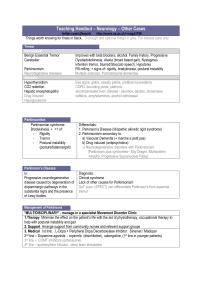
Table 1 – Overview of studies on Parkinsonism and risk factors in
advertisement

Table 1 – Overview of studies on Parkinsonism and risk factors in sub-Saharan African countries Author, year of Country publication Setting Bower [101], 2005 Hospital Ethiopia Akinyemi [102], Nigeria 2008 Hospital Design / Period of study Crosssectional 2003-2004 Population characteristics Diagnosis criteria 720 patients; 109 (15·1%) Not provided with movement disorders including 71 men; age 52 y. (13-80) Case-control 51 patients (men 37) with PD UK Parkinson’s 2005-2005 and 50 controls Disease Society (UKPDS) Brain Bank criteria Cosnett [103], 1988 South Africa Hospital- Crosssectional 1979-1985 2638 patients seen in neurological consultations Clinical Dotchin [104], 2008 Tanzania Community Crosssectional 161,071 inhabitants Screening questionnaire/ confirmed by a specialist Schoenberg [78], Nigeria 1988 USA Community Crosssectional Crosssectional Clinical Winkler [105], 2009 Hospital Black population aged 40+ 3412 participants Black population aged 40+ 3521 black participants and 5404 white participants. n = 8676 patients admitted (740 with neurological diseases) 1569 people, age 50-110 years Tanzania Community Community Kengne [39], 2006 Cameroon Hospital Lombard Zimbabwe [106],1978 Osuntokun [10], Nigeria 1979 Hospital Osuntokun [69], Nigeria 1987 Community Haylett [107], 2012 Hospital South Africa Hospital Crosssectional 2003 Crosssectional 2003-2005 Crosssectional 1993-2001 Clinical UK Parkinson’s Disease Society Brain Bank criteria UK Parkinson’s Disease Society Brain Bank criteria 4041 neurologic consultations Not provided 145 (3.9%) had neurodegenerative diseases Crosssectional Crosssectional 1966-1976 Total patients admitted: Not provided 83,453 blacks, 34,952 whites 217 patients with Etiological diagnosis via parkinsonism history, lab tests, neuroimaging and autopsy Crosssectional 1985 Crosssectional Total participants surveyed: 18,954 Questionnaire developed by author Prevalence Profile of Comments parkinsonism patients 7.2% of all admissions (PD: N:52; PD:88% Review of medical files 6.4% ) Age (at onset): 57y (30-80) Men: 75% NA N:51; PD: 100% 22% patients with PD had Age (at onset): 70y cognitive ddysfunction, with (41-80) age at PD onset as sole Men:72% predictor Blacks: 23.6/1000 N:81; PD: 14% Retrospective review of Indians: 45.5/1000 Age: NA medical files Whites: 61.6/1000 Men: NA Overall: 40/100,000 Men: 64/100,000 women: 20/100,000 N: 32; PD:100% Age adjustment to the UK Age (at onset): 69y population; Age at onset : 29– (37-90) 90; Mean duration 5.1 y Men: 72% Age adjusted: N: 2; PD:100% 67/100 000 Age/Men: NA Age adjusted: N: 12; PD: 100% Blacks: 341/100,000 Age: NA Whites: 352/100,000 Men: NA 0.1% (all patients) N: 8; PD:37% 1.1% (Patients with Age: >32y neurological diseases Men: 100% 235/100,000 N: 18 None of the 18 screenedAge: 50-100y positive was confirmed as Men: 50% havPD 48.8% of all N: 41; PD 100% 4 selected neurodegenerative neurodegenerative diseases; Age: 15-84y brain disorders: dementia, PD, 1.01% of all neurologic Men: 73.2% ALS, chorea consultation Blacks: 20.6/100,000 N: 50 (17 blacks) Retrospective review of Whites: 283.2/100,000 Age/men: NA medical files NA N: 217; PD 38% All patients evaluated by the Age: median 51- authors 70y, Men:75% 10/100,000 N. 2; PD 100% Age/men: NA 229 patients with PD UK Parkinson’s Disease NA including 163 whites (71%), Society Brain Bank diagnostic N: 229; PD 100% Mutation in the Parkin gene Age (at onset): 54y Homozygous or compound 1 Ekenze [40], 2010 Nigeria Hospital Owolabi [108], 2010 Nigeria Hospital Okubadejo [109], Nigeria 2004 Hospital Okubadejo [110], Nigeria 2005 Hospital Okubadejo [111], Nigeria 2010 Hospital Keyser [112], 2010 South Africa Hospital Van Der Merwe [113], 2012 South Africa Hospital Femi [114], 2012 Nigeria Hospital Cilia [115], 2012 Ghana Hospital 45 mixed ancestry (20%), 17 blacks (7%) and 4 Indians (2%) Cross8440 admission in the sectional medical ward; 1249 had 2003-2007 neurological diseases (men 640) Cross6282 admission in the sectional medical ward; 980 had 2005-2007 neurological diseases (men 586) Case-control 33 participants (men 25, mean age 60y ) with PD and 33 match controls criteria Not specified (17-80) Men: % NA 21.9/1000 of al neurological N: 14 admissions Age>70 y (71%) Men: 28.6% Clinical: any 3 out of tremor, 4.1/1000 of all neurological rigidity, admissions Akinesia/bradikinesia/postural and instability Clinical: any 3 out of tremor, NA rigidity, Akinesia/bradikinesia/postural and instability Case-control 28 participants (men 21, Clinical: Any 2 out of tremor, NA mean age 63y ) with PD and rigidity, 28 match controls Akinesia/bradikinesia/postural and instability, exclusion of other causes of parkinsonism Prospective 124 participants with Clinical: Any 3 of the 1.5% of all neurological 1996-2006 Parkinsonism including 24 following: tremors, rigidity, consultations between 01-2005 and 12bradykinesia, and postural or 2006 gait abnormality Cross154 patients with PD UK Parkinson’s Disease NA sectional including 51 whites (35%), Society Brain Bank diagnostic 45 Afrikaners (31%), 29 criteria mixed ancestry (20%), 17 blacks (12%) and 3 Indians (2%). Crosssectional 2007-2011 Crosssectional 2007-2011 111 patients with early onset PD (men 71) and 286 with late onset PD (men 62%) 1153 participants in 2 Neurologic clinics; 96 (men: 74) had parkinsonism Case-control 54 participants with PD and 46 healthy participants heterozygous mutations: 7 patients Heterozygous variant: 7 UK Parkinson’s Disease NA Society Brain Bank diagnostic criteria presence of at least three of 6.94% of all neurological the four cardinal features of consultations tremors, rigidity, bradykinesia, and postural or gait abnormality UK Parkinson’s Disease NA Society Brain Bank Brain Bank diagnostic criteria N: 4 Age: (50-68) Men; 100% N: 33 Age (at onset): 3680y Men: 75% Case fatality rate was higher in PD (25% vs. 7.1%), Factors associated with increased mortality: advanced age and disease severity N: 28 Autonomic dysfunction rate Age (at onset): 37- was higher in PD (61% vs. 76y 6%), Men: 76% N: 98; PD 79% Other causes of parkinsonism Age (at onset): 61y n(%): Vascular/drug Men: 76.5% induced/MSA/LBD: 9(35)/5(19)/4(15)/3(11) N: 154; PD 100% 16 sequence variants of the Age (at onset): 52 PINK1gene identified: 1 y homozygous mutation Men: 62% (Y258X), 2 heterozygous missense variants (P305A and E476K), and 13 polymorphisms N: 397; PD 100% A positive family history was Age (at onset): 57y associated with a younger age Men: 248 at onse. N: 96; PD (83.3%) Age: 58y Men: 63.5% N: 54; PD 100% Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 Age (at onset): 59 (LRRK2) gene found in no y participants Men: 61% NA: Not available; PD: Parkinson’s disease; UK: United Kingdom; USA: United States of America; y: year 2