2013 Scanning Electron Microscope booking form
advertisement

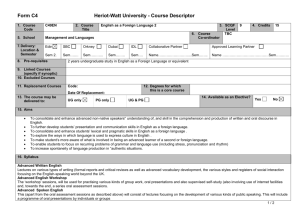
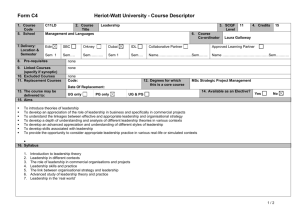
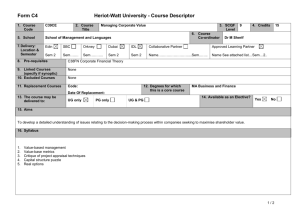
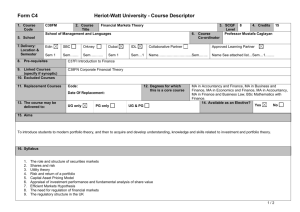
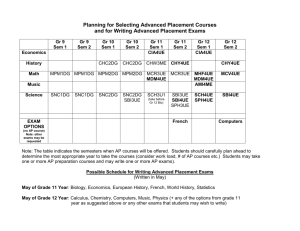
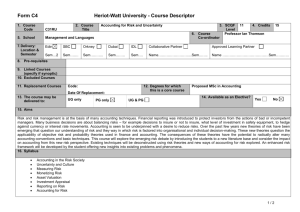
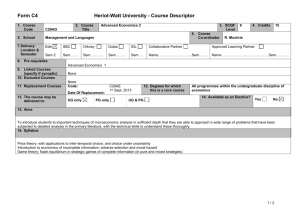
SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPE INFORMATION/BOOKING SHEET AND CONSENT FORM (To be fully completed BEFORE access to the electron microscopes is given. Please complete in typescript. Where applicable mark with an x.) Institution : Please indicate : (Tick one) Department: SEM (Leo) HR SEM (Auriga) USER DETAILS Date: Name: SEM (X650) Surname: : Tel. ext.: Cell: E-mail: Level of study: Hons. SUPERVISOR DETAILS MSc PhD Post-doc Name of Supervisor: : Name of Research Group: Contact no.: SPECIMEN DETAILS Other E-mail: Specimen description: : ...Briefly describe the type of materials you want to analyse (eg. Carbon nanotubes)… Purpose for SEM: Techniques required: (see table 1) COST AND CONSENT No. of specimens: (NB: maximum of 1 specimen per hour – see table 2) : No. of hours required: (for this booking only) Anticipated cost (see table 2): Name of person responsible for the account: E-mail address: Signature of consent (Designated Authority) Tel. no.: Date Disclaimer: Specimens which are not stable under the electron beam poses a huge challenge. It may become almost impossible to image such specimens or extract specific information. More time is therefore needed for such specimens. This is mainly applicable to HR-TEM. Table 1: Technique and Description SEM – (Scanning Electron Microscopy generally using the secondary electron signal)- for surface morphology studies. SEM -BSE – (SEM using the backscattered electron signal) – mainly for topographical and atomic number contrast. EDS – (Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy) – for elemental analysis for a large range of elements (from Boron and up). WDS – (Wavelength Dispersive Spectroscopy) – same as EDS - but more sensitive for low atomic number elements. X-Ray Mapping – Mapping of elemental compositions in EDS/WDS (This technique is comparatively more time consuming in TEM if good quality maps are required, as the x-ray signal is not as strong as in SEM of bulk material). STEM (Scanning TEM) combination of SEM and TEM, mainly used for analytical work and imaging. CC (Charge Compensation) –used for viewing uncoated, non-conducting specimens. CL (Cathodoluminescence) – used mainly for identifying special light emitting entities in minerals, semiconductors, polymers and some biological material during electron beam bombardment. PC (Plasma cleaning) – only used in situ in the HR SEM, but can be applied to all specimens ex situ. - used to clean special surfaces after contamination build-up. Contamination free surfaces are vital for HR SEM work. Table 2: Academic rates and average time allocation per specimen for normal imaging and EDS in TEM/SEM mode INSTRUMENT LEO SEM AVERAGE IMAGING RESOLUTION (nm) 4 HR SEM (AURIGA) 1.5 X650 SEM 10 TECHNIQUES AVAILABLE RATE PER HOUR SEM, EDS, WDS, CL, BSE, XRAY MAPPING R150.00 SEM, EDS, BSE, CC, PC, X-RAY MAPPING R300.00 SEM, EDS Free AVE. TIME PER SPECIMEN FOR NORMAL IMAGE ACQUISITION 30mins to 1 hr (X-ray mapping can take longer) 30mins to 1 hr (X-ray mapping can take longer) 30mins to 1 hr Disclaimer: Specimens which are not stable under the electron beam poses a huge challenge. It may become almost impossible to image such specimens or extract specific information. More time is therefore needed for such specimens. This is mainly applicable to HR-TEM.