ReduCtion - No Brain Too Small
advertisement

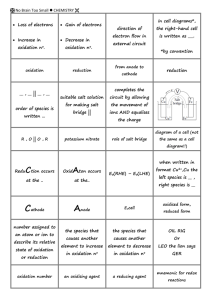
No Brain Too Small CHEMISTRY Loss of electrons Gain of electrons Increase in Decrease in oxidation no. oxidation no. oxidation reduction __ , __ || __ , __ order of species is in cell diagrams*, direction of the right-hand cell electron flow in is written as ___. external circuit *by convention from anode to cathode reduction completes the suitable salt solution circuit by allowing for making salt the movement of bridge || ions AND equalises written ... the charge diagram of a cell (not R , O || O , R potassium nitrate role of salt bridge the same as a cell diagram!!) Redu Ction occurs Oxid Aton occurs when written in Eo(RHE) – Eo(LHE) format Cu2+,Cu the left species is __ , at the .. at the.. Cathode Anode Eocell the species that the species that OIL RIG causes another causes another Or element to increase element to decrease LEO the lion says in oxidation no in oxidation no GER an oxidising agent a reducing agent number assigned to an atom or ion to describe its relative state of oxidation or reduction oxidation number right species is __ oxidised form, reduced form mnemonic for redox reactions No Brain Too Small CHEMISTRY Balance atoms (that are Balance atoms (that are not H or O) not H or O) Balance O (add water) Balance O (add water) Balance H (add H+) Balance H (add H+) Balance charge (add e- to Balance charge (add e- to more + side) more + side) Add OH- to both sides to cancel out H+’s -make H2O balancing half balancing half equations – acidic equations – alkaline conditions conditions a chemical reaction which results in the loss of electrons from a chemical species oxidation the process by which ionic compounds are split into their atoms using electric currents electrolysis Reaction at RHE as Reaction at LHE as drawn here drawn here oxidation reduction a chemical species a chemical reaction that has the ability which results in a to take electrons chemical species from other gaining electrons chemicals – i.e. it causes oxidation reduction oxidant oxygen, hydrogen, permanganate, thiosulfate, iron(II), dichromate, iron(III), halides, zinc, halogens, bromate, oxalate, sulfur iodate... are all … dioxide... are all… oxidising agents reducing agents Standard E° elements in pure form; Standard E° potentials are potentials are measured with K; concentrations 1.0 measured at a respect to the mol L–¹; Pressure of pressure of ___ kPa. standard ___ halfcell. 101.3 hydrogen a chemical species that has the ability to give electrons to another species – i.e. it causes reduction reductant strongest RA is… Na Temp. 25 °C or 298 gases 1.0 atm or 101.3 kPa standard conditions strongest OA … MnO4- No Brain Too Small CHEMISTRY blue solution copper(II), Cu2+ pale orange solution Fe3+(aq) iron (III) solution brown gas NO2 gas nitrogen dioxide orange solution dichromate, Cr2O72- orange-brown solution I2, iodine solution pale green solution Fe2+(aq) iron (II) solution blue/green solution purple solution chromium(III) ion, permanganate(VII), Cr3+ MnO4- In Zn(s)|Zn2+ green solution colourless solution manganate (VI), Cl-, Br-, I-, Mn2+, IO3-, BrO3-, MnO42- When two half-cells are connected with a voltmeter we measure the _____ electromotive force (emf of the cell) SO32-, SO42-, C2O42-, S2O32-, S4O62-, H+ (red)-orange solution Bromine solution, Br2 the | represents the phase boundary if two species are H+/H2 half-cell emf of zero is called the... IUPAC convention Zn(s)|Zn2+(aq)||Cu2+(aq)|Cu(s) both present in a single solution, we separate them with a _____ standard half-cell ‘cell diagram’ Comma , No Brain Too Small CHEMISTRY Left hand electrode Zn(s)|Zn2+(aq)|| Right hand electrode Pt(s)|H2(g)|H+(aq)|| ||Cu2+(aq)|Cu(s) Inert Pt reduced | oxidised || ||Cl–(aq)|Cl2(g)|Pt(s) || oxidised | reduced electrode placed to the outside Observation @ LHE Observation @ RHE Copper plated Fe electrode gets thinner, electrode, colour of solution becomes more solution fades green (pale) What emf could be made from this cell? Inert Pt electrode placed to the outside Can Fe3+ oxidise Cl- to chlorine Cl2? No (spontaneous Eo(cell) = +0.32V reaction is Cl2 oxidises Fe2+ to Fe3+) K2MnO4 MnO2 spontaneous reaction is..... H2O2 → O2 + H2O (unbalanced) strongest to weakest reductant Zn > Ga > Fe as zinc can reduce both Ga3+ and Fe2+ strongest OA is MnO4oxidation numbers of Mn are H2O2 +6, +4, +7 When looking at 2 When looking at 2 std redox potentials std redox