Healthy Volunteer Library
advertisement

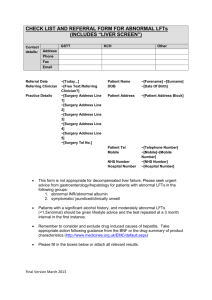
Common Protocol Template Healthy Volunteer Library v2.0 Common Protocol Template Healthy Volunteer Library v2.0 Section in Common Protocol Template (CPT) V1.0 Library Content 6.2 Exclusion Criteria Exclusion Criteria 8.1 Discontinuation of Study Treatment Liver Function Stopping Criteria QTc stopping criteria Appendix 7: Liver Safety: Suggested Actions and Followup Assessments [and Study Treatment Rechallenge Guidelines] 6.2 Liver Safety: Suggested Actions and Follow-up Assessments and Study Treatment Rechallenge Guidelines Exclusion Criteria MEDICAL CONDITIONS 1. [History or presence of/significant history of or current] cardiovascular, respiratory, hepatic, renal, gastrointestinal, endocrine, hematological, or neurological disorders capable of significantly altering the absorption, metabolism, or elimination of drugs; constituting a risk when taking the study treatment; or interfering with the interpretation of data 2. Abnormal blood pressure [as determined by the investigator] 3. Symptomatic herpes zoster within 3 months prior to screening 4. Evidence of active or latent tuberculosis (TB) as documented by medical history and examination, chest x-rays (posterior anterior and lateral), and TB testing: either a positive tuberculin skin test (TST; defined as a skin induration <5 mm at 48 to 72 hours, regardless of Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) or other vaccination history) or a positive (not indeterminate) QuantiFERON®-TB Gold test NOTE: The choice to perform a TST or a QuantiFERON-TB Gold test will be made by the investigator according to local licensing and standard of care. The QuantiFERON-TB Gold test can only be used in countries where it is licensed, and the use of this test is dependent on previous treatment(s). This test may not be suitable if previous treatment(s) produced significant immunosuppression. 5. Significant allergies to humanized monoclonal antibodies 6. Clinically significant multiple or severe drug allergies, intolerance to topical corticosteroids, or severe post-treatment hypersensitivity reactions (including, but not limited to, erythema multiforme major, linear immunoglobulin A (IgA) dermatosis, toxic epidermal necrolysis, and exfoliative dermatitis) 7. Lymphoma, leukemia, or any malignancy within the past 5 years except for basal © 2015 TransCelerate BioPharma 1 Common Protocol Template Healthy Volunteer Library v2.0 cell or squamous epithelial carcinomas of the skin that have been resected with no evidence of metastatic disease for 3 years 8. Breast cancer within the past 10 years 9. Abnormalities in lumbar spine previously known or determined by a screening lumbar x-ray (if conducted) 10. History of clinically significant back pain, back pathology, and/or back injury (for example, degenerative disease, spinal deformity or spinal surgery) that may predispose participant to complications or technical difficulty with lumbar puncture 11. Evidence or history of significant active bleeding or coagulation disorder or use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or other drugs that affect coagulation or platelet function within 14 days prior to lumbar catheter insertion 12. Allergy to lidocaine (Xylocaine®) or its derivatives 13. Medical or surgical conditions for which lumbar puncture is contraindicated <Start of common text> 14. ALT and bilirubin >1.5xULN (isolated bilirubin >1.5xULN is acceptable if bilirubin is fractionated and direct bilirubin <35%) 15. Current or chronic history of liver disease or known hepatic or biliary abnormalities (with the exception of Gilbert's syndrome or asymptomatic gallstones) 16. [QTc >450 msec for male participants] [or >470 msec for female participants] NOTES: The QTc is the QT interval corrected for heart rate according to Bazett’s formula (QTcB), Fridericia’s formula (QTcF), and/or another method. It is either machine-read or manually over-read. The specific formula that will be used to determine eligibility and discontinuation for an individual participant should be determined prior to initiation of the study. In other words, several different formulas cannot be used to calculate the QTc for an individual participant and then the lowest QTc value used to