Greek Gods and Goddesses
advertisement

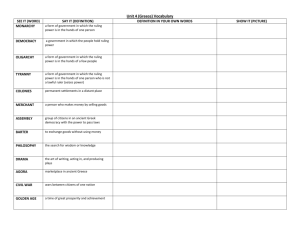
Name Assignment One- Heeeellllllo Greece! Directions: After reading pages 4-9 in the Ancient Greece book, answer the following questions in COMPLETE sentences in your notebook. Be sure to write neatly and with much detail because these will become your Ancient Greece notes! 1. How many years did the Greek civilzation last? It lasted from 2000B.C. to 200 B.C. 2. What was the period between 500 B.C. and 400 B.C. called? The Classical period. 3. Describe what a city-state was. A city-state, or polis, was based around one city and included all the surrounding farms, villages, and houses. 4. Describe the landscape of mainland ancient Greece and the islands that surround it. The mainland and islands are hot and dry with many high mountains and steepsided valleys. The mainland is surrounded almost entirely by water. 5. How did geography of the land affect farming? Because the mountainside was so rugged, the ancient Greeks had to farm near the coats and sheltered valleys. Their most important crops were wheat, barley, grapes and olives. 6. How did the ancient Greeks do most of their traveling and why? The Greeks traveled by sea whenevr they could because travel by land was so difficult. 7. Describe Athens. Athens was the city of education and learning. Athenian philosphers and artists were famous and about 300,00 people lived in the city and surrounding countryside. 8. Describe Sparta. Sparta was famous for its strength and Athens greatest rival. 9. Why were they rivals? They each tried to gain control of all of Greece. 10. What was the acropolis? It means “high city” and it was built on top of a high hill. 11. What was the Parthenon? It was the main temple of the city. 12. What was the Peloponnesian War? How long did it last? The rivalry between Athens and Sparta led to war and Sparta attacked Athens first. Sparta won but both cities were weak after 27 years of fighting. Assignment Two- Calling All Citizens Directions: After reading pages 10-13 in the Ancient Greece book, answer the following questions in COMPLETE sentences in your notebook. Be sure to write neatly and with much detail because these will become your Ancient Greece notes! 1. Compare citizens and slaves. How were they alike? How were they different? Citizens were most important and had the most rights. They could own property and take part in polictics and the law. Slaves were usually captured prisoners of war. They were brought and sold like property. Most were paid for their work and could buy their freedom. 2. What is a democracy? A democracy is a political system of government by the citizens. Only men with property were entitled to be citizens with the right to vote. 3. Who was Ptolemy and what did he believe? Ptolomey was a Greek scholar who believed the the Earth was the center of the universe. 4. Copy the chart below into your notebook and fill in the missing information. Philosopher Socrates Hippocrates Plato Aristotle Why he was important One of the first great philosophers, taught the value of questioning common beliefs in order to find new ideas and explore new truths. His pupil was Plato. Founded a medical school, where he practiced scientific medicine instead of magic or religion. He taught the value of knowing how the body worked. Founded a school for philospohers called the Academy. Pupil was Aristotle. He examined living things in nature. He also wrote onmany subjects,including politcis, and invented a method of thinking called logic. He was a student of Plato. Assignment Three- It’s All Greek to Me! Directions: After reading pages 14-17 in the Ancient Greece book, answer the following questions in COMPLETE sentences in your notebook. Be sure to write neatly and with much detail because these will become your Ancient Greece notes! 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 1. Use the Glossary to define the following terms: a. Soothsayer- a person who could predict the furture and tell fortunes b. Sacrifice- an offering made to a god to bring good fortune or to ask the god not to be angry c. Oracle- a holy place where the gods could be asked questions with the help of a priest or priestess What were The Olympic games? Give atleast three detaiols about them. The Olympic Games was an event held evry four years in honor of Zeus. People came from all over Greece to compete in athletic events. Events included: boxing, wrestling, discus throwing, javelin throwing, long jumping, running and chariot races. It lasted five days and wars were stopped. What was the earliest form of Greek writing? How did the Greeks pass down news or events before writing them down? Poetry was the earliest form of writing and Homer was the first major poet. Before writing, people passed on the news of events by word of mouth. How did drama develop? Drama developed from songs and dances to honor the gods. What were the two types of plays? Describe each one. There were two types of plays: comedies and tragedies. Comedies made fun of politics, religion, and important people. Tradegies were sad and violent tales of love and war. What did Greek actors always wear and what were they like? Greek actors always wore masks which depicted different facial expressions and moods. Wide mouths made it easier to project their voices. Assignment Four- Welcome Home Directions: After reading the final section, pages 18-24 in the Ancient Greece book, answer the following questions in COMPLETE sentences in your notebook. Be sure to write neatly and with much detail because these will become your Ancient Greece notes! 