potentials reduction (L R) oxidation (L R) occurs in the more occurs in the more ___ of the pair ___ of the pair positive negative standard cell diagram is... Fe | Fe2+ || Cu2+ | Cu RED CAT AN OX reduction @cathode oxidation @anode No Brain Too Small CHEMISTRY Test for chlorine gas... with starchiodide paper; colour change is.... starch-iodide paper turns blue-black Cu(s)|Cu2+(aq)||Cr2O72- Cu(s)|Cu2+(aq)||Cr2O72- (aq)|Cr3+(aq) (aq)|Cr3+(aq) Eocell = +ve Eocell = +ve ___ to move from What would you see What would you see one half-cell to the in the LHE? in the RHE? other Cu electrode shrinks, solution goes darker blue solution goes from orange to blue/green a salt bridge provides a path for ions draw (write) the cell draw (write) the cell draw (write) the cell draw (write) the cell diagram diagram diagram diagram Zn|Zn2+||Ag+|Ag Pb|Pb2+||Fe3+,Fe2+|C Cu(s)|Cu2+(aq)||MnO4–(aq), Pt(s)|Cl–(aq)|Cl2(g) Mn2+(aq)|C(s) ||BrO3–(aq), Br2(aq)|C(s) platinum or graphite is used as an _____ electrode for many half-cells inert E° (Cr2O72-,Cr3+)=1.33 V an oxidising agent oxidises E° (Hg2+/Hg)= 0.85V something else. Oxidation E° (Fe3+,Fe2+)= 0.77V is loss of electrons (OIL E° (I2,I-)= 0.54V RIG). An oxidising agent E° (S/S2-)= -0.48V takes electrons from that What’s the strongest other substance... ...so an oxidising agent must gain electrons. reductant? standard hydrogen electrode S2- No Brain Too Small CHEMISTRY OXIDANT OXIDANT O2 is reduced to…. Cl2 (pale green) is reduced to…. Oxide ion O2- Chloride ion Cl- Iodide ion I- Iron(II) ion Fe2+ (pale green) OXIDANT OXIDANT OXIDANT H+ (with metals) is reduced to…. MnO4- (in acidic conditions) is reduced to…. MnO4- (in basic conditions) is reduced to…. MnO4- (in neutral conditions) is reduced to…. Hydrogen gas, H2 Manganese(II) ion Mn2+ Manganate(VI) ion MnO42- (green) Manganese dioxide (brown ppt) MnO2 OXIDANT OXIDANT OXIDANT (blue) is reduced to…. Cr2O72- /H+ (orange) is reduced to…. Copper (metal) Cu (pinky orange) Chromium(III) ion Cr3+ (greeny blue) OXIDANT OXIDANT IO3is reduced to…. MnO2 is reduced to…. Iodine I2 (orange brown) Manganese(II) ion Mn2+ Cu2+ OXIDANT OXIDANT I2 (orange-brown) Fe3+ (pale orange) is reduced to…. is reduced to…. OXIDANT OClis reduced to…. Chloride Cl- OXIDANT Conc. HNO3 (NO3ion) is reduced to…. Nitrogen dioxide gas NO2 (brown) Oxidation number Oxidation number of underlined of underlined element element CuSO4 S4O62- +6 +2.5 No Brain Too Small CHEMISTRY REDUCTANT REDUCTANT REDUCTANT REDUCTANT Metal e.g. Mg is oxidised to…. C (black) is oxidised to…. CO is oxidised to…. Fe2+(pale green) is oxidised to…. Metal ion e.g. Mg2+ CO or CO2 gas CO2 gas Iron(III) ion Fe3+ (pale orange) REDUCTANT REDUCTANT REDUCTANT REDUCTANT Bris oxidised to…. Iis oxidised to…. H2 S is oxidised to…. SO2 is oxidised to…. Bromine Br2 (redorange) Iodine I2 (orangebrown) Sulfur S (yellow) Sulfate ion SO42- REDUCTANT REDUCTANT REDUCTANT REDUCTANT SO32is oxidised to…. S2O32is oxidised to…. H2 O2 is oxidised to…. H2C2O4 is oxidised to…. Sulfate ion SO42- Tetrathionate ion S4O62- Oxygen gas O2 Carbon dioxide gas CO2 Oxidising agents (oxidants) are themselves Reducing agents (reductants) are themselves reduced oxidised Oxidation is a loss of … Reduction is a gain of … (Leo the lion / OIL) (says GER / RIG) electrons electrons No Brain Too Small CHEMISTRY The oxidation number of any free, uncombined element e.g. Cu, Pb, H2, O3 and S8 is equal to…. The oxidation number of a simple (monatomic) ion e.g. Na+, Mg2+, Clis equal to …. The SUM of the oxidation numbers of a polyatomic ion e.g. SO42-, MnO4is equal to…. In compounds the sum of the oxidation numbers of all atoms is equal to…. Zero, 0 the charge on that ion the charge on that ion Zero, 0 The ox. number of The ox. number of oxygen (in hydrogen (in If its oxidation compounds/ions) compounds/ions) number increases, is __ , except in is __ , except in the element has peroxides where metal hydrides been…. it is __. where it is __. -2 -1 +1 -1 oxidised If its oxidation number decreases, the element has been…. reduced Oxidation number Oxidation number Oxidation number Oxidation number of underlined of underlined of underlined of underlined element element element element ClO- CrO42- CO2 N2 +1 +6 +4 0 Oxidation number Oxidation number Oxidation number Oxidation number of underlined of underlined of underlined of underlined element element element element SO3 H2S NaH KIO3 +6 -2 -1 +5 (NaH is a metal hydride) No Brain Too Small CHEMISTRY