include or discontinue the participant. <End of common text> PRIOR/CONCOMITANT THERAPY 17. [Past or] intended use of over-the-counter or prescription medication [including herbal medications] within [X] days prior to dosing [Specific medications listed in Section 7.7 may be allowed] 18. Live vaccine(s) within 1 month prior to screening, or plans to receive such vaccines © 2015 TransCelerate BioPharma 2 Common Protocol Template Healthy Volunteer Library v2.0 during the study 19. Treatment with biologic agents (such as monoclonal antibodies including marketed drugs) within 3 months or 5 half-lives (whichever is longer) prior to dosing PRIOR/CONCURRENT CLINICAL STUDY EXPERIENCE 20. Participation in the study would result in donation of blood or blood products in excess of [X] mL within [X] 21. Exposure to more than [4] new chemical entities within 12 months prior to the first dosing day 22. Current enrollment or past participation within the last [X] days before [signing of consent] in [this or] any other clinical study involving an investigational study treatment or any other type of medical research DIAGNOSTIC ASSESSMENTS <Start of common text> 23. Presence of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) or positive hepatitis C antibody test result at screening or within 3 months prior to starting study treatment. For potent immunosuppressive agents, presence of the hepatitis B core antibody (HBcAb) should also lead to exclusion from the study <End of common text> 24. Positive pre-study drug/alcohol screen 25. Positive HIV antibody test 26. Regular use of known drugs of abuse OTHER EXCLUSIONS 27. Regular alcohol consumption within [X] months prior to the study defined as: For UK sites: An average weekly intake of >21 units for males or >14 units for females. One unit is equivalent to 8 g of alcohol: a half-pint (~240 mL) of beer, 1 glass (125 mL) of wine, or 1 measure (25 mL) of spirits. For US sites: An average weekly intake of >14 drinks for males or >7 drinks for females. One drink is equivalent to 12 g of alcohol: 12 ounces (360 mL) of beer, 5 ounces (150 mL) of wine, or 1.5 ounces (45 mL) of 80 proof distilled spirits. © 2015 TransCelerate BioPharma 3 Common Protocol Template Healthy Volunteer Library v2.0 28. Sensitivity to heparin or heparin-induced thrombocytopenia 29. Sensitivity to any of the study treatments, or components thereof, or drug or other allergy that, in the opinion of the investigator or medical monitor, contraindicates participation in the study 8.1 Discontinuation of Study Treatment Liver Function Stopping Criteria <Start of common text> Study treatment will be discontinued for a participant if liver function stopping criteria are met. Phase I Liver Function Stopping Algorithm Continue Study Treatment No ALT ≥ 3xULN Yes Discontinue Study Treatment Must refer toLiver Safety Required Actions and Follow up Assessments section in the Appendix Report as an SAE if possible Hy’s Law case: ALT≥3xULN and Bilirubin ≥2xULN (>35% direct) Or INR>1.5, if measured* *INR value not applicable to participants on anticoagulants Liver Safety: Suggested Actions and Follow-up Assessments can be found in Appendix [X]. <End of common text> QTc Stopping Criteria <Start of common text> A participant who meets [the OR either] bulleted criterion based on the average of triplicate ECG readings will be withdrawn from the study. [QTc, QTcB, QTcF] >500 msec, [Change from baseline: QTc >60 msec] © 2015 TransCelerate BioPharma 4 Common Protocol Template Healthy Volunteer Library v2.0 <End of common text> Appendix 7: Liver Safety: Suggested Actions and Follow-up Assessments [and Study Treatment Rechallenge Guidelines] <Start of common text> Phase I liver function stopping criteria are designed to assure participant safety and to evaluate liver event etiology. Phase I Liver Function Stopping Criteria and Follow-Up Assessments Liver Function Stopping Criteria ALT-absolute ALT ≥3xULN If ALT ≥3xULN AND bilirubin 2xULN (>35% direct bilirubin) or INR >1.5, report as an SAE1,2 See additional actions and follow-up assessments below Required Actions and Follow-up Assessments Actions Follow-Up Assessments Immediately discontinue study treatment Report the event to the [sponsor] within 24 hours Complete the liver event CRF, and complete an SAE