File
advertisement
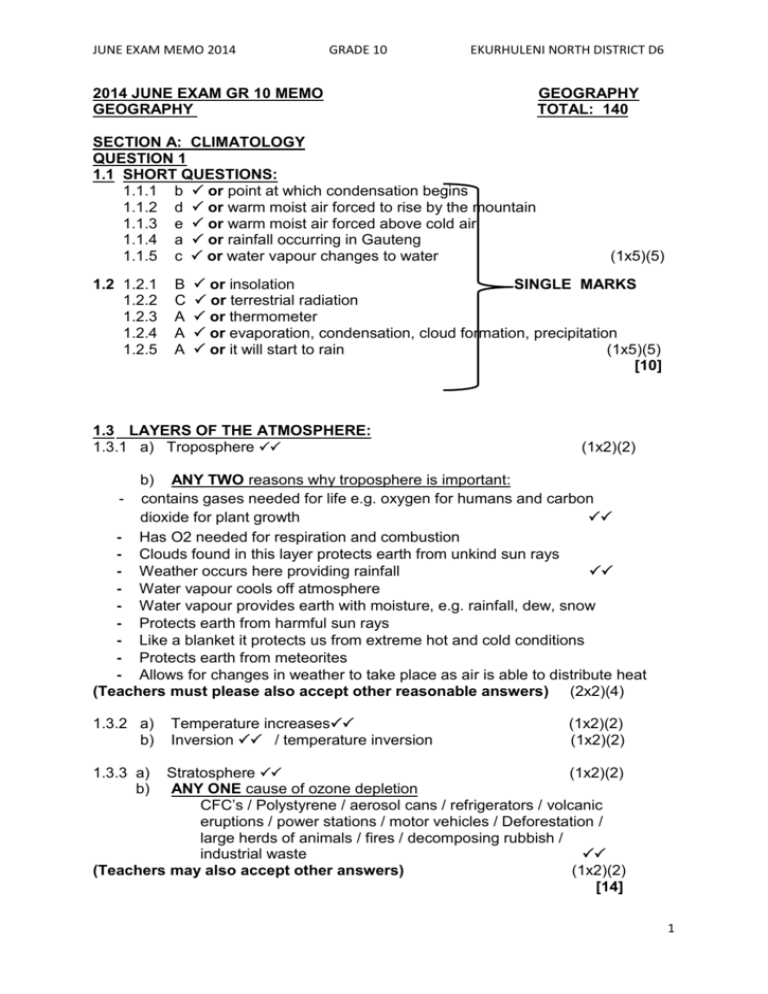
JUNE EXAM MEMO 2014 GRADE 10 EKURHULENI NORTH DISTRICT D6 2014 JUNE EXAM GR 10 MEMO GEOGRAPHY SECTION A: CLIMATOLOGY QUESTION 1 1.1 SHORT QUESTIONS: 1.1.1 b or point at which condensation begins 1.1.2 d or warm moist air forced to rise by the mountain 1.1.3 e or warm moist air forced above cold air 1.1.4 a or rainfall occurring in Gauteng 1.1.5 c or water vapour changes to water 1.2 1.2.1 1.2.2 1.2.3 1.2.4 1.2.5 B C A A A GEOGRAPHY TOTAL: 140 (1x5)(5) or insolation SINGLE MARKS or terrestrial radiation or thermometer or evaporation, condensation, cloud formation, precipitation or it will start to rain (1x5)(5) [10] 1.3 LAYERS OF THE ATMOSPHERE: 1.3.1 a) Troposphere (1x2)(2) b) ANY TWO reasons why troposphere is important: - contains gases needed for life e.g. oxygen for humans and carbon dioxide for plant growth - Has O2 needed for respiration and combustion - Clouds found in this layer protects earth from unkind sun rays - Weather occurs here providing rainfall - Water vapour cools off atmosphere - Water vapour provides earth with moisture, e.g. rainfall, dew, snow - Protects earth from harmful sun rays - Like a blanket it protects us from extreme hot and cold conditions - Protects earth from meteorites - Allows for changes in weather to take place as air is able to distribute heat (Teachers must please also accept other reasonable answers) (2x2)(4) 1.3.2 a) b) Temperature increases Inversion / temperature inversion (1x2)(2) (1x2)(2) Stratosphere (1x2)(2) ANY ONE cause of ozone depletion CFC’s / Polystyrene / aerosol cans / refrigerators / volcanic eruptions / power stations / motor vehicles / Deforestation / large herds of animals / fires / decomposing rubbish / industrial waste (Teachers may also accept other answers) (1x2)(2) [14] 1.3.3 a) b) 1 JUNE EXAM MEMO 2014 GRADE 10 EKURHULENI NORTH DISTRICT D6 1.4 HEATING OF THE ATMOSPHERE AND GLOBAL WARMING 1.4.1 Global warming = the rapid increase in average atmospheric temperature (Teachers may also accept other definitions) (1x2)(2) 1.4.2 Increased fossil fuels from cars / aeroplanes / industries (factories) / more CO2 / methane / increased CFC gasses / volcanic eruptions / asteroid impacts / ANY ONE (Teachers may also accept other answers) (1x2)(2) Results of global warming: ANY TWO Global warming will result in the earth’s temp increasing Polar ice caps melting Polar bears may drown - Sea level will rise(as a result of ice caps melting) Coastal cities will flood (as a result of rising sea levels) Weather patterns may change certain species of plants and animals will be effected Extinction of certain species droughts may be experienced – which may lead to loss of money, poverty, famine, malnutrition and even death i.e. everything that causes global