Quiz #3
advertisement

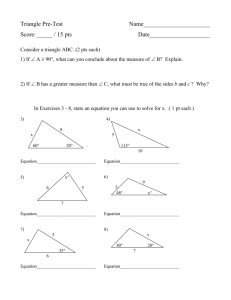
Chem 102 – Quiz 3 Multiple Choice (10 pts TOTAL) 1. The analytical technique GC is useful to forensic scientists because it identifies samples by their a. Molecular weight b. Retention time c. Both (a) and (b) 2. Mountain Dew appears yellow-green because it a. absorbs yellow-green light b. transmits yellow-green light c. transmits violet-red light d. both (a) and (c) 3. The correct order of increasing frequency of the following types of electromagnetic radiation is a. Radio < UV < visible < x-ray b.Radio < visible < UV < x-ray c. X-ray < UV < visible < radio 4. The unit for energy is a. watts b. m/s c. Joules d. watts/s 5. The following is one type of spectrophotometry that you used in analyzing CASE #102 so far a. MS b. UV c. IR Fill-in-the-Blank (10 pts TOTAL) 1. Light is defined as a wave and a 2. A common detector in spectrophotometers is a PMT. PMT stands for 3. A nanometer is times smaller than a meter. 4. Energy of electromagnetic radiation is wavelength. (inversely or directly) related to 5. The sample holder in a spectrophotometer is referred to as a Short Answer (10 pts) 1. Benzene (structure below – all 6 corners in the molecule are representing Carbons) is a known carcinogen. A woman is found to have aggressive cancer after being very healthy for many years. Her husband is a chemist and is brought in for questioning. It just so happens that his research centers on the molecule benzene. Meanwhile, the CSI agents talk with the woman and determine that she has had the same routine for the last 20 years which includes putting a special lotion that her husband buys for her. The agents notice that the lotion has quite a minty smell (characteristic of benzene). They take it to the lab for the criminalist (which it YOU!) to analyze. a. (4 pts) What spectrophotometric technique will you use to analyze it and why have you chosen this technique for this particular molecule? (BE SPECIFIC) b. (2 pts) You decide that you will also use mass spectrometry to analyze the lotion for benzene. A typical mass spectrometer contains an ion source and a mass analyzer. Name one type of ion source (type of ionization) that can be used in a mass spectrometer. c. (4 pts) A typical mass analyzer is a TOF analyzer. What does TOF stand for and how does it separate ions by mass? Calculations (20 pts TOTAL) (Each problem is worth 5 pts. If you want the problem to be worth 10 pts then only do 2 of them and I will count those problems double) 1. (5 pts) It is your first day on the job as a criminalist and you need to make a 20M solution of some Arsenic that was found at the scene of a crime in order to do some testing. You decide to use all 10 grams of Arsenic to make the 20 M solution. How many liters can you make? 2. (5 pts) A man was found dead from a heart attack. It is later determined that this man used a salt substitute of potassium chloride quite often in his bloody mary drinks (150mL) that he drank twice a day, once in the morning and once in the evening. Too much potassium can lead to heart attacks. The criminalist must measure the bloody mary that this man was drinking the morning that he died in order to estimate how much potassium in grams that this man was ingesting every day. The criminalist determined from Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry that the man was ingesting 100 ppm of potassium in his morning bloody mary. How many grams of potassium did this man ingest every day? 3. You have been working on a case in a town where it is thought that people are dying from radiation poisoning. It is uncertain whether this is from X-rays due to faulty machines at the local hospital that many people frequent or from Gamma-rays from a local research lab. To put things into perspective, you want to determine the following: Some important info needed: h = 6.63 x 10-34 Js c = 3.00 x 108 m/s a. (2 pts) How much energy is in Gamma-ray radiation of a wavelength of 0.01nm? b. (2 pts) How much energy is in X-ray radiation of a wavelength of 0.1nm c. (1 pt) How much energy is in visible light (pick any wavelength of visible light)? 4. Hopefully some easy calculations for you: a. (1 pt) How many moles are there in 5 L of a 10 M solution? b. (2 pts) Convert 2 grams of NaCl to moles. c. (2 pts) Convert 10ppm to mg/L.