ASKING BETTER QUESTIONS Schema Activator
advertisement

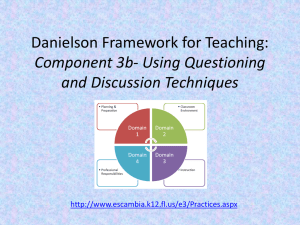
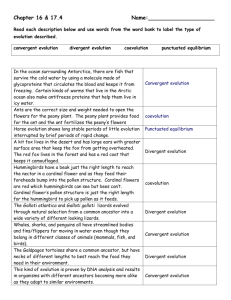
ASKING BETTER QUESTIONS Schema Activator Think-Pair-Share: – – – Review the questions you have collected from teacher observations. Reflect: Which ones do you consider to be “higher level”? Pair & Share: Compare your questions with those of a colleague. Characteristics of Teachers Who Expect Students to Learn at High Levels High Expectations Challenging Curriculum Instruction: High-level Questioning Instruction: Differentiation and Multiple Intelligences 4 Models of Questioning New Bloom’s Taxonomy Ciardello’s Four Types of Questions Quality Wierderhold Question Matrix QUESTIONS New Bloom’s Taxonomy OLD NEW Ciardiello’s Four Types of Questions Question Types Cognitive Operations Memory Naming, defining, identifying Convergent Thinking Explaining, comparing, contrasting Divergent Thinking Predicting, hypothesizing, inferring Evaluative Thinking Valuing, judging, justifying, choices CIARDIELLO Question Types Memory Convergent Thinking Divergent Thinking Evaluative Thinking BLOOM Cognitive Operations Characteristics of Good Questioning Q - quality U - understanding E - encourage multiple responses S - spark new questions T - thought-provoking I - individualized O - ownership shifted to students N - narrow and broad S - success building Question Matrix Chuck Wiederhold designed the Question Matrix in 1991. As you proceed through the matrix, the questions become more complex and open-ended. I II III IV LINKING CIARDIELLO / WIEDERHOLD Question Types Memory Convergent Thinking I II Divergent Thinking III IV Evaluative Thinking WIEDERHOLD QUESTION MATRIX Event What is? Present Situation Where / When is? Choice Person Reason Means Which is? Who is? Why is? How is? Past What did? Where / When did? Which did? Who did? Why did? How did? Possibility What can? Where / When can? Which can? Who can? Why can? How can? Probability What would? Where / When would? Which would? Prediction What will? Where / When will? Which will? Imagination What might? Where / When might? Which might? Who would? Why would? How would? Who will? Why will? How will? Who might? Why might? How might? Ask Questions That: • • • • Stimulate a wide range of student participation from both volunteering and non-volunteering students. Redirect initially asked questions to other students! Probe initial student answers. Encourage them to complete, clarify, expand, or support their answers Require students to generate questions of their own Results in Student Behaviors When Wait Time is Increased • Decrease in “I don’t know” responses • Length & accuracy of answers increases • Increase in volunteered, appropriate responses • Increased achievement test scores Results in Teacher Behaviors When Wait Time is Increased Questioning strategies became more flexible and varied Quantity of questions asked decreased, while the quality and variety of questions increased Higher-order, divergent questions were asked more often Classroom “Look fors” • Encourage teachers to prepare questions in advance. Questions should be scaffolded from easy to hard. • • Look for an environment that is studentled. Students should be working collaboratively, raising questions, and responding to their peers. Academy of Aerospace & Engineering Middle School Math Classroom English/Language Arts Classroom Exit Slip Review questions from Schema Activator. Review ratings of these questions. Would you change these? Why? What suggestions would you give to the teacher(s) who originally developed these questions to help them improve their techniques?