FOR BIO104 FUNDAMENTALS OF CELL BIOLOGY 2 SECTIONS
advertisement

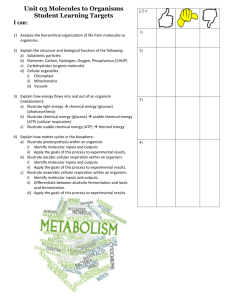
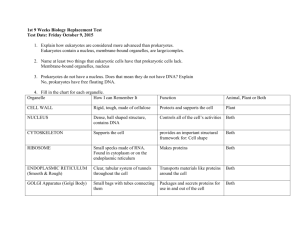
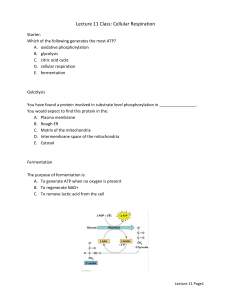
FOR BIO104 FUNDAMENTALS OF CELL BIOLOGY 2 SECTIONS TAUGHT TUE/THUR 2 HOURS EACH DAY 1 SECTION WED HYBRID MEETS 3 HOURS TOTAL Compare and contrast aerobic cellular respiration and fermentation in eukaryotes and prokaryotes Week s of Oct 26 and Nov 2 LEARNING OBJECTIVE LEARNING OUTCOMES: SWBAT 2) Describe ATP, ADP, phosphorylati on and their importance to cellular activity * Summarize the inputs/outcom es of the steps of aerobic respiration and fermentation and be able to point out commonalities and differences TAXONOMY LEVEL/ CATEGORY Remember Understand Understand Apply LEARNING ACTIVITIES Before Oct 27/28 Outside of class: Vocabulary building of terms – make flash cards Before Oct 27/28 Outside of class: Draw and label the ATP/ADP cycle including which reactions release ATP and which reactions require an input of ATP Oct 27/28 In class: -Give 15 minute over view of CR - Individually make a table of what goes in and what comes out for both CR -Continue with details of CR focusing on big picture – include e-and H+ - Muddiest point -Give 10 minute over view of Fermentation -Add in fermentation input/outcomes Oct 28/29 In class: White Board - Make drawings of CR using tables - – include e-and H+ - Compare drawings. -Use drawings to answer free response review questions in groups. -Students write and answer one more question to compare CR to fermentation (keep answers off white board) FORMATIVE ASSES (assignment SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT questions) (graded assignment) Match the following terms with their definition: ATP/ADP/ Phos-phorylation: Lower level short answer question on unit exam: Draw the ATP/ADP cycle and explain the role of each molecule Blackboard Online Quiz prior to class 1. Rate tables as -v+ 2. Cover muddiest points 3. Rate drawings as - v + 4. Rate group free response answers as - v + 5. Grade written answers as – v + Overall group discussion Take brief Blackboard quiz on basic concepts Multiple choice questions on unit exam: See below Grade Respiration and Fermentation lab: Copyright protected lab but standard lab of measuring yeast fermentation/re spiration and CO2 concentration in exhaled air pre/post exercise -Share responses to questions and answer other groups questions 4) Compare and contrast aerobic and anaerobic cellular respiration in writing. *Explain the implications of disruption to energy production in humans (as an example of a eukaryote) and bacteria Understand Apply Analyze Evaluate and create Complete respiration and fermentation lab Still Oct 28/29 Do a 2 minute written summary (not chemical equations) comparing CR to fermentation- “Exit Letter” Before class Nov 3/4 Outside of class- to discuss in class - modified case study: Mystery of the 7 Deaths Nov 3/4 In class- discuss case “Exit Letter” Students discuss case and apply what we have learned- submit group answers on case study Short answer question on unit exam: See below POTENTIAL EXAM QUESTIONS 1. a. b. c. d. e. Aerobic cellular respiration releases the energy in food: little by little all at once occasionally rapidly explosively 2. a. b. c. d. e. What is the initial source of energy for all living things on earth? Aerobic cellular respiration The sun Photosynthesis Fossil fuels Glycolysis 3. a. b. c. d. e. All of the following are true statements about enzymes EXCEPT: Enzymes are inorganic molecules. Enzymes must bind to a substrate in order to function. Enzymes can become inactivated by changes in pH. Enzymes are catalysts. The shape of an enzyme is critical to its function. 4. a. b. c. d. What is the final acceptor of the electrons stripped from glucose during aerobic cellular respiration? Water Hydrogen NADH Oxygen 5. a. b. c. d. Glycolysis occurs in which part of the cell? Cytoplasm Nucleus Mitochondria Plasma membrane Base your answers to questions 6 through 8 on the reactions shown below. 2 ATP + C6H12O6 → 2 pyruvic acid (pyruvate) + 4 ATP lactic acid OR alcohol + 2CO2 6. a. b. c. d. The series of reactions shown above includes the process known as: digestion fermentation dehydration synthesis the Krebs cycle 7. a. b. c. d. Which organic molecule is represented by C6H12O6? Glucose Starch Chlorophyll Acetyl-CoA 8. a. b. c. d. Which end product of these reactions is of greatest benefit to the organism in which these reactions occur? Lactic acid Pyruvic acid Alcohol ATP 9. a. b. c. d. Where are the electron transport chains for the aerobic cellular respiration located? Cytoplasm Mitochondrial matrix (inner compartment) Outer mitochondrial membrane Inner mitochondrial membrane (cristae) 10. a. b. c. d. Pyruvate is the end product of: fermentation. the Krebs cycle. glycolysis. All of the above. 11. a. b. c. d. e. According to the first law of thermodynamics: one form of energy cannot be converted into another. energy can be neither created nor destroyed. entropy is increasing in the universe. energy can neither be converted into matter nor matter into energy. all of these are true. 12. a. b. c. d. e. Which of the following molecules has the greatest total energy? Pyruvate ADP ATP NADH Glucose 13. a. b. c. d. e. Which of the following processes liberates the most energy from glucose? Glycolysis Aerobic cellular respiration Alcoholic fermentation Lactate fermentation All liberate the same amount, but through different means 14. Which ions accumulate between the inner and outer membranes of the mitochondria during oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport phosphorylation)? a. Calcium b. Oxygen c. Phosphorus d. Hydrogen e. Sodium 15. a. b. c. d. What is the function of the molecules NAD+ and FAD? They are reactants that are converted by the appropriate enzymes into ATP. They transport high energy electrons from one region of the cell to another. They are enzymes that speed up the production of pyruvate. They absorb energy from sunlight. 16. Which of the following lists the stages of aerobic cellular respiration in the correct operational sequence (from first to last)? i. ii. iii. glycolysis oxidative phosphorylation (electron transfer phosphorylation) Krebs cycle a. b. c. d. e. II >>> I >>> III III >>> I >>> II II >>> III >>> I I >>> III >>> II I >>>II>>>III 17. Which process generates the greatest number of ATP molecules per glucose molecule? a. Glycolysis. b. Alcoholic fermentation. c. Oxidative phosphorylation (electron transfer phosphorylation). d. The Krebs cycle. 18. Explain the connection between the air we breathe in and exhale, and cellular respiration. Include the following vocabulary: O2, CO2, cells, sugar/glucose, mitochondria 19. Explain what happens to a runner during a marathon in terms of energy. Include the following vocabulary: O2, CO2, mitochondria, cellular respiration, aerobic, fermentation 20. Give one example of a chemical that disrupts and how it could affect the organism.