Earthquake Notes (Part 2)
advertisement
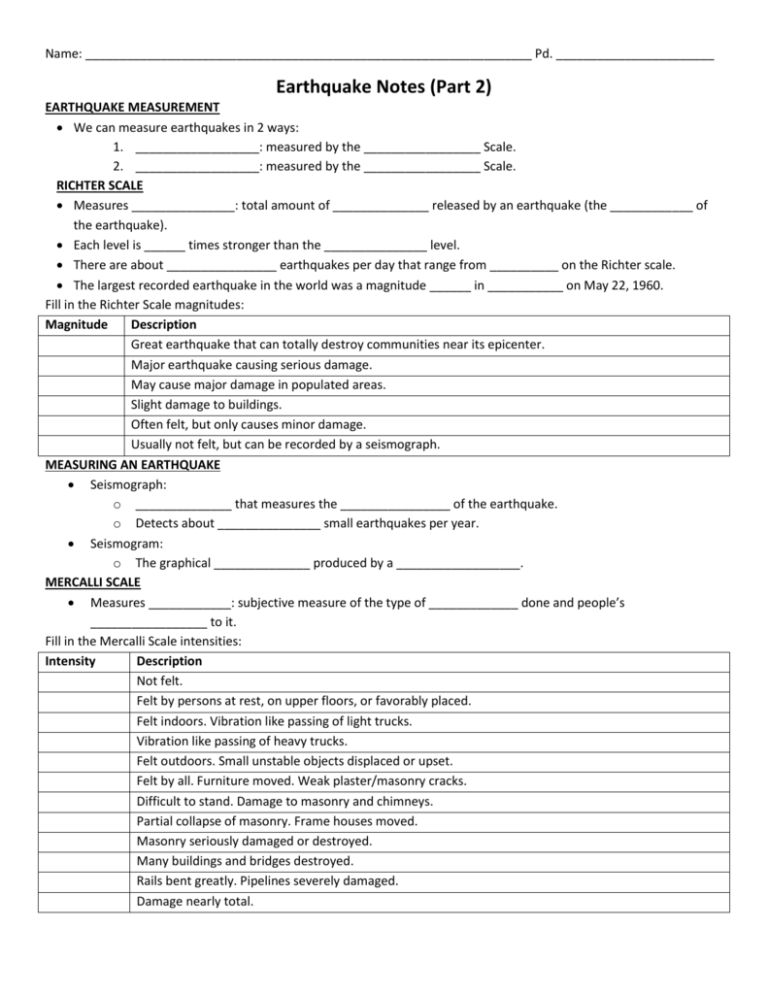
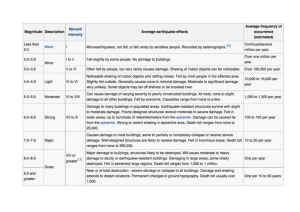
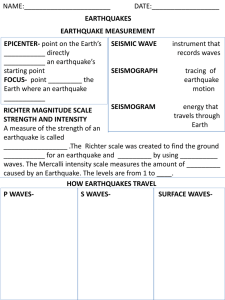
Name: _________________________________________________________________ Pd. _______________________ Earthquake Notes (Part 2) EARTHQUAKE MEASUREMENT We can measure earthquakes in 2 ways: 1. __________________: measured by the _________________ Scale. 2. __________________: measured by the _________________ Scale. RICHTER SCALE Measures _______________: total amount of ______________ released by an earthquake (the ____________ of the earthquake). Each level is ______ times stronger than the _______________ level. There are about ________________ earthquakes per day that range from __________ on the Richter scale. The largest recorded earthquake in the world was a magnitude ______ in ___________ on May 22, 1960. Fill in the Richter Scale magnitudes: Magnitude Description Great earthquake that can totally destroy communities near its epicenter. Major earthquake causing serious damage. May cause major damage in populated areas. Slight damage to buildings. Often felt, but only causes minor damage. Usually not felt, but can be recorded by a seismograph. MEASURING AN EARTHQUAKE Seismograph: o ______________ that measures the ________________ of the earthquake. o Detects about _______________ small earthquakes per year. Seismogram: o The graphical ______________ produced by a __________________. MERCALLI SCALE Measures ____________: subjective measure of the type of _____________ done and people’s _________________ to it. Fill in the Mercalli Scale intensities: Intensity Description Not felt. Felt by persons at rest, on upper floors, or favorably placed. Felt indoors. Vibration like passing of light trucks. Vibration like passing of heavy trucks. Felt outdoors. Small unstable objects displaced or upset. Felt by all. Furniture moved. Weak plaster/masonry cracks. Difficult to stand. Damage to masonry and chimneys. Partial collapse of masonry. Frame houses moved. Masonry seriously damaged or destroyed. Many buildings and bridges destroyed. Rails bent greatly. Pipelines severely damaged. Damage nearly total. Name: _________________________________________________________________ Pd. _______________________ ISOSEISMIC MAPS Isoseismal lines identify and _____________ areas of _______________ intensity. MERCALLI VS. RICHTER SCALE A 2.0 magnitude on the Richter scale is equal to what intensity on the Mercalli Scale? _________ A 5.0 magnitude on the Richter scale is equal to what intensity on the Mercalli Scale? _________ A 7.0 magnitude on the Richter scale is equal to what intensity on the Mercalli Scale? _________ A 8.0 magnitude on the Richter scale is equal to what intensity on the Mercalli Scale? _________ CAN EARTHQUAKES BE PREDICTED? Earthquake precursors o Changes in ______________ or ________________ of land surface. o Fluctuations in ________________ levels, _______________ resistance of the ground. o Seismic ______________. Seismic gaps o Segments of an _____________ _____________ known to produce significant earthquakes, that has not ______________ in an unusually ___________ time when compared with other segments along the same structure. o Any _______________ and longstanding _________________ is therefore considered to be the fault segment most ______________ to suffer ______________ earthquakes. Earthquake Prediction Programs o Conduct laboratory and field studies of rocks __________, __________, and ___________ earthquakes. o Monitor ___________ along ____________ faults. o Produce ____________ assessments. EARTHQUAKE PREPAREDNESS Adequate __________________ can limit the loss of ___________ and decrease the _______________ caused by earthquakes: o __________________ o __________________ planning o Construction of _______________, more ____________, more safely designed ________________. SEISMIC ACTIVITY IN THE UNITED STATES 1. Which state ranks #1 for seismic activity? _____________ 2. What number does Nevada rank for seismic activity? ____________ TSUNAMIS Large sea __________ caused by an underwater earthquake. TSUNAMIS VS. TIDAL WAVES Although both are sea waves, a tsunami and a tidal wave are two different ________________ phenomena. o Tsunamis are caused by _________________ earthquakes. o Tidal waves are produced by high _____________.