File - Mrs. Glazebrook
advertisement

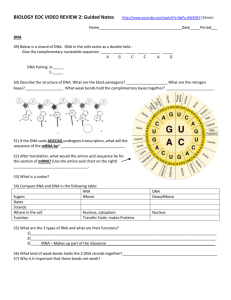
Name:____________________________ Genetics Review DNA vs RNA: SB2a. Distinguish between DNA and RNA. Word bank: Single stranded Acid Two Thymine Deoxyribose Ribose Uracil Ribose Nucleic Double helix There are _____ types of nucleic acids: DNA and RNA. Nucleic Acids are macromolecules that are made up of the monomer _________________. Although DNA and RNA are both nucleic acids there are some differences between the two. The first major difference is the sugar found in each molecule. DNA contains the sugar ___________________ and RNA contains the sugar ________________. DNA and RNA both contain the nitrogenous based Guanine, Cytosine, and Adenine. The base ______________________ is only found in DNA, and the base ____________________ is only found in RNA. One last major difference between DNA and RNA is that DNA is a ___________________ _________________ and RNA is ____________________ DNA structure: ________________. What are the names of the following? ________________________ Word bank: homologous ________________________ chromatin condenses centromere chromosome A long thread like strand of DNA is called a __________________. When the chromatin ________________, it becomes a ________________________. Chromosomes contain all the genes of an organism. A chromosome is held together in the center by a _____________________. In meiosis, the chromosomes form pairs. These pairs are called __________________ pairs. Protein Synthesis: SB2b. Explain the role of DNA in storing and transmitting cellular information. Word bank: Polypeptide Codon mRNA Unzip Nucleus Ribosome Translation Transcription Amino Acids Genes provide a chemical code for the synthesis (creation) of a certain protein. In order for a gene to make a protein the DNA double helix first has to ___________. When the DNA unzips it exposes the group of DNA _________, which are sets of three bases. During _______________, a copy of the DNA that is exposed is made in the form of _________. All of this takes place in the ______________. The mRNA molecule moves out of the nucleus and towards the _______________. The final stage of protein synthesis is called _____________. During this stage the bases of the mRNA codons are translated into _____________ ________. When the amino acids attach to one another they create a protein, also called a ______________________. Label the Picture Below: Word Bank: Codon Polypeptide chain Template mRNA Anticodon Amino Acid Ribosome tRNA DNA Mitosis: SB2c. Explain the role of meiosis in reproductive variability using Mendel’s laws. Word Bank: Daughter Replication Prophase Somatic/body Poles Metaphase Telophase Copies Cytokinesis Cells Most cells within the human body go through the CELL CYCLE. The first stage in the cell cycle is _________________. During this phase the cell _____________ each of the chromosomes. After interphase comes MITOSIS, which is the process _________ cells use to divide. The first stage of MITOSIS is ________________. In this phase the centrioles begin to appear. During the next phase, which is ___________________, the chromosomes begin to line up near the equator (middle) of the cell. In Anaphase, the next phase of Mitosis, the chromosomes begin to separate and get pulled to the two opposite ______________ of the cell by the centrioles. The last phase of Mitosis is ______________. During this phase two new _____________ appear and the cell prepares to divide. The last phase of the cell cycle is _______________, which is where the cytoplasm splits in two and creates two identical cells called ________________cells. Draw the steps of mitosis in the boxes below: INTERPHASE Drawing: PROPHASE Drawing: METAPHASE Drawing: ANAPHASE Drawing: TELOPHASE Drawing: CYTOKINESIS Drawing: Explanation: Explanation: Explanation: Explanation: Explanation: Explanation: Meiosis: SB2c. Explain the role of meiosis in reproductive variability using Mendel’s laws. Word Bank: Diploid Genetic Variation Two Gametes Haploid Four Meiosis occurs in two phases: Meiosis I and Meiosis II. Meiosis I is very similar to Mitosis, however something called ______________-____________ happens with the DNA. This process results in the genes ‘mixing’ with one another so that they are not perfect duplicates like in mitosis. At the end of Meiosis I there are ________ cells. During Meiosis II the two cells from Meiosis I split again, results in ________ cells total. These cells are sex cells, so they are called _________________. The cells in Meiosis are _____________, which means that they must combine with another gamete to become _______________. What are the ADVANTAGES of meiosis? 