warming must be reduced TEACHERS MUST MARK WHAT THEY HAVE TAUGHT (2X2)(4) 1.4.4 Paragraph reducing global warming: Reduce the amount of greenhouse gasses released by reducing burning of fossil fuels Planting more trees to absorb CO2 Encourage government to make more use of renewable energy resources Make use of more nonpolluting energy resources e.g. wind power instead of coal driven power stations Industries must reduce pollutants released into the atmosphere / place filters on chimneys to absorb smoke (Teachers may also accept other answers) (4x2)(8) [16] 1.4.3 1.5 1.5.1 1.5.2 FACTORS AFFECTING TEMPERATURE Ocean currents (1x2)(2) Mozambique is warm because: It flows from warm equatorial waters Benguela is cold because: It flows from cold polar regions (2x2)(4) 1.5.3 Winter (1x2)(2) 1.5.4 Windhoek (1x2)(2) 1.5.5 Continental climate = inland with temperature extremes e.g. hot days Cold nights (1x2)(2) TEACHERS MUST MARK WHAT THEY HAVE TAUGHT 1.5.6 Maritime climate is at the coast with moderate temperatures and no extremes (1x2)(2) TEACHERS MUST MARK WHAT THEY HAVE TAUGHT [14] 2 JUNE EXAM MEMO 2014 1.6 1.6.1 1.6.2 1.6.3 GRADE 10 EKURHULENI NORTH DISTRICT D6 SYNOPTIC WEATHER MAP Isobars Kalahari Hp or Kalahari anticyclone a) Winter (1x2)(2) (1x2)(2) (1x2)(2) b) Reason why it is a winter map? ANY TWO High pressure dominating over land (Kalahari H) No clouds over interior of S.A. No rain over the interior of S.A. Mid latitude cyclone is present Cold front near Cape Town Clouds in Cape Town (SW Cape) Rainfall at Cape Town (SW Cape) There are NO tropical cyclones in winter (2x2)(4) a) Cloud cover: 8/8 or 100% or overcast b) Wind direction: NE North east or ENE East north east c) Wind speed: 25 knots SINGLE MARKS d) Air temperature: 17˚C or 17˚ (not just 17) e) Dew point temp: 15˚C or 15˚ (not just 15) f) Weather: Rainovercast/cloudy (6x1)(6) [16] SUBTOTAL: 70 __________________________________________________________________ 1.6.4 SECTION B: GEOMORPHOLOGY QUESTION 2: 2.1 FOLDING 2.1.1 Symmetrical fold 2.1.2 Overthrust fold or thrust 2.1.3 Anticline 2.1.4 Syncline 2.1.5 Limb (5x1)(5) SINGLE MARKS 2.2 INTERIOR OF THE EARTH 2.2.1 Mantle 2.2.2 Outer core (only) 2.2.3 Crust 2.2.4 Mantle 2.2.5 Inner core or 4 (5x1)(5) [10] 3 JUNE EXAM MEMO 2014 GRADE 10 2.3 IGNEOUS INTRUSIONS AND ROCKS 2.3.1 A= Dyke B= Sill C= Lopolith EKURHULENI NORTH DISTRICT D6 (3x2)(6) 2.3.2 Igneous extrusions = rocks that form from magma that has cooled OUTSIDE or ON the Earth’s crust e.g. lava flow that has cooled or volcanoes (1x2)(2) 2.3.3 Paragraph – distinguish between Igneous, Sedimentary and metamorphic rocks Igneous rock formation is linked to volcanoes – molten rock reaches Surface as lava – lava cools quickly – which forms igneous rocks – which Has tiny crystals - It may contain valuable minerals