Warm-up: (9-30-15) *ch.4-2 video lec/rubric out for stamp! Soil lab in
advertisement

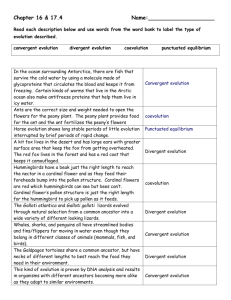
Warm-up: (9-30-15) *ch.4-2 video lec/rubric out for stamp! Soil lab in the hw tray! Do not put this under warm-ups! Begin working on Journal #2: Finch article due Friday. No complete sentences. Do not copy the Q’s. Graphs are on the back. Use your same paper as Journal #1: Cartoon guide ch.2 Q’s. Finish for hw. It is posted on my website under handouts. Q/A: Contrast punctuated equilibrium and gradualism. How did the oxygen in earth’s atmosphere develop? Contrast prokaryotes and eukaryotes List in order: A. Single celled eukaryotic organism B. Anaerobic prokaryotic organism C. Multicellular eukaryotic organism D. Photosynthetic prokaryotic organism E. aerobic prokaryotic organism What can be used as evidence for evolution? What info can you get from a trace fossil? Why do fossils show an incomplete picture of past organisms? Which is least likely to be preserved? Teeth, shells, bone, leaves, muscle Chapter 4-2: Evolution Mrs. Boyd Evidence of Evolution: Homologous and Analogous Structures Homologous structures: features in different species that are from a shared ancestor. Features can look similar but function differently. Analogous Structures Analogous structures: serve same function and look similar but are not from a common ancestor. Patterns of Evolution: Coevolution Coevolution: change of 2 species is closely associated with each other. Each of the species involved exerts selective pressure on the other, so they evolve together Predator/prey, parasites/host, plant eating animal/plant it eats, plant/pollinator. Ex. Yucca moth/yucca plant Leafcutter ants: Gather fragments of leaves from different plants and trees to feed to the fungus. Fungus secretes an enzyme that breaks down the cellulose sugar in the leaves Without the fungi, the ant colonies die. Without the ants, the fungi cannot survive. Some ants are equipped with a bacterium that acts as a pesticide on a particular mold, the largest threat to their fungus gardens. Why do they use this sparingly? T/F. Homologous structures are features in different species that are not from a shared ancestor. Give an example of an analogous structure. Give an example of a homologous structure. Give one example of coevolution. Patterns of Evolution: Convergent Evolution Convergent evolution: when organisms that aren't closely related evolve similar traits due to similar environments. Ex. Mara and rabbit Example of Convergent Evolution T/F. Convergent evolution is when unrelated organisms become more structurally similar. Patterns of Evolution: Divergent Evolution Divergent evolution: related species become more dissimilar due to dissimilar habitats. Ex. Red fox/kit fox Geographic Isolation …can lead to reproductive isolation, divergence of gene pools and speciation. Artificial selection: artificially speed up divergence by selective breeding Ex. Dog breeding. Artificial selection is an example of (convergent, divergent) evolution. Reproductive isolation Behavioral: different behaviors may lead to a species mating with certain individuals Ex. Albatross, bower birds Satin Bowerbird What type of evolution is occurring? convergent, divergent, coevolution, artificial selection Bumble bees are just heavy enough to open the petals of a snapdragon to reach its pollen. This is an example of …. convergent, divergent, coevolution, artificial selection Humans continue to plant corn that does not lose its seeds (kernels). This is an example of… convergent, divergent, coevolution, artificial selection Notothenioids from Antarctica and arctic cod are not related but have both evolved to have antifreeze in their blood. This is an example of … convergent, divergent, coevolution, artificial selection A photosynthetic algae lives with the polyp and feeds it sugar. The polyp provides the algae a home. This is an example of … convergent, divergent, coevolution, artificial selection Termites have a protist that lives in their gut that helps them break down plant cellulose. This is an example of … convergent, divergent, coevolution, artificial selection This is an example of … convergent, divergent, coevolution, artificial selection Check for Understanding: 1. The process in which one species evolves into 2 different species is called _____ 2. Artificial selection uses _____ to gain one or more desirable traits. 3. Give one example of coevolution.