Anatomy of the Accessory Organs (GI Unit 2) Liver, Gallbadder and
advertisement

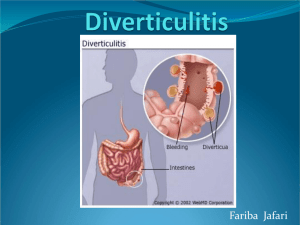
Anatomy of the Accessory Organs (GI Unit 2) Liver, Gallbadder and Pancreas (2012) WORD WALL ASCITES ERUCTATION ICTERUS CIRRHOSIS Assessment of the patient with Liver Disease Health History Past Medical History Review of Systems Functional Assessment PE Diagnostic Tests and Procedures For Lower GI System Review Stool Specimens O&P C&S OB( occult blood) Fecal Fat Imaging Studies HIDA scan CT MRI US Another Radiological Study.. Barium Enema NPO after MN Cathartics and enemas (observe results) Assess abdomen Colonoscopy To visualize colon and obtain specimens NPO 6-8 hrs prior Bowel cleanse Sedation Sigmoidoscopy Visualize rectum and sigmoid colon Enema prior to exam Sedation optional Observe for bleeding after Lower GI Disorders and Related Nursing Interventions Diverticulosis Multiple Diverticula present in colon Cause: unknown Related factors: low fiber diet, age, constipation, obesity and emotional tension Signs & Symptoms Asymptomatic Change in bowel habits (Constipation/Diarrhea) Pain in left lower abdomen Tx. High fiber diet Diverticulitis Inflammation of diverticula Complication of diverticulosis Cause: stool impacted in diverticula Complications…. Severe bleeding Obstruction Perforation (rupture) Peritonitis Fistula formation Medical Treatment Bedrest NPO and IV Fluids GI decompression Analgesics ABX Surgical Treatment Colon resection Colostomy Hartmann Procedure Colostomy Surgical opening between the colon and the surface of the body; creation of a stoma Named for the part of colon where located Temporary or Permanent Ostomy Care Assess: Stoma color Q shift Bowel function Bowel sounds, distention, tenderness Clean w/ H20, cover w/ ointment or paste (see pg. 434) Abdominal Hernia Muscle weakness resulting in intestine protruding through muscle Reducible Irreducible or incarcerated Incarcerated hernias have obstructed peristaltic flow; severe abd. Pain, distention, vomiting & cramps Strangulated hernia is deprived of blood flow Types of Hernias Inguinal Femoral Umbilical Incisional Surgical Treatment Herniorrhaphy Hernioplasty Truss What are Post Op Nursing Interventions for Hernia Pts. Assess bowel and bladder function Assess wound healing Teach to avoid stress on healing wound Intestinal Obstruction Adhesions Strangulated hernia Tumor Volvulus Intussuseption Volvulus Intussuseption Normal Anatomy Adhesions Signs & Symptoms Abdominal pain N/V ( possible projectile) Constipation Bloating Medical Treatment NGT for decompression IV hydration Surgery may be needed Medications… Non-narcotic analgesics Antibiotics THINK…. What are 3 nursing diagnosis and related nursing interventions for the patient with an intestinal obstruction??? Irritable Bowel Syndrome AKA Spastic colon, spastic colitis, mucus colitis, irritable colon Most common GI complaint Unknown cause Signs & Symptoms Abdominal pain Cramping Flatulence Constipation/Diarrhea Diagnostic Tests UGI BE Sigmoidoscopy Treatment Reduce stress Counseling High fiber diet/Metamucil Lifestyle changes Adeq. Fluids & regular meal patterns Medications Sedatives Xanax Anti-spasmodic Bentyl Anti-diarrheal Immodium Constipation Infrequent, hard, dry stools Tumors Frequent laxative use Inactivity low Fluid intake & low fiber diet Treatment Fiber supplements Laxatives Stool softeners Or a combination of above Nursing Interventions Teach patient to Increase… Fiber Fluids Activity Diarrhea Loose stools with increased frequency S/S pain, abdominal cramps, urgency, flatus Complications…. Dehydration Electrolyte imbalances Metabolic acidosis Malabsorption leading to malnutrition and anemia Nursing Interventions NPO, IV, TPN if severe sx I&O, daily weight Record T-A-C of stool Time-Amount-Color Motility reducers Monitor electrolytes Inflammatory Bowel Disease ( IBD ) Crohn’s Disease Ulcerative Colitis Unknown cause ? Autoimmune reactions tx with steroids Crohn’s Disease Lesions affect the entire thickness of bowel; can occur anywhere in the colon or small intestine Signs & Symptoms Variable depending upon areas affected N/V & epigastric pain Abdominal pain, tenderness and cramping Rectal bleeding & diarrhea S/S ( cont’d) Weight loss Steatorrhea When sm bowel involved Electrolyte imbalance Iron deficiency anemia Amino acid mal-absorption Long Term Complications Hemorrhage Bowel obstruction Fistulas Abscesses Perforation(rupture) Ulcerative Colitis Inflammation & ulceration of the mucous membrane in colon S/S: Fever, anorexia, wt. loss Frequent, watery stools with mucous & blood Long Term Complications Fissures Abscesses Increased risk of colon CA