitational force exerted on the astronaut by these two objects would be A) directed toward Earth. B) zero. C) directed toward the Moon. 22) Answer: D 1) Answer: FALSE 3) Answer: FALSE 4) Answer: TRUE 5) Answer: TRUE 13) Answer: FALSE 14) Answer: FALSE 3) Answer: A 4) Answer: A 13Answer: A 17) Answer: A