Earthquake magnitude and intensity
advertisement

Earthquake magnitude and
intensity:
What is the difference
between the magnitude
and the intensity of an
earthquake?
Magnitude is the energy
released at the source of an
earthquake. Magnitude is
found by measuring
earthquakes on a
seismograph. Intensity is
the strength of shaking
produced by the
earthquake at a certain
location. Intensity is
determined from effects on
people, human made
structures, and the natural
environment.
Why did the February 21st
2011 earthquake in
Christchurch cause so much
damage?
There was a high amount of
energy released in the
earthquake at the centre of
the fault and the ground
accelerations in
Christchurch were as much
as four times higher than
the highest accelerations
measured in the magnitude
9.0 earthquake off the east
coast of Japan on 11 March
2011.
This is the ring of fire; along
this red line is where high
amounts of earthquakes
and volcanic activity occur.
As you can see the red line
goes right through New
Zealand.
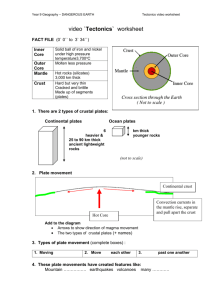
Convergent: This is when
two plates collide. When an
oceanic plate and another
oceanic plate and a
continental plate and an
oceanic plate collide the
more dense plate sub ducts
{dives downward} into the
mantle. And a continental
and a continental plate
colliding makes volcanoes
and mountain ranges.
What do Scientists think
causes the earth’s tectonic
plates to move?
According to scientist’s
theory, the earth’s crust is
made up of about twelve
plates and on them sits the
continents and oceans.
These plates are continually
shifting because the surface
beneath them {hot soft
mantle} is moving slowly
like a conveyor belt, driven
by heat and other forces at
work in the Earth’s core.
The plates are moving
about a centimetre to
fifteen centimetres per year
in different directions. The
earth’s tectonic plates can
move apart, collide, or slide
past each other.
Explain what happens at the
following plate boundaries:
a) divergent b) convergent
c) transform
Transform: This is when two
plates slide past each other
in a parallel position. But,
movement is not smooth
due to friction between the
rocks of the two plates. So,
sometimes the two plates
can get ‘stuck’ and lock
together. But since the
currents of magma are still
dragging the plates, much
tension and pressure is built
up at the transform
boundary. When there is
sufficient build up of
pressure, rocks on the
plates break and get jerked
apart. This results in
earthquakes.
Plate tectonics:
This is a picture of the
world’s tectonic plates and
the directions they are
moving in.
Divergent: This is when two
plates move away from
each other and allow
magma through the crack
to come up between the
two plates and dry on the
plates creating new crust
{rock}.
This is a picture showing
how the mantle circulates
beneath the plates.
What is magma?
Magma is hot molten rock
{melted rock} usually
formed in the earth’s upper
mantle circulating like a
conveyer belt. Some finds
its way onto the plates due
to earthquakes or cracks in
the crust and some onto
the earth’s surface, where it
solidifies to form igneous
rock {solid rock}.
How is it that new crust
forms at divergent
boundaries?
At a divergent boundary
plates are going away from
each other allowing magma
to come up through the gap
which then dries and forms
new crust {rock} on the
surface of a plate or on the
surface layer of the earth in
different forms e.g. Ridges.
other plate is forced down
the process is called
subduction.
What plate boundary does
New Zealand straddle?
New Zealand straddles the
Pacific plate and the
Australian plate, the plates
as you can see below meet
right in the middle of New
Zealand. These plates do
different things in different
parts of the boundary,
some parts transform and
others may collide but they
do not spread apart/
diverge.
How is it that material is
destroyed at convergent
boundaries?
Some of the plate material
is destroyed because one
plate is diving under the
other plate, the plate enters
in to the magma and
eventually it is completely
melted from the extreme
heat of the melted rock or
magma around it.
What is a subduction zone?
A subduction zone is where
one massive plate, normally
a continental plate will
force the other plate, an
oceanic plate down
beneath it. This is called the
subduction zone. When the
What do plates do A] In the
north B] to the south and C]
Within the south island?
At the southern end of the
South Island, the Australian
plate dives down {sub
ducts} below the Pacific
plate.
In the north Island the
opposite situation occurs
with the Pacific plate being
pushed under by the
Australian plate.
In between, through most
of the South Island, the two
plates grind past each other
along the Alpine fault.
What does this plate
movement result in?
This plate movement
results in volcanic activity in
the north and earthquakes
throughout the country.