Lab Report: Meiosis - Advanced Academics
advertisement

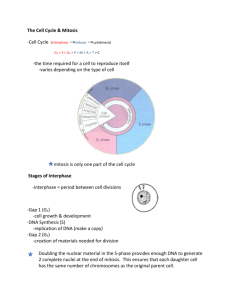
Lab Report: Meiosis Part 1 Directions: First, review mitosis by labeling the phases of the cells in the onion root picture below. Put your answers in the table below the image of the cells. Picture Number 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Phase of Mitosis Picture Number 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 Phase of Mitosis Part 2 Directions: Review meiosis by reading the material in the lessons and view the links below to compare mitosis and meiosis. The two sites that provide animations of meiosis are: Cells Alive!: Animal Cell Meiosis Tutorial: Meiosis The following site compares the two processes: What is Mitosis/Meiosis? Complete the chart of differences between mitosis and meiosis using the bank of phrases below. Insert the corresponding letter in each box. You will only use each letter once. Mitosis Meiosis Begins with/Ends with: Occurs in: Results in: Type of reproduction Function Phrase bank for the chart above Answer Option A Type of reproduction in which the number of chromosomes are reduced 50% to allow for transmission of the genes to offspring. B Growth, replacing of old cells, asexual reproduction. C Cellular Reproduction, regeneration of the individual organism. D One diploid cell; two diploid cells. E Human, animals, plants. F Sexual Reproduction, Seeds. G A process of asexual reproduction in which the cell divides in two producing a replica with an equal number of chromosomes. H One diploid cell; four haploid cells. I Biological Reproduction, generation of the species. J Human, animals, single cell species, others. Part 3: Phases of Meiosis Directions: Fill in the chart using the diagram below. You will put your answer in the column titled, “Name of Phase.” Use each phase of meiosis once for the: prophase I, prophase II, metaphase I, metaphase II, anaphase I, anaphase II, telophase I, telophase II. Number on Diagram 1 2 3 4 5 6 Name of Phase Description A new spindle forms around the chromosomes. Spindle fibers move homologous chromosomes to opposite sides or poles of the cell. Nuclear membrane reforms, cytoplasm divides, 4 daughter cells formed Chromosomes line up along equator (not in homologous pairs) Chromosomes become visible. The nuclear envelope breaks down. Crossing-over occurs. Centromeres divide. Chromatids move to opposite poles of the cell. 7 Pairs of homologous chromosomes move to the equator of the cell. Chromosomes gather at the poles. Cytoplasm divides, 2 daughter cells are formed. 8 Diagram and chart above are from http://www.biologycorner.com/worksheets/meiosis2.html Part 4 Directions: Refer to the diagram below to answer the three questions. Questions: 1. A diploid cell in the male (spermatocyte) undergoes meiosis I and II and produces how many sperm? 2. A diploid cell in the female (oocyte) undergoes meiosis I and II and produces how many eggs? Be careful. Four cells result, but they combine to form how many eggs? 3. Which cell is larger, the egg or the sperm cell?