such as gold, diamonds, zink, etc. Sedimentary rocks are usually deposited in layers – they may contain fossils - also fossil fuels such as oil, coal and natural gas. - Rocks are eroded by wind, water and ice – broken material are transported away – materials are deposited, compressed and cemented into rocks Metamorphic rocks are exposed to great heat or pressure – usually near volcanic activity – rocks melt partially, cools and solidifies – small crystals may be found – sometimes clear layers may also be found TWO MARKS FOR IGNEOUS TWO MARKS FOR SEDIMENTARY TWO MARKS FOR METAMORPHIC TWO MARKS FOR ANY FACT UNDER ANY OF THE ROCK TYPES (Teachers may also accept other answers) (4x2)(8) [16] 2.4 PLATE TECTONICS AND CONTINENTAL DRIFT 2.4.1 Constructive Reason= When the plates move apart new magma seeps through to form new crust (2x2)(4) 2.4.2 Because the continents move in that direction i.e. to the west so it folds at the leading edge (e.g. N and S America) 2.2.4 Panthalassa (1x2)(2) (1x2)(2) 2.2.4 Evidence of continental drift: ANY TWO Matching coastlines: Coastlines fit together like a large jigsaw puzzle Similar plants on opposite continents Similar animals on opposite continents Same animal fossils on opposite continents Fold Mountains on opposite continents are similar: The Mountains in South Western Cape is similar to the mountains on the east coast of South America 4 JUNE EXAM MEMO 2014 GRADE 10 EKURHULENI NORTH DISTRICT D6 Mineral belts on opposite coastlines are similar Same rock type is found on the east coast of South America, Southern Africa, Antarctica and Australia Similar vegetation on opposite continents Glaciation - Similar glacial features on opposite coastlines 2.4.5 San Andreas Fault (2x2)(4) (1x2)(2) [14] 2.5 FOLDING AND FAULTING 2.5.1 2.5.2 Indo-Australian plate and Eurasian plate (2x1)(2) A=convergence B=divergence SINGLE MARKS (2x1)(2) 2.5.3 A=constructive B=destructive (2x2)(4) 2.5.4 B (1x2)(2) 2.5.5 Folding=when rock layers bend Faulting=when rock layers break 2.6 EARTHQUAKES 2.6.1 Lateral faulting Tear fault Transverse fault Strike slip fault (2x2)(4) [14] ANY ONE (1x2)(2) 2.6.2 Focus= the exact point or origin underground Epicentre= the point on the surface immediately above the focus Where the quake is first felt (2x2)(4) 2.6.3 Tsunami= ocean wave created by earthquake (1x2)(2) 2.6.4 Paragraph discuss effects of large earthquake People are killed - people are injured - people are trapped buildings collapse - fires start - workers lose jobs - insurance companies lose money - tourism suffers - tsunamis can destroy farmlands - water and as lines break - electricity cuts occur landslides take place - transport systems are damaged ADD TO THIS LIST PLEASE (Teachers may also accept other answers) (4x2)(8) [16] SUBTOTAL: 70 GRAND TOTAL: 140 5