9 erosion
advertisement
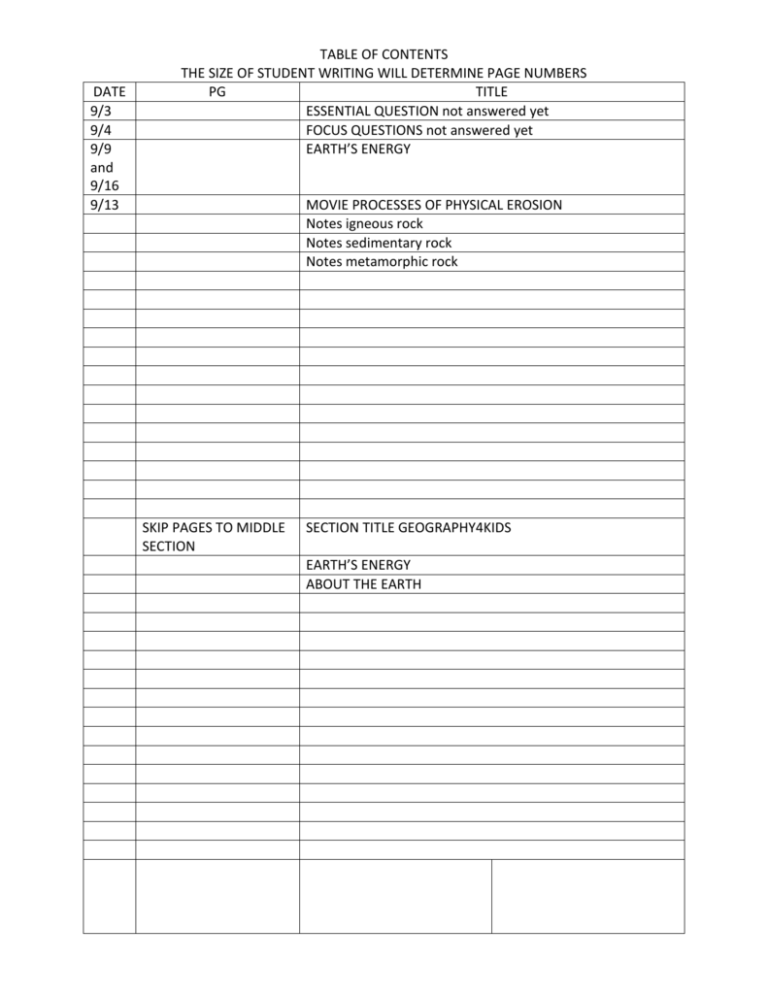
DATE 9/3 9/4 9/9 and 9/16 9/13 TABLE OF CONTENTS THE SIZE OF STUDENT WRITING WILL DETERMINE PAGE NUMBERS PG TITLE ESSENTIAL QUESTION not answered yet FOCUS QUESTIONS not answered yet EARTH’S ENERGY MOVIE PROCESSES OF PHYSICAL EROSION Notes igneous rock Notes sedimentary rock Notes metamorphic rock SKIP PAGES TO MIDDLE SECTION SECTION TITLE GEOGRAPHY4KIDS EARTH’S ENERGY ABOUT THE EARTH SKIP TO LAST PAGE VOC WORKS TOWARDS THE FRONT 1. QUALITATIVE 2. QUANTITATIVE 3. INDUCTIVE REASONING 4. DEDUCTIVE REASONING 5. INFERENCE 6. POTENTIAL ENERGY 7. KINETIC ENERGY 8. RADIATION 9 weathering 10 erosion 11 deposition 12 uplifting 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 EARTH HISTORY NOTES 9/3 ESSENTIAL QUESTION: How have Earth processes changed the formation of the Earth over geologic time? 9/4 Focus Questions What features make up the Earth? How are the Earth's features formed? How has Earth Changed over time? How old is the Earth? 9/9 AND 9/16 EARTH’S ENERGY 1. What element (a metal) makes up the outer core of the earth? Iron and nickel that is super heated 2. Is the outer core liquid or solid? liquid 3. What is energy? The ability to do work, cause motion, and change 4. What is heat? Transfer of energy to matter 9/13 Movie “Weathering and Erosion” PROCESSES OF PHYSICAL EROSION 1 Abrasion wearing away the surface sediments by contact 2 Frost ice wedging by expansion and contraction 3 Insolation or Thermal Expansion by extreme temperature variances 4 Slaking cyclic wetting and drying 5 Burrowing by animals 6 Wedging by roots not fungi or lichen they go in chemical weathering erosion 7 Water other than runoff like rain 8 Run off water on or in the land flows the path of least resistance and carries sediments 9 Mass Wasting by gravity mud slides 10 Deflation by wind dust storms 9/16 GEOGRAPHY4KIDS QUIZ 3 “Breaking Apart Earth” 1 If the densest matter moved toward the center of the earth, then how does the mantle (inner and outer mantle) make up 2/3 the mass of the earth? 2. Create using COLORED PENCILS Draw the picture SHOWING layers from inner to the outer and show density of layers 3. Label and Define Drawing UPPER MANTLE - Lithosphere (Sial and Sima) - Asthenosphere (Molten Rock River) - Mesosphere LOWER MANTLE OUTER CORE (Liquid Iron and Nickel) INNER CORE (Solid Iron Compounds) 9/20 HIGHLIGHTED GRAPHIC ORGANIZER OF IGNEOUS ROCK WORKSHEET 13 AND 14 LITHOSPHERE (LITHO MEANS ROCK AND SPHERE) o Crust, thin o Mostly granite and basalt make up most of mixture composition of rocks TEXTURES o Discrete or one type of mineral – course grains – gypsum, quartz, calcite o Not discrete one or more than one type of mineral – glassy o Or organic – living matter – coal LUSTER o Bright, Shiny, Dull 3 CATAGORIES OF ROCK (mostly made of feldspar or quartz) o IGNEOUS INTRUSIVE – magma- cools slower – larger crystals Granite, syenite, peridotite, gabbro, diorite EXTRUSIVE- lava-fissures (cracks in the crust) cools quicker – smaller crystals Basalt and rhyolite Tossed lava no crystals glass like obsidian (volcanic glass) Tossed lava that is bubbling still has holes (pumice or scoria) Granite INTRUSIVE COURSE GRAINS most