1. _____________________________________________________________________ 2. _____________________________________________________________________ 3. _____________________________________________________________________ Punnett Squares: SB2c. Explain the role of meiosis in reproductive variability using Mendel’s laws. Word Bank: Phenotype Top Genes Box Alleles Side Genotype Punnett Squares are a simple way to organize all of the possible ______________ of _______________ from a particular set of parents. To make a Punnett square you should first draw a ________ and divide it into four sections. Then, you write the letters that represent alleles (genes) from the first parent along the ______ of the box. You will write the letters that represent the alleles (genes) from the other parent along the _______ of the box. The word _________________ refers to the gene combinations, and ________________________ refers to the physical characteristics of the offspring. Complete the following crosses: A a a How many of the offspring are HOMOZYGOUS DOMINANT for the trait? ______ out of 4 How many of the offspring are HOMOZYGOUS RECESSIVE for the trait? a ______ out of 4 How many of the offspring are HETERZYGOUS for the trait? ______ out of 4 G g G How many of the offspring are HOMOZYGOUS DOMINANT for the trait? ______ out of 4 How many of the offspring are HOMOZYGOUS RECESSIVE for the trait? g ______ out of 4 How many of the offspring are HETERZYGOUS for the trait? ______ out of 4 Asexual vs. Sexual Reproduction: SB2e. Compare advantages of sexual and asexual reproduction in different situations. Type of Organism Most animals Sexual or Asexual? Method of Reproduction Fertilization Products of Reproduction? Bacteria, and some protists Hydra, Coral, and Yeast Binary Fission Fungi, Algae, and some molds Many plants Spore Production Many spores Vegetative Reproduction Structures that will grow into new plants Budding PEDIGREES Directions: Answer the following questions to create a key to solve a pedigree 1. Squares represent _________________ and circles represent _______________. 2. If a shape is filled in, the individual____________________ the disease. 3. If the shape is partially filled in, the individual is a _________________. They carry the disease, but do not show any signs of the disease. 4. Lines going between male and female indicate a ______________________. 5. Lines going down between the married couple indicate their ___________________. Non-Mendelian Traits: Fill in the chart below from your notes Description Example Incomplete Dominance Co-dominance Multiple Alleles Polygenetic Traits Directions: Use the marker provided at your station to complete the dihybrid cross on the poster. After you have finished fill in the Punnett square below and be sure to answer the questions. BB = Black Bb = Black bb = White LL = Short Ll = Short ll = Long Dihybrid Cross: Use the picture on the page before to solve the questions 1. How many of the offspring are black with short hair? ______________ 2. How many of the offspring are black with long hair? _______________ 3. How many of the offspring are white with short hair? ______________ 4. How many of the offspring are white with long hair? _______________ SEX-LINKED TRAITS Word Bank: X Y Dominant Y 2 Recessive X Sex-linked traits are traits that are carried on either the _____ or the ____ chromosome. Sex-linked traits can also be either ________________ or ________________. Sex-linked traits appear in different frequencies in males and females since males have an _____ and a _____ sex chromosome and females have _____ X chromosomes. A Punnett square can be used to determine the probability of offspring to have certain sex-linked traits. --------------------------------------------------------------DNA TECHNOLOGY: Describe the following: Cloning: Human Genome Project: Recombinant DNA and genetic Engineering: Mutations: Fill in the chart below Mutation Name Substitutions/ Point Mutation Deletion Duplication Deletion Inversion Insertion Non-disjunction Translocation Gene or Chromosome? Description/ Definition Example