Literacy Squared Writing Rubric 2013_Eng trans
advertisement

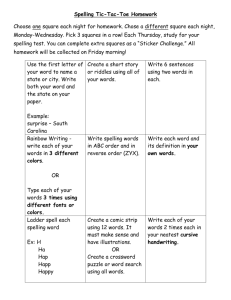
Literacy Squared® Writing Rubric Quantitative Rubric Assumptions General Assumptions: The students’ Spanish and English writing samples will be scored side-by-side. Critical descriptors are cumulative. To receive a 10 in Content, the student must exhibit all of the relevant indicators listed in the previous levels. All samples should be scored, but if the student did not respond to the prompt, this should be indicated at the top of the rubric. Samples written in a language other than the language of the prompt are scored as a 1 for Content. This score credits the child for demonstrating an understanding of the task and the topic. Additionally, it recognizes that bilingual students bring multiple linguistic resources to the learning environment. All other constructs are scored 0. Children are not penalized for non-standard syntax (noun/adjective- agua frio; noun/article- los serpiente; verb/adjective- están grande). Content “Descriptive language (use of adjectives/adverbs at the word level)” – this includes more than basic adjectives such as my blue bike. Instead, to be considered descriptive language, the student must include more extensive descriptions. For example, I like my bunny that is white and soft contains adjectives but is not considered descriptive language. Me gusta el perro porque me obedece cuando le digo siéntate. También porque está bonito, tiene pelaje y lo puedo vestir como quiera, is an example of descriptive language. (I like my dog because he obeys me when I say, “Sit.” Also because he is cute, he has fur, and I can dress him as I wish.) “Varied sentence structures” - Just because each sentence starts a different way does not necessarily qualify as “varied sentence structures”. To be varied sentences, the composition should be contain some combination of: o Simple sentences- independent clause, contains a subject and verb, includes a complete thought o Compound sentences- two independent clauses connected by a coordinator: for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so o Complex sentences- independent clause joined by one or more dependent clauses contains subordinators (because, since, although, when), relative pronouns (that, who, which), etc. Structural Elements Structural Elements are those elements the writer uses to guide readers through the text. They include the use of capitalization, punctuation marks, and paragraphing. Punctuation marks include: periods, commas, question marks, guiones, quotation marks, exclamation points, apostrophes, hyphens. Accent marks are NOT considered punctuation- they are part of spelling. “Controls” in critical descriptor 3, means mostly controls (at least 85% or more) Spelling Children are not penalized in the spelling section for approximated codeswitches. Majority = at least 50% Most = at least 85% or more Reversed letters are counted as spelling approximations if the reversed letter is a different letter (b/d). However, if the reversed letter does not represent another letter (reversed letter c) it is not counted as a spelling approximation. Words that are written with hyper- (con migo/conmigo, snow man/snowman) or hypo- segmentation (ala/ a la, a lot/ a lot) are counted as spelling approximations. Rater ID: ___________ Student ID: ____________ Not to prompt (Circle) Literacy Squared® Writing Rubric: Grades K, 1, 2, 3, 4 & 5 2012-2013 ____ SPANISH SCORE 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 Span (Circle Grade) CONTENT Focused composition, conveys emotion or uses figurative language, is engaging to the reader; clearly addresses the prompt; book language Organization of composition includes effective transitions & vivid examples Writing includes complex sentence structures and has a discernable, consistent structure Sense of completeness – Clear introduction and clear conclusion Includes descriptive language (use of adjectives, adverbs at the word level) or varied sentence structures Main idea discernable with supporting details, or main idea can be inferred or stated explicitly, or repetitive vocabulary: may include unrelated ideas Two ideas– I like my bike and/because it is blue One idea expressed through a subject & predicate, subject may be implied (I like my bike, amo, or run) Label(s), list of words. May communicate an idea w/o subject & predicate Prewriting: Picture only, not readable, or written in a language other than the prompt The student did not prepare a sample ENGLISH SCORE 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS 5 4 3 2 1 0 Multi-paragraph composition with accurate punctuation and capitalization Controls most structural elements and includes paragraphing Controls beginning and ending punctuation in ways that make sense and is attempting additional structural elements (commas, question marks, guiones, apostrophes, ellipses, parentheses, hyphens, and indentation) Uses one or more of the structural elements correctly Uses one or more of the structural elements incorrectly Structural elements not evident 5 4 3 2 1 0 SPELLING 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 Accurate spelling Most words are spelled conventionally Majority of HFW are correct and child is approximating standardization in errors Most words are not spelled conventionally but demonstrates an emerging knowledge of common spelling patterns Represents most sounds in words and most high frequency words are spelled incorrectly Represents some sounds in words Message is not discernable 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 | Eng Literacy Squared® Qualitative Analysis of Student Writing Bilingual Strategies (Spanish English) (English Spanish) Spanish English (bidirectional) DISCOURSE Rhetorical structures (first, next, last) Punctuation (signals awareness of codeswitches- me gusta “basketball,” or ¡Run fast!) SENTENCE/PHRASE Syntax (subject omission, word order- the bike of my sister) Literal Translations (agarré todas bien/I got them all right) Code-switching (no puedo hablar in just one language) WORD LEVEL Code-switching Loan words (soccer, mall) Nativized words (spláchate/splashed) PHONICS Spanish English (japi/happy) English Spanish (awua/agua) Spanish English (bihave/behave, lecktura/lectura) Developmental Language Specific Approximations SPANISH ENGLISH Structural elements, syntax, spelling, hypo/hyper segmentation Structural elements, syntax, spelling, hypo/hyper segmentation