abundant most of the continent is made of some of granite in mixtures- HALF DOME MT IN YOSEMITE NP, CA USED IN BUIDLINGS AND MONUMENTS SYENITE, DIORITE, PEGMATITE EXTRUSIVE IGNEOUS o Obsidian –dark black-glass like rapid cooling lava o Pumice – light gray to white – floats- gas holes from bubbling lava that cooled so fast o Basalt – dark gray – fine grained texture – HI Sedimentary Notes 9/25 1. Sedimentary rocks are made from sediments AND FORMED by natural cement 2. Sediments include plants & animal remains, and chemicals 3. Three classes – 1 Mechanical – (EXAMPLES conglomerates , sandstone, shale) weathering and erosion (RUNNING WATER, GLACIERS, WIND, GRAVITY, CURRENTS) a. MOST SEDIMENTS ARE DEPOSITED IN SHALLOW WATERS i. SHALLOW WATERS ARE NEAR SHORE LINES CONTINENTAL SHELVES – SHALLOW AREAS ALONG THE CONTINENTAL COASTS Velocity of Flowing Water 4. River meets lake or ocean & velocity decreases 5. Velocity decreases so carrying capacity decreases 6. Heavy sediments fall out first 7. Then sand deposits a. Heavy sediments and sand must be cemented together i. Natural cements are silica, lime, hematite, and limonite in water ii. 8. Then silt and clay deposit 9. Buildup along the continental shelf and hardening makes sedimentary rocks 10. 2 ,Organic – dead plants and animals 3 Chemical – minerals in water that evaporates compact and compress MECHANICAL SEDIMENTARY ROCK FORMATION CONGLOMERATESANDSTONE SHALE ORGANIC SEDIMENTARY ROCK LIMESTONE COQUINA CHALK COAL BITUMINOUS ANTHRACITE CHEMICAL SEDIMETNARY ROCK Metamorphic Notes GEOGRAPHY4KIDS MIDDLE SECTION USE CORNELL METHOD: ALL ANSWERS MUST BE WRITTEN: CIRCLE CORRECT ANSWER 9/3 BIOLOGY4KIDS REVIEW KINGDOMS FROM LAST YEAR 9/4 BIOLOGY4KIDS REVIEW SCIENTIFIC METHOD FROM LAST YEAR QUIZ 1 GEOGRAPHY4KIDS EARTH’S ENERGY 10 ? 9/9 QUIZ 2 GEOGRAPY4KIDS ABOUT THE EARTH 10 ? QUIZ 3 IN NOTES SECTION (NO ONLINE QUIZ-NOT DONE USING CORNELL) VOCABULARY (LAST PAGE WORKING TOWARDS FRONT OF NOTEBOOK) 1. qualitative ANSWERS BASED ON OBSERVATIONS 2. quantitative ANSWERS BASED ON QUANTITY OR NUMBERS 3. inductive reasoning THE THEORY IS BASED ON A PREMISE MADE FROM KNOWN FACTS. Clues are an example of inductive reasoning. They are facts, like in a crime or mystery, and are used to form a conclusion. Inductive reasoning uses observations, facts, and inferences to form a logical conclusion. GENERALLY, INDUCTIVE REASONING MOVES FROM THE SUPPORTS TO THE CONCLUSION WHEN PRESENTING AN ARGUMENT. 4. deductive reasoning THE THEORY OR OUTCOME IS BASED ON PREMISES THAT THROUGH EXPERMENTATION (CAN BE QUALITATIVE OR QUANTITATIVE) FORM A CONCLUSION. The conclusion is known and then evidence is looked for to logically support the conclusion. AN EASY WAY TO REMEMBER AND MORE ON INDUCTIVE AND DEDUCTIVE REASONING Inductive: Evidence · Conclusion (IEC) Deductive: Conclusion · Evidence (DCE) 5. inference-A logical explanation or answer based on prior knowledge, proven facts, laws, and/or tested theories know to be true and accurate at the time 6. POTENTIAL ENERGY – stored energy while at rest and 7. KINETIC ENERGY – energy while in motion or doing work 8 weathering 9 erosion 10 deposition 11 uplifting 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30









