Biomes - Solon City Schools
advertisement

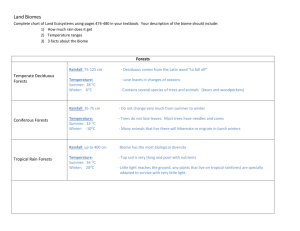
Biome Notes Tundra -location: 55-70 degrees latitude, on high mountains above the timberline -average temperature: -20--30 degrees F -average rain: 10-25cm/4-10 inches annually -type of climate: E=Polar Climate -causes of climate: indirect sunlight due to the tilt of the earth causing seasons and days without a sunset(summer) or days without sunrise(winter), possible high elevations causing decreased temperatures and low air density, cold Arctic Ocean waters surround much of this biome stabilizing its cold temperatures Local Animals: Polar Bear, Carribou, Arctic Fox, Arctic Hare, Snowy Owl, Music Ox, Rock Ptarmigan Local Vegetation: dwarf shrubs, sedges, grasses, mosses, liches Percentage of Earth: 8% Fun Facts: youngest soil, low primary productivity, No Reptile or Amphibians except the Wood Frog( lives in Arctic Ponds) Polar Ice Caps Latitude 0-10 - Longitude 0-360 Location: Greenland and Antarctica Average Temperature: <10°C Average Rainfall: 6.5 inches per year Type of Climate: Cold and Dry Polar ice caps form because the high-latitude regions receive less energy in the form of solar radiation from the sun than equatorial regions. This results in lower surface temperatures. Local Animals: Polar bears, arctic wolves, arctic foxes, lemmings, musk oxen, beluga whales, penguins. Local Vegetation: Wildflowers, Arctic Poppies, Arctic Azaleas, Arctic Lupine, Mosses, Grasses, Lichens, Small Shrubs Regions cover 20% of the Earth Taiga Latitude: 45-75 degrees north, covers both western and eastern parts of continents of North America and Europe/Asia Lower precipitation rates than in other biomes – generally 200-750 mm of precipitation a year Temperatures are variable , but characterized by long and cold winters and short, humid and warm summers Climate is generally Dfc by the Koppen classification system! D means “humid continental”, f is enough precipitation for all months and c is generally low temperatures Causes of climate are latitude: far distance from sun/less direct rates in general meaning lower temperatures, but in summer when NH is tilted t/w sun, can have up to 20 hours of sunlight, in winter 20 hours of darkness because it’s away from the sun. Warm ocean currents from tropics flow up to Atlantic Ocean to make some parts of Northern Europe mild Local animals: spruces, firs, conifers, bogs, bald eagle, marshes, warblers, moose, arctic foxes, arctic wolves Local vegetation: needleleaf, coniferous trees, evergreens, scots pine FUN FACT! One of the biggest problems facing the taiga is acid rain. It has killed off parts of Scandanavia and Russia. Temperate (Deciduous) Forest Location: Deciduous forests can be found in the eastern half of North America, and the middle of Europe. There are many deciduous forests in Asia. Some of the major areas they are in are southwest Russia, Japan, and eastern China. South America has two big areas of deciduous forests in southern Chile and Middle East coast of Paraguay. There are deciduous forests located in New Zealand and southeastern Australia also. They are also often located by oceans. Latitude: Temperate Forests are located between approximately 25° and 50° latitude in both hemispheres. Avg. Rainfall: 30-60 inches per year Avg. Temperature: 50°F Climate • Four distinct seasons; spring, summer, autumn, and winter. • Summer months usually begin in early June and end in late August. Winter months don't begin until December. • Cold winters, hot summers (big range). • Mild rain. Cause of the Climate: The ocean and the wind are two big factors of why the temperature and climate change so much in this biome. Exposed to warm and cold air masses. Earth tilted on its axis Percentage of Land Covered By This Biome: 30% Interesting Fact: Many of the trees in temperate forests contain sap which they use to keep their roots from freezing during the winter. Chaparral Approximate Position: 30-50 degrees N and 30-50 degrees S latitude Temperature: 30-100 degrees Average 64F Rainfall: 10-17 inches all year, mostly in winter Type of Climate: mid-latitude climate - Cs (C= warm temp climates, s= dry season in the summer) What Causes Climate? -Lie