1. Describe a typical home in ancient Greece. Greek houses were arranged around a courtyard with and atler in the middle. They were made from mud bricks dried in the sun. 2. Describe a chiton. A plain square of material that was fastened over one or both shoulders and belted around the waist. 3. What was a peplos? Women wore this long tunic. 4. How did the Greeks keep clean? The Greeks had public baths where they used olive oil to get clean. 5. Describe the foods of ancient Greece. The ancient Greek diet was simple and very healthy. The ate bread, cheese, fruit, vegtables, eggs and very little meat. Fruits such as pomegranates, dates, melons, and figs. Vegetables such as peas, beans, turnips, garlic and onions. 6. What was a symposium? A symposium was a drinking party after a meal where men would continue discussions. 7. What was sweetmeats? Sweetmeats were treats made from dates, figs, nuts, sesame and honey. 8. Give some examples of Greek art. Greek art consisted of elegant pots covered in patterns and paintings, statues made from stone or bronze. 9. What was it like for boys and girls growing up in ancient Greece? Greek boys went to school from the age of 7 to 15. They learned reading, writing, math, music, poetry, and sports. Girls were taught to cook and look after the house by their mothers. Chapter 2 Textbook Notes Ancient Greece Myths- stories about the origins and doings of the gods. They attempt to explain how and why things happen; explain natural events and the joys and tragedies of life. History- is an account of what actually happened Epic- a long narrative poem about great heroes and their deeds. Homer- a blind Greek poet who lived between 800 B.C. and 700 B.C. Two epics he wrote were: the Illiad and the Odyssey. Illiad- epic poem about the Trojan War. Odyssey- is the story about Odysseus’ travels. Troy vs. Greece Lasted ten years Began because the son of the king of Troy, named Paris, carried off Helen, the wife of the king of Sparta Based on Homer’s account, Odysseus, a Greek solider, thought of a plan to defeat the Trojans They pretended to be defeated and withdrew their troops to the river to sail home A large wooden horse was left behind, hiding inside was the best Greek warriors After the Trojans pulled the horse behind its walls, the warriors came out at night and won the bloody conflict Herodotus- was the first Greek historian Greek gods and goddesses played an important role in ancient Greece Each had a special function or job They were believed to never grow old and were more powerful than humans They had favorite humans that they helped and protected They sent misfortune to those that displeased, angered them The twelve most important gods and goddesses lived on Mount Olympus, the highest mountain in Greece. They were called the Olympians. God/ Goddess Gender Role Zeus male rule the gods on Mount Olympus Poseidon, Zeus’ male god of the sea and earthquakes brother Hera, Zeus’ wife female goddess of marriage Hestia, Hera’s sister female protected homes Hephaestus male blacksmith for the gods Aphrodite female goddess of love Athena female goddess of war and wisdom Ares male god of battle Apollo male god of music, poetry, purity Artemis, Apollo’s twin female goddess of hunting sister Demeter female goddess of agriculture Hermes male messenger of the gods Other gods and goddesses: God/ Goddess Gender Role Hades, Zeus’ brother male god of the underworld Dionysus male god of grapes and winemaking Other information about Ancient Greece Direct democracy- the democracy of Athens where all citizens participated directly in the making of decisions. This form was good for Athens because it was a small community. Indirect democracy- citizens do not directly participate in the everyday workings of government. This is the form of democracy here in the United States. Our citizens elect representatives, the members of Congress, to make laws and important decisions. A direct democracy would not work in the U.S. because there are so many people that it would be impossible for all of them to assemble in one place. Textbook Lesson 3- Alexander the Great Who was Alexander the Great? Alexander the Great was a Macedonian ruler at the age of 20. He united Greece and conquered many lands, including Egypt, Persia and beyond. He wanted to spread Greek culture because he thought it was the best in the world. Culture is made up of a people’s language, ideas, arts, and general way of life. He did this by establishing Greek colonies in Egypt and the Middle East. A colony is a settlement of people living in a new territory far from the country that rules it. Alexander was known as “the Great” because he conquered the largest empire the world had ever known. Gymnasiums were places where Greeks could gather to hold discussions, read, and participate in athletic training. Textbook Lesson 4- Greek Achievements Philosophy- the love of wisdom; famous philosophers: Socrates, Plato, Aristotle Architecture- Parthenon: the temple to Athena that sat on the Acropolis- a high rocky hill so all could see. Columns: three styles: Doric- plain capital, or top Ionic- capital with scrolls Corinthian - capital has carved stone leaves Amphitheaters- large open-air theaters in a semi-circle shape. Stone seats ascend into the hillside.