Physics Optics Homework: Reflection, Refraction, Diffraction
advertisement

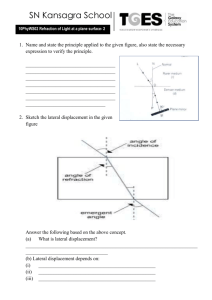
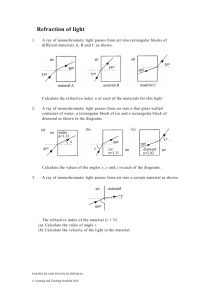
Homework #6 Physics 112-4 Fall 2011 p1 Homework #6: optics Chapter 30: Reflection and Refraction Page #541: #2: Why does a spoon appear bent when it’s in a glass of water? #3: Why do a diamond and an identically shaped piece of glass sparkle differently? #7: Why can’t you walk to the end of the rainbow? #11: Through what angle should you rotate a mirror so that a reflected ray rotates through 30°? #16: Information on a compact disk is stored in “pits” whose depth is essentially one-fourth the wavelength of the laser light used to “read” the information. The wavelength is 780nm in air, but the wavelength on the pit depth is based is measured in the n=1.55 plastic that makes up most of the disk. Find the pit depth. #22: Find the critical angle for total internal reflection in (a) ice (n=1.309), (b) polystyrene (n=1.49), and (c) rutile, also known as titanium oxide, (n=2.62), when the surrounding medium is air. ##26: Blue and red laser beams strike an air-glass interface with incidence angle 50°. If the glass has refractive indices of 1.680 for blue light and 1.621 for red light, what will be the angle between the two beams in the glass? Page #542: #29: The refractive index of the human cornea is 1.40. If 550mm light strikes a cornea at incidence angle 25°, find (a) the angle of refraction and (b) the wavelength in the cornea. Page #543: #60: You’re an automotive engineer charged with evaluating safety glass, which is made by bonding a layer of flexible plastic between two layers of glass, thus eliminating dangerous glass fragments during accidents. A new product uses glass with refractive index n=1.55 and plastic with n=1.48. You’re asked to determine whether total internal reflection at the glass-plastic interface could cause problems with visibility. What do you conclude and why? Chapter 31: Images and Optical Instruments Page #561: #1: How can you see a virtual image when it’s not “really there”? #5: What is the meaning of negative object distance? Negative focal length? ##12: Does a fish in a spherical bowl appear larger or smaller than it actually is? ##17: A shoe store uses small floor-level mirrors to let customers view prospective purchases. At what angle should such a mirror be inclined so that a person standing 50cm from the mirror with eyes 140cm off the floor can see her feet? Homework #6 Physics 112-4 Fall 2011 p2 #27: A magnifying glass enlarges print by 50% when it is 90cm from a page. What’s the focal length? #35: You’re an optometrist helping a nearsighted patient who claims he can’t see clearly beyond 80cm. Prescribe a lens that will put the images of a distant object at 80cm, giving you patient clear vision at all distances beyond the normal near point. Page #562: #66: You are taking a photography class, working with a camera whose zoon lens covers the focal-length range 38-110mm. Your instructor asks you to compare the sizes of the images of a distant object when photographed at the two zoom extremes. Your answer? #71: You stand with your nose 6.0cm from the surface of a reflecting ball, and your nose’s image appear three-quarters full size. What is the ball’s diameter? Page #563: #75: Show that identical objects placed equal distances on either side of the focal point of a concave mirror or converging lens produce images of equal size. Are the images of the same type? Chapter 32: Interference and Diffraction Page #581: #1: A prism bends blue light more than red. Is the same true of a diffraction grating? #5: You can hear around corners, but you can’t see around corners. Why? #14: The 546nm green line of gaseous mercury falls on a double-slit apparatus. If the fifth dark fringe is at 0.113° from the centerline, what’s the slit separation? #21: Find the minimum thickness of a soap film (n=1.333) in which 550nm light will undergo constructive interference. #32: What is the longest wavelength of light that you could use to resolve a structure with angular diameter 0.44mrad, using a microscope with aperture 1.2mm in diameter? Page #582: #61: While driving at night, your eyes’ irises dilate to 3.1mm diameter. If your vision were diffraction limited, what would be the greatest distance at which you could see as distinct the two headlights of an oncoming car 1.5m apart. Take λ=550nm.