on Chemical Reactions
advertisement

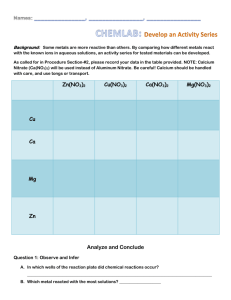
Year 8 Chemical Reactions Topic 9 Summary Sheets Chemical reactions In a chemical reaction a new substance is always formed. Most chemical changes are not easily reversed; they are irreversible. In a physical change no new substance is formed. Melting and evaporation are examples of physical changes. Physical changes are usually reversible. You can tell that a reaction has occurred if there is a colour change or when a gas is given off. Most chemical reactions also involve an energy change. This is usually in the form of heat, but can also involve light being given off (for example, when something burns). Fire – a very important chemical reaction A fire needs three things to keep burning: fuel, oxygen and heat. We show these three things on the Fire Triangle. If any one of these three things runs out, the fire will go out. Fire extinguishers are used for putting out fires. There are different types of fire extinguisher, and it is important always to use the correct sort for a particular fire. Sand or fire blankets can also be used to put out fires. Water is often used to put out fires, because it takes away the heat. However, water should never be used on oil or petrol fires, because it makes the burning fuel spread out. Foam, powder or carbon dioxide (CO2) extinguishers work by stopping oxygen getting to the flames. Burning Metals Reactions with Air When a metal burns, the metal combines with oxygen from the air to form a chemical called an oxide. We can show this using a word equation. The chemicals that you start with are called the reactants. The chemicals at the end are called the products. magnesium + oxygen reactants magnesium oxide products Fossil fuels contain a lot of carbon and hydrogen. When they burn they use up oxygen from the air and produce water and carbon dioxide. We can show the reaction using a word equation. Energy is in brackets in this equation because it is not a chemical substance. fuel + oxygen carbon dioxide + water (+ energy) Reactions of Metals and Water The metals that react quickly with air also tend to react with water. When metals react with water they form hydrogen gas and a metal hydroxide. metal + water metal hydroxide + hydrogen Reactions of Metals and Acids Some metals react with acids, and hydrogen gas is produced. When acids react with chemicals called carbonates, carbon dioxide gas is given off. Carbonates are found in rocks such as limestone or marble, and in some cooking ingredients and indigestion tablets. You can test the gas made in a reaction to find out what it is: • Hydrogen burns with a squeaky pop if a lighted splint is held near the test tube. • Carbon dioxide will put out a lighted splint, and it makes limewater turn milky. • Oxygen makes flames burn more brightly, and will relight a glowing splint. Some gases are more reactive than others. In the air, oxygen is the most reactive gas. Nitrogen is not very reactive. When metals react with the oxygen in the air they form oxides. metal + oxygen metal oxide The metals that react with water also react very quickly with acids. Some metals that don’t react with water do react with acids. When metals react with acids, they produce hydrogen and a salt. metal + acid salt + hydrogen The name of the salt formed depends on the name of the acid: • • • sulphuric acid makes sulphates nitric acid makes nitrates hydrochloric acid makes chlorides. Potassium Hydroxide + sulphuric acid → potassium sulphate + water. The metal part of the alkali comes first and second part comes from the acid. Reactivity Series K Na Ca Mg Al C Zn Fe Sn Pb H Cu Ag Au Pt Metals can be arranged in a Reactivity Series. The most reactive metals are placed at the top of the table. More reactive metals can displace less reactive metals from their compounds. In a displacement reaction, the more reactive metal will form a compound, and the less reactive metal is left on its own as the pure element. For example, iron is more reactive than copper, so it will displace copper from a compound. iron + copper chloride iron chloride + copper Zinc is more reactive than iron, so iron will not displace zinc from a compound. iron + zinc chloride no reaction You can use displacement reactions to work out the position of a metal in the Reactivity Series. For instance, zinc will displace lead from a compound, so we know that zinc is more reactive than lead. The Reactivity Series can also be used to predict whether reactions will occur. The reactivity of metals can be linked to their uses. Metals used for construction need to have a low reactivity, otherwise they will corrode away. Some metals, such as aluminium, have a natural protective oxide layer. Others, such as iron, have to be protected from corrosion, e.g. by painting. Many low reactivity metals have been known for hundreds or thousands of years. They can be extracted by heating their compounds in a fire. More reactive metals are extracted by electrolysis. This means that they have only been discovered in the last two hundred years, since the invention of the electric battery. Rusting of Iron For rusting to occur both water and oxygen are needed. Stopping either of these reaching the metal prevents corrosion. Methods of rust prevention remove one or both. Method of rust prevention Paint Used for Advantages Cars, bridges, boats. grease Moving parts –bicycle chains. Hard shiny silver surface Motorway crash barriers Cheap, can be coloured, but scratches easily. Needs to be checked often and re-applied. expensive Chemical and physical protection. Tough Chrome plating Galvanized (zinc coating) Plastic powder coating Sacrificial anode Motorcycle frames Bicycle frames Boats Chemical protection Energy from reactions: Burning Fuels Hydrocarbon fuels are made from the elements carbon and hydrogen. Coal, oil and natural gas (methane) are all hydrocarbons. When hydrocarbons burn they form carbon dioxide and water, and release heat energy. methane + oxygen carbon dioxide + water petrol + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water If there is not enough oxygen available, carbon monoxide or even soot is produced. Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas, it causes global warming.. More on Chemical Reactions Bases are compounds which react with acids. All metal oxides, metal hydroxides and metal carbonates are bases. Bases which dissolve in water are called alkalis (e.g. sodium hydroxide). Metal oxides and hydroxides and acids A metal oxide or a metal hydroxide reacts with an acid to form water and a salt. This reaction is called neutralisation. The general equation is: acid + metal oxide salt + water (or hydroxide) For example: hydrochloric acid + potassium hydroxide potassium chloride + water sulphuric acid + copper oxide copper sulphate + water We can check to see if neutralisation has occurred using universal indicator. The pH of the solution gets closer to neutral (pH7). Formula of Acids Sulphuric acid H2SO4 Nitric Acid HNO3 Hydrochloric Acid HCl