Toxic megacolon Megacolon Hirschsprung's disease Presents as Megacolon Hirschsprung's disease is a condition that affects the large intestine (colon) and causes problems with passing stool. It's present when a baby is born (congenital) and results from missing nerve cells in the muscles of a portion of the baby's colon. Diagnostic Tests IBD BE w/ small Bowel follow- through Colonoscopy w/ biopsy Ultrasound CAT Med/Surg. Management Control inflammation steroids Relieve symptoms Maintain fluid and electrolytes Provide adequate nutrition Prevent complications Limit milk products High cal, low residue, non-spicy, caffeine free diet Surgical Intervention Colectomy curative for ulcerative colitis NOT for Crohn’s disease Recurrence can recur at site of anastamosis Medications used alone or in combination…. Corticosteroids Immunosupressants Antidiarrheals Anticholinergics Antibiotics and others… Appendicitis Inflammation of the appendix If ruptured peritonitis develops which may be fatal Signs & Symptoms Pain at McBurney’s Point N/V Fever Rebound tenderness Pt also cannot straighten the right leg without pain. Treatment Appendectomy Pre-op Orders: NPO IV fluids Appendectomy Post-op Orders NPO until BS return then advance diet as tolerated V.S., TC & DB Assess wound for s/s infection OOB ASAP Peritonitis Inflammation of peritoneum Contamination of the peritoneal cavity Abscesses, septicemia, hypovolemic shock, paralytic ileus and organ failure. Signs & Symptoms Pain over affected area Fever Tachycardia N/V Tachypnea S/S (cont’d ) Distended, board-like abdomen ( rigidity ) Paralytic ileus Treatment Surgery to repair cause Abdominal cavity irrigation with NS and abx soln IV abx. Nursing Interventions NPO w/ NGT IV fluids Monitor drains Elevate HOB For abd. Distention and BS V.S. Activity as tolerated C&DB Cough and Deep Breath Analgesics Colorectal CA rd 3 most common CA in women Risk factors: Over 45 Hx of polyps Hx of IBD Signs & Symptoms Change in bowel habits Wt loss Abd cramping Rectal bleeding Diagnostic Tests Colonoscopy BE CEA Carcinoembryonic Antigen CBC Surgical Treatment Polypectomy Colon resection Chemo Radiation What are Post Op Nursing Interventions for Colorectal CA NPO w/ NGT C&DB (Cough and deep breath) Early ambulation Assess wound for infection Opioid analgesics Hemorrhoids Varicosed veins of rectum Internal or external Risk factor: Increased intra-abd pressure Signs & Symptoms are ??? Non surgical treatment consists of ??? Surgical Treatment Ligation Sclerotherapy Thermocoagulation Laser surgery hemorrhoidectomy Post op Nursing Interventions Pain control Assess for rectal bleeding, keep area clean Monitor stools passed after surgery, provide stool softeners VS Ambulate Anal Fissure Laceration between the anal canal and perianal skin Usually heal spontaneously Anorectal Abscess Infection of tissue around the anus What are s/s…..? Treatment…? I&D Anal Fistula Abnormal opening between anal canal and perianal skin S/S pruritus and discharge TX sitz baths, excision of fistula & surrounding skin Temporary colostomy PRN Pilonidal Cyst Cyst in sacrococcygeal area Easily infected Usually requires surgical excision Care similar to hemorrhoidectomy Critical Thinking Question A 44-year-old man presents to the emergency department with severe nausea and vomiting that he has been experiencing for 2 days. He complains of severe abdominal pain and a fever. His abdomen is distended and tender. What type of data should the nurse include in the assessment of this patient? What is the significance of these data? Disorders of the Accessory Organs Gallbladder, Pancreas and Liver WORD WALL FLATUS DYSPEPSIA REGURGITATION CATHARTIC Diagnostic Tests CT Liver Scan Ultrasonography MRI Biopsy ( liver, needle, open) ERCP Lab Tests PT, PTT, INR Bilirubin Serum protein Alk. Phosphatase AST, ALT,LDH Cirrhosis of the Liver Chronic, progressive disease of the liver 40-60 yrs. highest incidence Related to alcoholic liver disease or chronic viral infection Signs & Symptoms Early weight loss, fever, fatigue, heaviness in rt. Upper abdomem Progimpaired metabolism, GI disturbances, congestion of bloodflow causes ^ pressure of intestines, stomach, esophag. Later signs and symptoms… Jaundice From >Bilirubin Ascites Abd pain Peripheral neuropathy Bilirubin is the yellow breakdown product of normal heme catabolism. Heme is found in hemoglobin, a principal component of red blood cells. Bilirubin is excreted in bile and urine, and elevated levels may indicate certain diseases. It is responsible for the yellow color of bruises, urine, and the yellow discoloration in jaundice. Dyspnea Bleeding disorders Dry puritic skin Confusion Clay colored