ELEN 214 Solar Lab assignment 1
advertisement

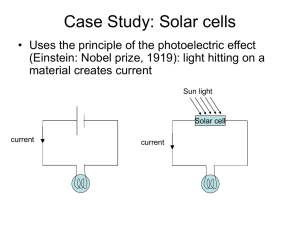
Solar Lab: Assignment 1 How solar cells work There are various different types of solar panels but I’ll describe the most commonly used type, p-n junction silicon. Basically you array doped n-type silicon very close to p-type silicon. A p-n junction is formed. I’ll spare the reader an extensive description of p-type and n-type doping, but it’s important to note that the n-type side has an excess of unbonded electrons, and the p-type has an excess of “holes”, which simply means there is an atom in want of an electron. At the junction, the electrons diffuse from the n-type side to the p-type side until the resulting electric field prevents them from moving across the junction. The junction is then in equilibrium. The electric field is oriented in such a way that the edge of the n-type side is positive from the leaving electrons, and the excess of electrons on the edge of the ptype side cause it to be negative. So at this point the solar cell is ready. A photon comes along and hits an electron with enough force to knock it out of the valence band (an energy level where it is connected to the atoms sharing it) and into the conduction band, where its high energy level allows it to move about without being bonded. This electron leaving also creates a hole where it left. The electron being negatively charged and the hole being positively charged, if they venture anywhere near the p-n junction’s electric field, the electron will get sucked to the n-type side and the hole will get pushed further into the p-type side. This movement of electron and hole is the same as a movement of electric charge and a current is formed. Solar systems A solar system is a group of solar cells connected together. Solar cells work act very similarly to batteries. They can be combined in parallel to create a higher current or in series to create a higher potential. It doesn’t seem necessary to point out, but a simple flow of electrons from point a to b in a circuit forms a direct current. For this reason the use of solar systems in conjunction with an alternating current system or devices which use alternating current, an inverter is required. An inverter is a fairly simple electrical device which uses a switch and a transformer to convert direct current to alternating current and heat. Renewable energy sources 1. Wind power. Wind power is happily becoming more and more widely used throughout the world. Actually, my brother and I are currently developing a 175 million dollar 100MW wind power facility in Oklahoma. We’re currently working on installing a $15,000 100 meter met tower. Nice little after graduation project wouldn’t you say? Anyway, wind power is basically being fed into power grids or stored in huge battery arrays and then fed into the electrical system to supplement the amount of natural gas generation used. There are also small scale uses such as powering your home or net metering or to run small devices such a windmill pumps in the country. 2. Hydroelectric power. Hydroelectric power is used in places such as the Hoover damn where the force of gravity acting on water can be used to run turbines. These generators are also used to supplement the power grid. There are also historically smaller scale systems which operate on rivers to transfer the kinetic energy of water to another physical system with no electricity involved. 3. Biofuels. Biofuels are sortof an extension of solar energy in that plants use photosynthesis to grow. These biofuels can be burnt to generate heat, and are now being converted to liquid for use in automobiles. Other uses for solar energy There are a few obvious uses for solar energy besides photovoltaic generation of electricity. The most obvious that jumps out is heating. Sun light makes me hot when I stand in it, so obviously everything it hits gains some level of hit. In areas of the world where it’s cold and winters are harsh. Solar energy heats buildings without any special equipment whatsoever. It may not be a great amount of heat, but even the dinosaurs used it. Solar grills are small devices which use concave mirrors to direct sunlight at a grill surface. This idea can be used to heat houses or pools but it is much more useful on a larger scale where a huge array of mirrors can be used to focus the sun’s energy on a heat tower which can then run a steam generator. My new personal favorite use for solar energy is hybrid solar lighting. HSL is being developed at Oak Ridge National Labs outside of Knoxville Tennessee. The way it works is similar to the way a solar grill works except instead of a grilling surface the sunlight is focused on an optical fiber array and the fact that the dish has GPS based sun tracking. An optical fiber is a glass or plastic fiber that carries light along its length. Traditionally optical fiber is used for communication but since it efficiently carries light down its length, ORNL decided to have to carry sunlight. The sunlight is then harvested of its infrared energy and passed on to hybrid lighting elements which supplement it with electrically produced light depending on the amount of sunlight available. The full spectrum sunlight is healthier and cheaper than light produced electrically, and using the light in this manner is far more efficient than photovoltaic methods. In addition the IR energy removed can be used to power high efficiency photovoltaic cells. I’m not really sure why a second paragraph about HSL is necessary as the first described it so comprehensively so this seems like a good place to say I’m pretty excited about finding it. In fact this find has made the course worthwhile to me. I’ve already started planning the creation of my own HSL system for lighting purposes. I’ve been a long time admirer of fiber optics and this use is just stunning. I must have it.