Review the techniques used to identify minerals, including Moh`s
advertisement

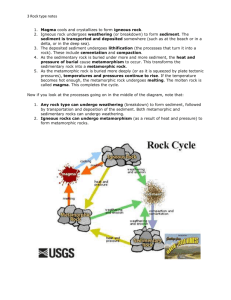
ROCKS TEST STUDY GUIDE Review the techniques used to identify minerals, including Moh’s Scale . 3 types of Rocks: a) igneous B) sedimentary c) metamorphic Define: Rock: mixture of minerals, organic matter, volcanic glass and other materials Sediment: broken pieces of rock, dirt, glass, quartz, mineral grains, and plant and animal remains Weathering: breakdown of rock into sediment due to forces on Earth- wind, water, ice, sand, snow Erosion: carrying away of sediment due to wind, water, gravity Deposition: depositing of sediment that has been carried away by erosion Compaction: over thousands to millions of years, layer upon layer of sediment pushes down, making the fluids force out, making sediment harder, so it can turn into rock. Cementation: minerals dissolve in water and recrystallize around the sediment grains making the sediment and minerals stick together. What is formed from weathering and erosion of rock? sediment Which type of rock is made from weathering and erosion? Sedimentary rock Igneous rocks: Rocks formed from magma or lava Intrusive: formed from magma Extrusive: formed from lava Fine-grained ( small or tiny ) crystals means the rock cooled quickly Large crystals form from rock that has cooled slowly Note: igneous rocks usually have a combination of minerals in them, making them multicolored like granite. Use these rocks , and classify them using your textbook: obsidian, granite, basalt, pumice ( pg 122) Examples of Intrusive Igneous rocks: Granite Examples of Extrusive igneous rocks: obsidian, basalt, pumice Sedimentary rocks: rocks made from weathered and eroded rock. Note: sedimentary rocks usually have only one dominant mineral, like quartz in them. Formed in 3 different ways: a) organic ( biochemical) b) detrital (clastic ) Define: c) chemical use pg. 126-129 Clastic ( detrital ): made up of broken pieces of minerals and rock fragments. The broken pieces and fragments are the “clasts” . can be pebbles, sand, shells, glass Chemical: ( formed from evaporates or precipitates ): these rocks form when minerals crystallize directly from the water. The water evaporates, leaving the minerals, or the minerals crystallize from the water. Organic ( biochemical ) : formed by organisms, or contain the remains of organisms. Ex: limestone is made from shells. Use these rocks , and classify them using your textbook: ( pg. 127-129) clastic: conglomerate , shale , sandstone chemical: limestone, salt , gypsum organic (biochemical): coal Metamorphic rocks: changed rock due to changes in: a) temperature b) pressure or c) addition of chemical fluids Met. Rock can be classified as : foliated or nonfoliated Which one is layered or “banded” in appearance? foliated What is the rock that is changed called? The parent rock ( pg. 134 ) Use these rocks , and classify them using your textbook: ( pg. 133-136): Foliated: Nonfoliated: slate, gneiss, schist, phyllite marble, quartzite THE ROCK CYCLE: Be able to analyze a rock cycle and answer questions. Why is the rock cycle not just a simple circle?