Identify minerals by their characteristic properties
advertisement
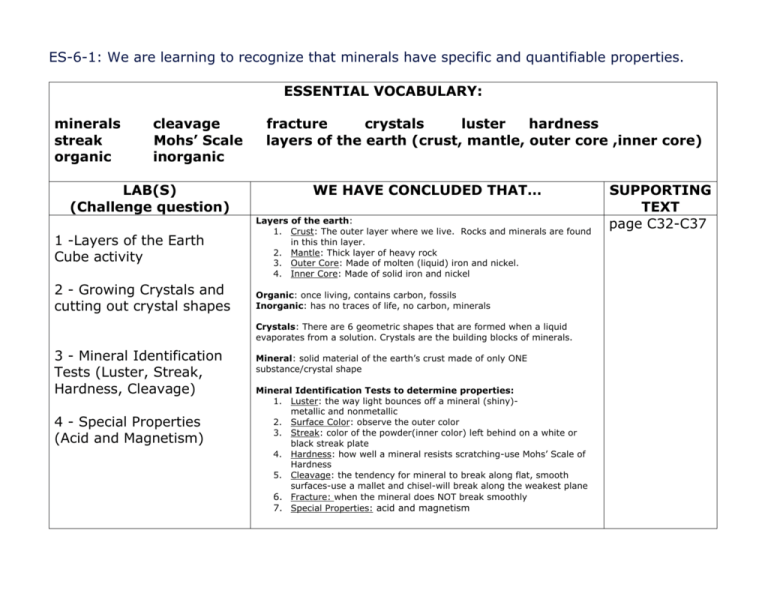
ES-6-1: We are learning to recognize that minerals have specific and quantifiable properties. ESSENTIAL VOCABULARY: minerals streak organic cleavage Mohs’ Scale inorganic LAB(S) (Challenge question) fracture crystals luster hardness layers of the earth (crust, mantle, outer core ,inner core) WE HAVE CONCLUDED THAT… 1 -Layers of the Earth Cube activity Layers of the earth: 1. Crust: The outer layer where we live. Rocks and minerals are found in this thin layer. 2. Mantle: Thick layer of heavy rock 3. Outer Core: Made of molten (liquid) iron and nickel. 4. Inner Core: Made of solid iron and nickel 2 - Growing Crystals and cutting out crystal shapes Organic: once living, contains carbon, fossils Inorganic: has no traces of life, no carbon, minerals Crystals: There are 6 geometric shapes that are formed when a liquid evaporates from a solution. Crystals are the building blocks of minerals. 3 - Mineral Identification Tests (Luster, Streak, Hardness, Cleavage) 4 - Special Properties (Acid and Magnetism) Mineral: solid material of the earth’s crust made of only ONE substance/crystal shape Mineral Identification Tests to determine properties: 1. Luster: the way light bounces off a mineral (shiny)metallic and nonmetallic 2. Surface Color: observe the outer color 3. Streak: color of the powder(inner color) left behind on a white or black streak plate 4. Hardness: how well a mineral resists scratching-use Mohs’ Scale of Hardness 5. Cleavage: the tendency for mineral to break along flat, smooth surfaces-use a mallet and chisel-will break along the weakest plane 6. Fracture: when the mineral does NOT break smoothly 7. Special Properties: acid and magnetism SUPPORTING TEXT page C32-C37 ES-6-2: We are learning to explain that rocks are made of one or more minerals and are formed in different ways. ESSENTIAL VOCABULARY: rock, sedimentary rock, metamorphic rock, igneous rock, sediments, weathering, erosion, deposition, cementation, compaction, magma, lava LAB(S) (Challenge question) Building a sedimentary rock in a cup Igneous lab with the spoons Metamorphic lab with the clay Rock cycle diagrams WE HAVE CONCLUDED THAT… Rock – naturally formed solid in the earth’s crust made up of 2 or more minerals Sediments – sand, silt, clay, etc… 1 - Sedimentary rock - WEDC Weathering – breaking of rock into pieces Erosion – movement of sediments Deposition – settling of sediments Cementation – compacting over time Properties of Sedimentary rock include: Layers, found near water, can have fossils, soft 2- Metamorphic rock – HP - change form due to heat and pressure Properties of Metamorphic rock include: Wavy bands, rock that changes, has a “parent rock”, hard, compacted 3- Igneous rock– MCH - cooling and hardening of magma (molten rock deep below the surface which cools slowly with large crystals) or lava (magma that reaches the earth’s surface which cools quickly with little or no crystals) Properties of Igneous rock include: Porous, large or small crystals SUPPORTING TEXT Page 52 42-47 ES-6-3: We are learning to explain the make-up of soil. ESSENTIAL VOCABULARY: soil, sand, clay, humus, loam LAB(S) (Challenge question) WE HAVE CONCLUDED THAT… Paper plate activity Soil components = air, water, organic material, mineral matter that build over time Composition of soil – looking at sand, clay and humus Humus = part of soil that contains organic material Color lab Texture lab Percolation lab SUPPORTING TEXT ES-6-4: We are learning to describe how nonrenewable geologic resources (minerals, rocks, soil, and fossil fuels) can be extracted, used, stored, and disposed. ESSENTIAL VOCABULARY: Renewable resource, nonrenewable resource, conservation, fossil fuels, LAB(S) (Challenge question) Renew a Bean Looking at coal samples Drilling for oil in muffins WE HAVE CONCLUDED THAT… Renewable = biomass, wind, hydropower, solar, geothermal Nonrenewable = coal, petroleum/oil, natural gas, nuclear, propane Renewable – can be replenished by nature in a short amount of time Nonrenewable – takes millions of years to replenish Fossil fuels = coal, oil, natural gas are the result of the remains of ancient plants and animals decomposed SUPPORTING TEXT