in best of westerly winds (most Chaparral biomes lie on west side of continent). Created when cool ocean water merges with a land mass of high temperature. Local Animals: - Muledeer, wood rats, chipmunks, lizards, and hares Local Vegetation: - Cacti, Poison Oak, Shrub Oak, Evergreen Shrubs (have leather like leaves to resist water loss) How Much Does the Chaparral Biome Cover? - Found in five regions which make up 2% of land, but contain 20% of plant diversity Fun Fact - Plants in Chaparral contain flammable material yet their barks resist fire Tempurate Grasslands (AKA: Prairie, Steppe,Pampus) Location: 23.5o latitude (Tropics of Capricorn and Cancer) Temp: Summer highs of 100o F. Winter Rainfall: 20-35 in (55-95cm) Climates: GROUP C: Temperate climates (two seasons) Causes of climate: In America the Rocky Mountains reduce the moisture in the air causing dry areas good for grass growth. Natural fires help to keep clear trees and large shrubs for better grass growth. Because of their locations, these areas are affected by the change in direct sunlight during the year. Local Animals: Low diversity- bison, prairie dogs, wolves, ferrets fox Local Veg: Grasses, small shrubs, some trees, flowers 13% of the earth’s land mass is temperate grasslands Fact: Soil in these areas is very rich with nutrients and has mostly been ruined by excessive farming. Tropical Forest Average Position on Earth: 0- 30 latitude, primarily centered around the equator in-between the Topic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn Average Temperature: 68-98 F Average Rainfall: 125-660 cm. (50-260 in.) Tropical Wet climate Local animals: spider monkey, red-eyed tree frog, gorilla, toucan, boa constrictor, tree snail, sloth, leopard Local Vegetation: venus fly trap, orchids, buttress roots, mangroves, strangler figs Interesting Facts: produces 40% of the world’s oxygen, average humidity ranges between 77 and 88%, 4 layers of trees: emergent, canopy, understory, and forest floor. More than 2/3 of all the world’s plants originate from the Tropical Forests also known as the “world’s largest pharmacy;” home to many medicines The position of the tropical forest determines its warm and humid climate. Due to it’s location on the equator, the forest receives direct and large amounts of sunlight. This leads to evapotranspiration, which is when the water vapor released from plants on land is combined with evaporation of ocean water (hence why the forests are close to the ocean). The rising hot air cools and sheds moisture, causing constant and heavy rainfall. However, local variation can also be great due to the trade winds, ocean currents, landmasses, and mountain ranges, which is basically saying not all tropical forests are alike due to where they are located. Desert 12% of the world is desert Average temps range from 43 to 49°C 15 to 26 cm per year of precipitation Most animals are nocturnal Plants have adapted to hold water for a very long time Found 30 degrees latitude to the North and South SAVANNAH Climate: Wet/Dry around 68-78 degrees (F) in winter, 78 to 86 degrees (F) Wildfires are common due to the dry climate Köppen Climate Group: Aw The A stands for a tropical climate, and the w for a dry season in the winter. Section on earth: Africa, strips across central and eastern Africa, most famous are the Serengeti Plains of Tanzania. Some spots in: northern Australia, India and brazil Lat/Long: 15 degrees N, 30 degrees S, and 15 degrees W, 40 degrees E Causes: Very porous thin layer of organic matter, allows rain to drain quickly, not suitable for farming. Usually on large flat expanses of land. AVG: Rainfall: 59 inches of rainfall a year Area: 2.5 million mi2 in South America, Animals: Zebras,Lions, Elephants, Giraffes. Land animals with hooves and long legs used for great migrations,while birds have large wingspans to travel great distances. The saltwater crocodile lives in the Australian savannah, which is the world’s largest reptile. Vegetation: The plants in the savannah have long tap roots that can reach deep in the water tables, thick bark to resist annual fires, trunks that can store water, and leaves that drop of during the winter to conserve water Acacia Trees