data collection tool if the event also met the criteria for an SAE2 Perform liver function follow-up assessments Monitor the participant until liver function test abnormalities resolve, stabilize, or return to baseline (see MONITORING) MONITORING: If ALT ≥3xULN AND bilirubin 2xULN or INR >1.5 Repeat liver function tests (include ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin) and perform liver function follow-up assessments within 24 hrs Monitor participant twice weekly until liver function test abnormalities resolve, stabilize © 2015 TransCelerate BioPharma 5 Viral hepatitis serology3 Blood sample for pharmacokinetic (PK) analysis obtained [insert time interval recommended by clinical pharmacokinetics representative] after the most recent dose4 Serum creatine phosphokinase (CPK) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) Fractionate bilirubin, if total bilirubin 2xULN Complete blood count with differential to assess eosinophilia Record the appearance or worsening of clinical symptoms of liver injury, or hypersensitivity, on the AE report form Record use of concomitant medications (including acetaminophen, herbal remedies, and other over-the-counter medications) on the concomitant medications report form Common Protocol Template Healthy Volunteer Library v2.0 or return to baseline A specialist or hepatology consultation is recommended If ALT ≥3xULN AND bilirubin <2xULN and INR ≤1.5: Repeat liver function tests (include ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin) and perform liver function follow-up assessments within 24 to 72 hours Monitor participants weekly until liver function abnormalities resolve, stabilize, or return to baseline Record alcohol use on the liver event alcohol intake CRF If ALT ≥3xULN AND bilirubin 2xULN or INR >1.5: Anti-nuclear antibody, anti-smooth muscle antibody, Type 1 anti-liver kidney microsomal antibodies, and quantitative total immunoglobulin G (IgG) or gamma globulins Serum acetaminophen adduct HPLC assay (quantifies potential acetaminophen contribution to liver injury in participants with definite or likely acetaminophen use in the preceding week [James, 2009]) NOTE: Not required in China. Liver imaging (ultrasound, magnetic resonance, or computerized tomography) and/or liver biopsy to evaluate liver disease; complete liver imaging and/or liver biopsy CRFs 1. Serum bilirubin fractionation should be performed if testing is available. If serum bilirubin fractionation is not immediately available, discontinue study treatment if ALT 3xULN and bilirubin 2xULN. Additionally, if serum bilirubin fractionation testing is unavailable, record the absence/presence of detectable urinary bilirubin on dipstick which is indicative of direct bilirubin elevations suggesting liver injury. 2. All events of ALT 3xULN and bilirubin 2xULN (>35% direct bilirubin) or ALT 3xULN and INR >1.5 may indicate severe liver injury (possible ‘Hy’s Law’) and must be reported as an SAE (excluding studies of hepatic impairment or cirrhosis). The INR measurement is not required and the stated threshold value will not apply to participants receiving anticoagulants. 3. Hepatitis A IgM antibody; hepatitis B surface antigen and hepatitis B Core Antibody (HBcAb); hepatitis C RNA; cytomegalovirus IgM antibody; Epstein-Barr viral capsid antigen IgM antibody (or if unavailable, heterophile antibody or monospot testing); and hepatitis E IgM antibody. 4. PK sample may not be required for participants known to be receiving placebo or non-comparator treatments. Record the date/time of the PK blood sample draw and the date/time of the last dose of study treatment prior to the blood sample draw on the CRF. If the date or time of the last dose is unclear, provide the participant’s best approximation. If the date/time of the last dose cannot be approximated OR a PK sample cannot be collected in the time period indicated above, do not obtain a PK sample. Instructions for sample handling and shipping are in the [Study Reference Manual]. References James LP, Letzig L, Simpson PM, Capparelli E, Roberts DW, Hinson JA, Davern TJ, Lee WM. Pharmacokinetics of Acetaminophen-Adduct in Adults with Acetaminophen Overdose and Acute Liver Failure. Drug Metab Dispos 2009; 37:1779-1784. <End of common text> © 2015 TransCelerate BioPharma 6