stool Complications… Portal hypertension Esophageal varices Ascites Hepatic encephalopathy Esophageal Varices Distended esophageal blood vessels Caused by ^ pressure in portal system Bleed easily TX for Bleeding Varices Drug therapy Surgical ligation Esophageal – gastric balloon Sclerotherapy TX for Ascites Na+ restriction diet and diuretics Paracentesis Shunts pic 854 Fig. 39-6 TIPS –Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt is often preferred as it reduces pressure in the portal system with fewer complications. Hepatic Encephalopathy Liver unable to detoxify ammonia Ammonia is a breakdown product of protein metabolism. Excessive ammonia in the blood causes neurologic symptoms including cognitive disturbances declining level of consciousness and changes in neuromuscular function Ammonia Tx is directed toward reducing ammonia formation. Goal is achieved by drug therapy and reduction of protein intake. Lactulose decreases ammonia absorption in the bowel. Hepatic Encephalopathy Asterixis- most common sign Asterixis ( Liver Flap) is a motor disturbance marked by irregular flapping of fingers and wrists when hands and arms are outstretched. Assess by asking the pt. to extend both arms. Nursing Care for the patient with Cirrhosis Emollient baths( oatmeal or baking soda ) Blood transfusions Due to bleeding varicies Low Na, high vitamin diet Small frequent meals Nrsg Care (cont’d) No ETOH Diuretics Vitamin K Daily weight Abd. girth measurements THINK…. What are 3 nursing diagnosis and related nursing interventions when caring for the patient with cirrhosis of the liver??/ Critical Thinking Question A patient who has end stage liver disease is experiencing signs and symptoms of hepatic encephalopathy. What interventions should the nurse implement for a patient with this diagnosis. Liver Transplantation Only cure for end stage liver disease Patients ranked by acuity and need Nursing assessments focus on: neuro status, VS, respiratory status, and indicators of bleeding. Provide usual post op care Lifelong drug therapy is needed Hepatitis Inflammation & swelling of the liver Bile channels are compressed Blood flow through liver is impaired Signs & Symptoms Fatigue / lethargy Nausea Abd pain Joint and muscle aches Decreased appetite S/S ( cont’d) Jaundice Hepatomegaly Dark urine Puritis Treatment Goal… To promote healing and manage symptoms Allow liver to regenerate Prevent transmission Medications Alphainterferon Ribavirin Antipyretics Antiemetics Avoid hepatotoxic drugs Dietary Changes High cal, high carb, high pro Low fat Vitamin supplements No ETOH Liver Cancer Primary site rare Frequent site metastasis Signs & Symptoms Same as cirrhosis Tx Lobectomy, Chemo, Radiation Gallbladder Disease Cholecystitis - inflammation of gallbladder Cholelithiasis – gallstones 5 F’s Signs & Symptoms RUQ pain 2-4 hours after meals N/V Flatulence Indigestion, belching S/S ( cont’d) Steatorrhea Clay colored stools Increased WBC, serum and urinary bilirubin and enzymes Medical Treatment Low fat diet Demerol ABX UDCA, and MTBE Ursodeoxycholic acid is the oral bile salt in current use. It is prescribed for small cholesterol stones or for those who are poor surgical risks. MTBE Methyl tert-butyl ether are agents which are instilled in the GB through a catheter. The physician instills and aspirates the drug repeatedly until fluoroscopy show the stones have dissolved or are not responding Surgical Treatment Endoscopic Sphincterotomy Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy Cholecystectomy Post Op Nursing Care T, C, & DB NGT Monitor T-tube IV’s Incentive spirometer Common Bile Duct Obstruction Stones block bile flow within common bile duct Intense spasmotic pain Trmt ERCP Nursing Care VS IV hydration ABX Analgesics Monitor lab results Pancreatitis Inflammation of the pancreas May be acute or chronic Causes Signs & Symptoms Severe, sudden onset abdominal pain in ULQ Vomiting Flushing Fever S/S (cont’d) Tachypnea Tachycardia Tender, distended abdomen Bowel sounds may be absent Elevated serum amylase Medical Management Pain control Demerol NPO; TPN Anticholinergics, Antispasmodics Pancrease to reduce steatorrhea THINK??? What are Nursing Interventions for Pancreatitis? Pancreatic Cancer Tumors usually malignant Prognosis poor Metastasizes quickly Most die within 1 yr of diagnosis Signs & Symptoms Pain Jaundice Weight loss Glucose intolerance Surgical Procedures See page 874 Figure 39-13 Most often procedures preformed are Side-to-side and the Whipple Nursing Care PCA for pain control Monitor I & O VS Monitor blood glucose Emollient lotions/Benadryl You’re done with GI Unit 2….. Time for the Post Test ! YIPPEEE !!!!